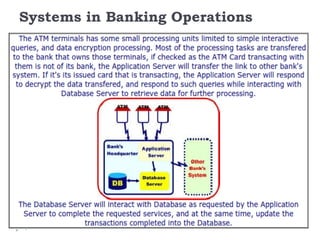
This document summarizes key concepts from a lecture on computer applications:
1. John Von Neumann's concepts of computing established that memory would contain both data and instructions, and that only one instruction would be executed at a time. Current computer systems are based on these concepts and are multi-programming or multi-tasking.
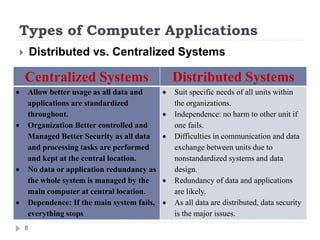
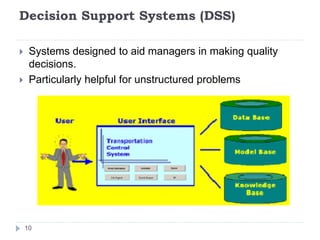
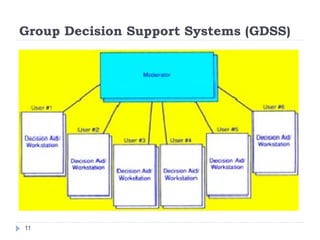
2. Computer applications can be categorized as interactive systems, fault-tolerant systems, parallel systems, clustered computers, and supercomputers. Distributed and centralized systems each have their own advantages and disadvantages.
3. Computer programming languages have evolved from machine language to various generations of high-level languages like FORTRAN, Pascal, and languages that more closely resemble natural languages.