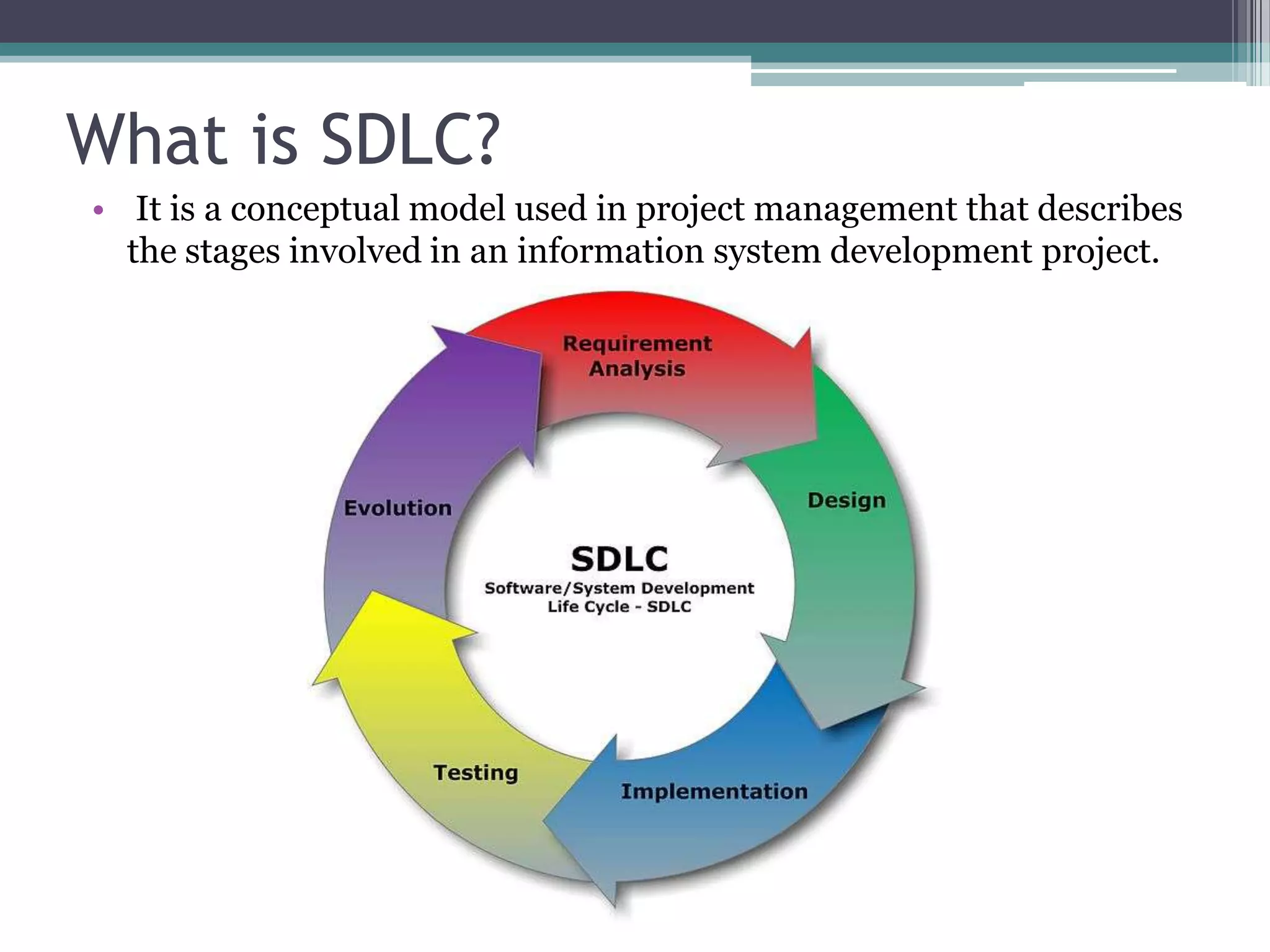
