Recommended
PPTX
PPTX
Systemic sclerosis Detailed Management and CLINICAL FEATURS
PPT
PPTX
medr-scleroderma-18011015535dndndn9.pptx
PPTX
Systemic sclerosis new.pptx
PPTX
PPTX
PPTX
sclerodema.pptx Clinical Immunology, Scleroderma
PPTX
Rhumatology System and Diseases : Scleroderma
PPT
PDF
_SS ✅.pdf rheumatology lecture in university of Jordan for med students
PPTX
Systemic Sclerosis - Rivin
PPTX
systemicsclerosis-160704050105-converted (1).pptx
PPTX
PPT
PPTX
PPTX
systemicsclerosis- VIK.pptxsystemicsclerosis- VIK.pptx
PPTX
Scleroderma final all about to know .pptx
PPTX
Scleroderma all to know about final.pptx
PPTX
Scleroderma, and it's all about it to know
PPTX
Systemic sclerosis (. Scleroderma).pptx
PPTX
Systemic sclerosis (. Scleroderma).pptx
PPTX
connective tissue disorders with ankylosing spondylitis.pptx
PPT
PPTX
Systemic Sclerosis (Scleroderma): Clinical Features, Investigations, and Mana...
PPT
PPTX
Esclerodermia: mitos, verdades y retos
PPTX
PPTX
Introduction to Malaria Historical overview.pptx
PPTX
NOMENCLATURE OF ECG DEFLECTIONS.pptx FOR 1ST BHMS STUDENTS
More Related Content
PPTX
PPTX
Systemic sclerosis Detailed Management and CLINICAL FEATURS
PPT
PPTX
medr-scleroderma-18011015535dndndn9.pptx
PPTX
Systemic sclerosis new.pptx
PPTX
PPTX
PPTX
sclerodema.pptx Clinical Immunology, Scleroderma
Similar to Approach_to_Systemic_Sclerosis_50_Slides.pptx
PPTX
Rhumatology System and Diseases : Scleroderma
PPT
PDF
_SS ✅.pdf rheumatology lecture in university of Jordan for med students
PPTX
Systemic Sclerosis - Rivin
PPTX
systemicsclerosis-160704050105-converted (1).pptx
PPTX
PPT
PPTX
PPTX
systemicsclerosis- VIK.pptxsystemicsclerosis- VIK.pptx
PPTX
Scleroderma final all about to know .pptx
PPTX
Scleroderma all to know about final.pptx
PPTX
Scleroderma, and it's all about it to know
PPTX
Systemic sclerosis (. Scleroderma).pptx
PPTX
Systemic sclerosis (. Scleroderma).pptx
PPTX
connective tissue disorders with ankylosing spondylitis.pptx
PPT
PPTX
Systemic Sclerosis (Scleroderma): Clinical Features, Investigations, and Mana...
PPT
PPTX
Esclerodermia: mitos, verdades y retos
PPTX
Recently uploaded
PPTX
Introduction to Malaria Historical overview.pptx
PPTX
NOMENCLATURE OF ECG DEFLECTIONS.pptx FOR 1ST BHMS STUDENTS
PDF
Management of medication MOM PHARMACY Training NABH 6th Edition.pdf
PPTX
Main supply (basics physics electro therapy
PPTX
PAEDIATRIC HISTORY TAKING.........Dr J.S.Chikakuda.pptx
PPTX
anatomy of eyeball and extraoccular muscles.pptx
PPTX
Sympathetic Nervous System in Pain Medicine | Anatomy, CRPS & Sympathetic Blo...
PDF
COLLOIDAL DISPERSION PPTx. S.Y B-PHARM .
PPTX
TYPES AND SOURCES OF ERRORS IN EPIDEMIOLOGY .pptx
PDF
Safe and Comfortable Plagiocephaly Helmet Solutions| Plagiocephaly Helmet Tre...
PPTX
THE STUDY OF MIND content intro and basics.pptx
PPTX
Cardiovascular Disease ppt. S.Y D-Pharm.
PPTX
Introduction to public health practice and principles.pptx
PDF
Police Officer Mental Health & Wellness Programs | MyOmnia
PPTX
Preformulation Studies for new Pharmaceutical substances
PPTX
Atrial Fibrillation and difference with Atrial flutter
PDF
Code of Ehics PPT, T.Y. B-PHARM ,5TH SEM
PPTX
IPHS - SC, PHC, CHC. pptx.
PPTX
AHN I UNIT - 1 - 3 III SEMESTER.pptx.BSC NURSING
PPTX
Template for presentation of patients at the MDT Meeting
Approach_to_Systemic_Sclerosis_50_Slides.pptx 1. 2. Learning Objectives
• Understand the spectrum of systemic sclerosis
• Develop a structured diagnostic approach
• Recognize organ involvement early
• Plan organ-based management
3. What is Systemic Sclerosis?
• Chronic autoimmune connective tissue
disease
• Characterized by vasculopathy, fibrosis,
autoimmunity
• Skin and internal organ involvement
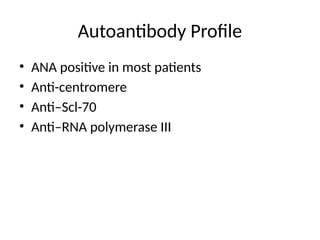
4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. Sine Scleroderma
• No skin thickening
• Internal organ involvement present
• Diagnosed by antibodies and organ disease
12. 13. Key History Points
• Raynaud phenomenon
• Skin tightness or swelling
• Dyspnea, dysphagia, chest pain
14. 15. 16. 17. 18. Modified Rodnan Skin Score
• 17 body areas assessed
• Score 0–3 per area
• Used for severity and follow-up
19. Face and Oral Findings
• Mask-like facies
• Microstomia
• Telangiectasia
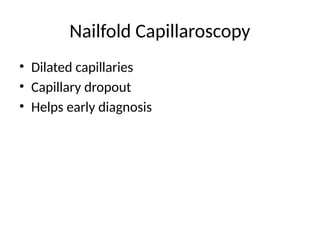
20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. 31. 32. 33. 34. When to Suspect Early SSc
• Raynaud with positive ANA
• Abnormal nailfold capillaries
• Puffy fingers
35. 36. 37. 38. 39. 40. 41. 42. 43. 44. Key Take-Home Messages
• Early recognition is crucial
• Systematic organ-based approach needed
• Regular monitoring improves outcomes