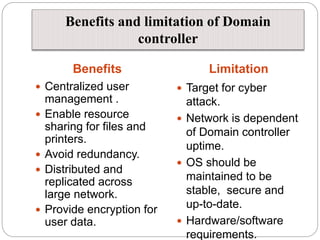
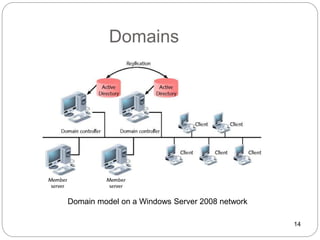
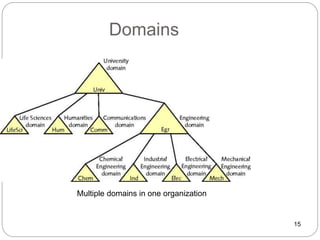
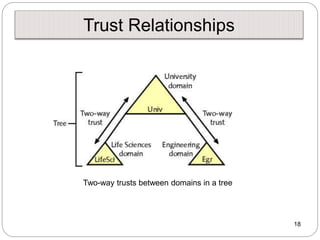
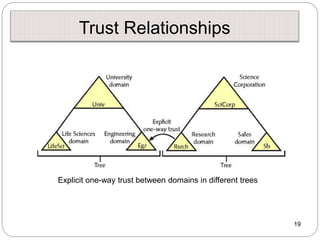
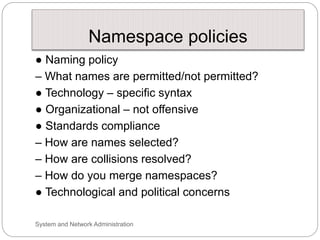
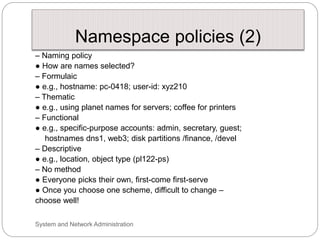
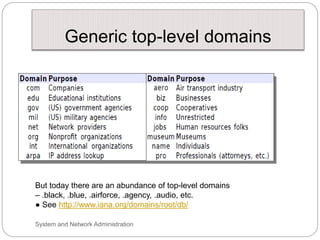
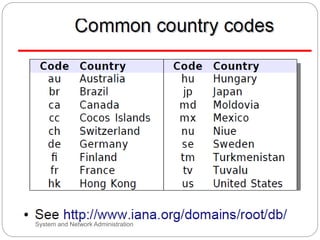
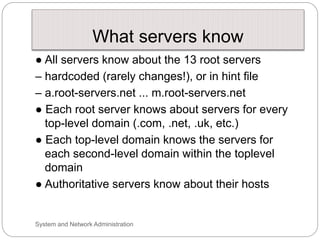
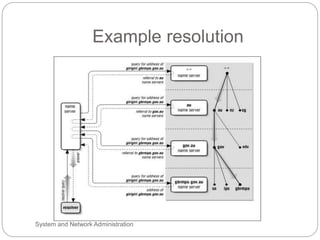
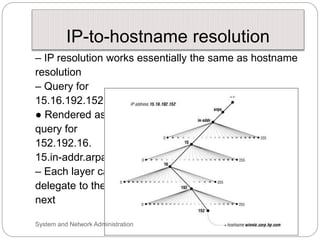
Windows networks can be configured as either a workgroup or domain model. A workgroup treats each computer as equal peers where users directly access shared resources, while a domain uses a centralized domain controller server to authenticate users and allow single sign-on access to resources across multiple client computers. The domain controller contains user and system access credentials and policies to securely manage the network domain. DNS is the domain name system that translates hostname requests to IP addresses through a hierarchical global namespace and allows networks and Internet resources to be located and identified.