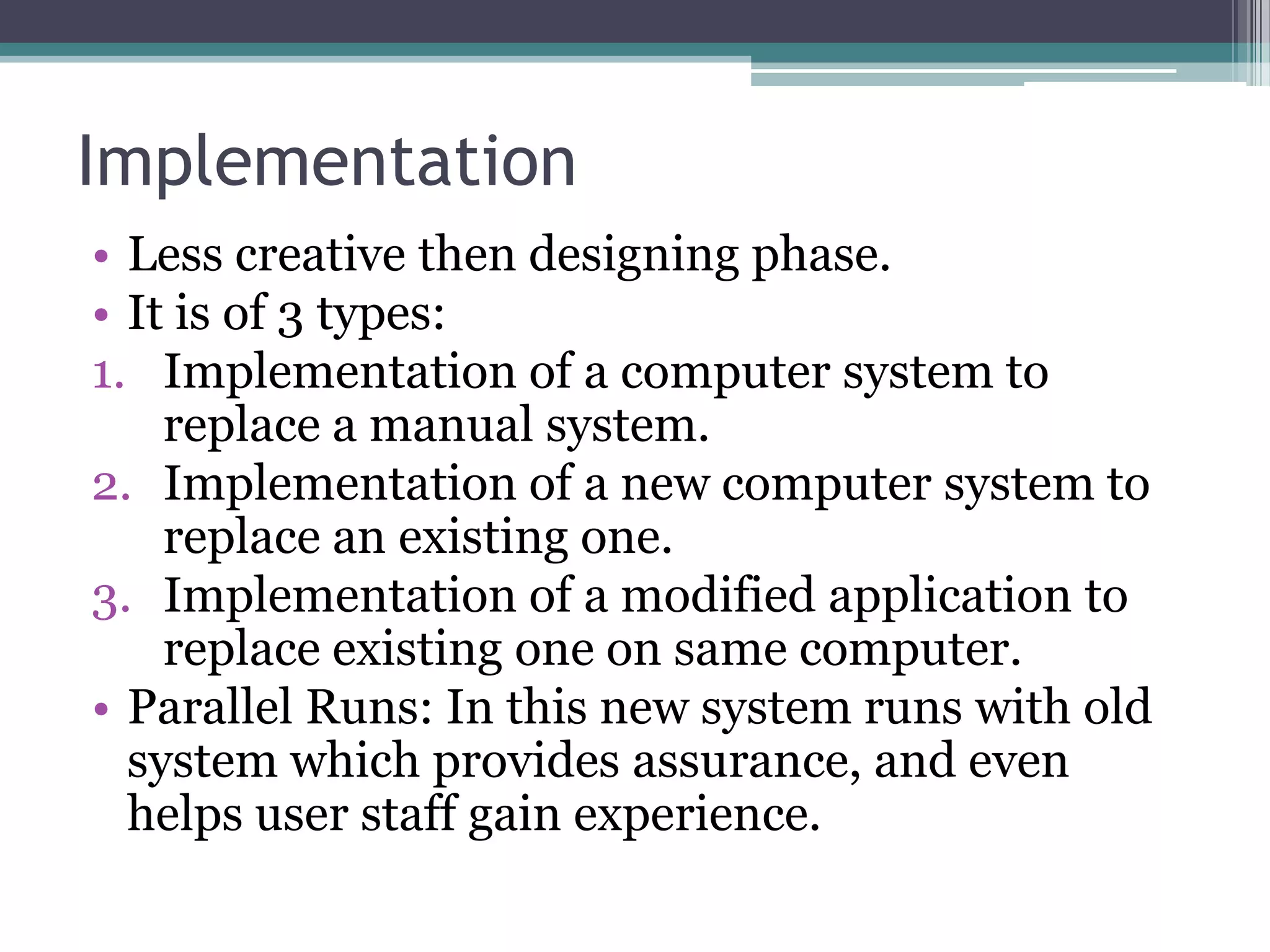
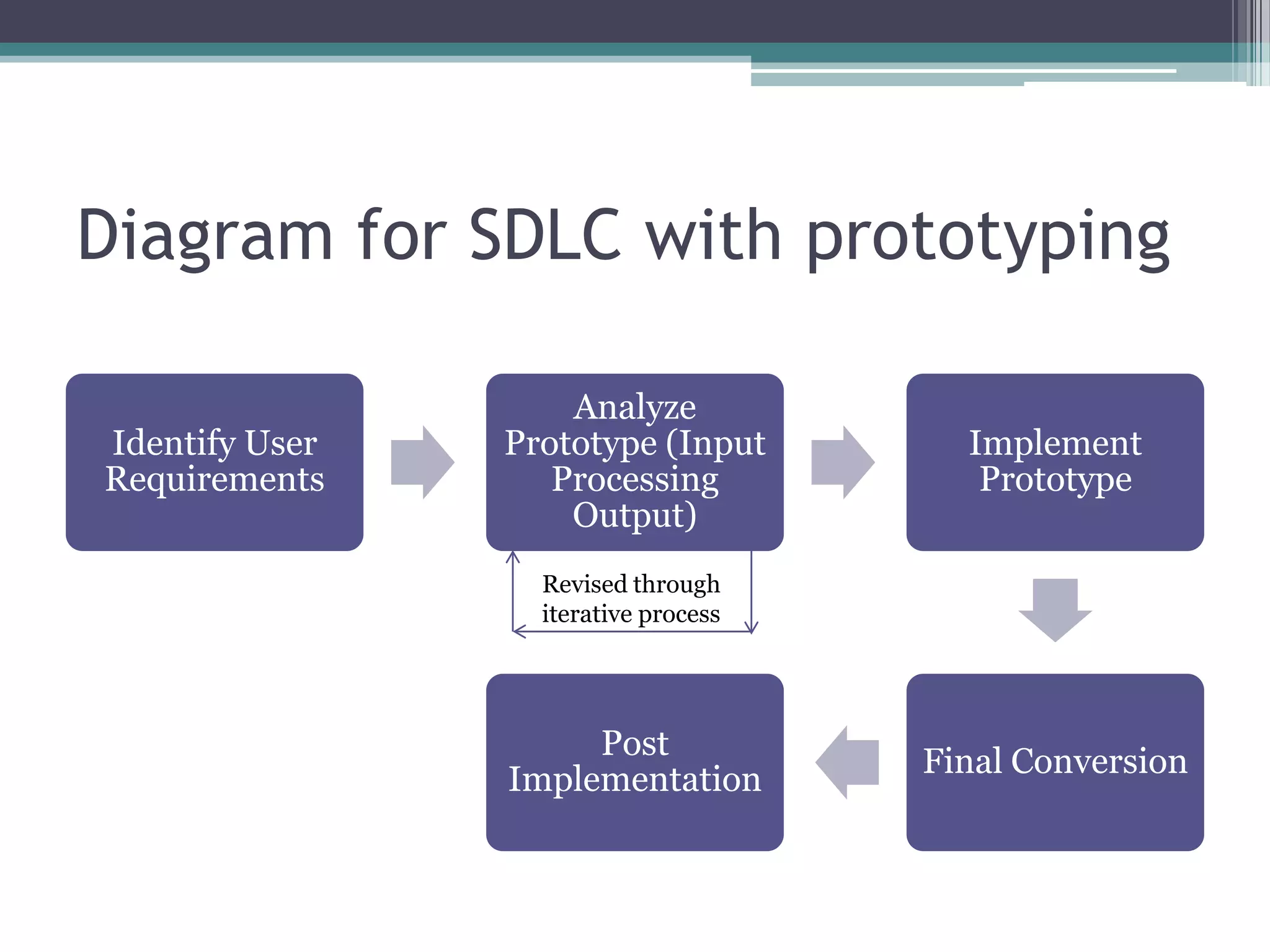
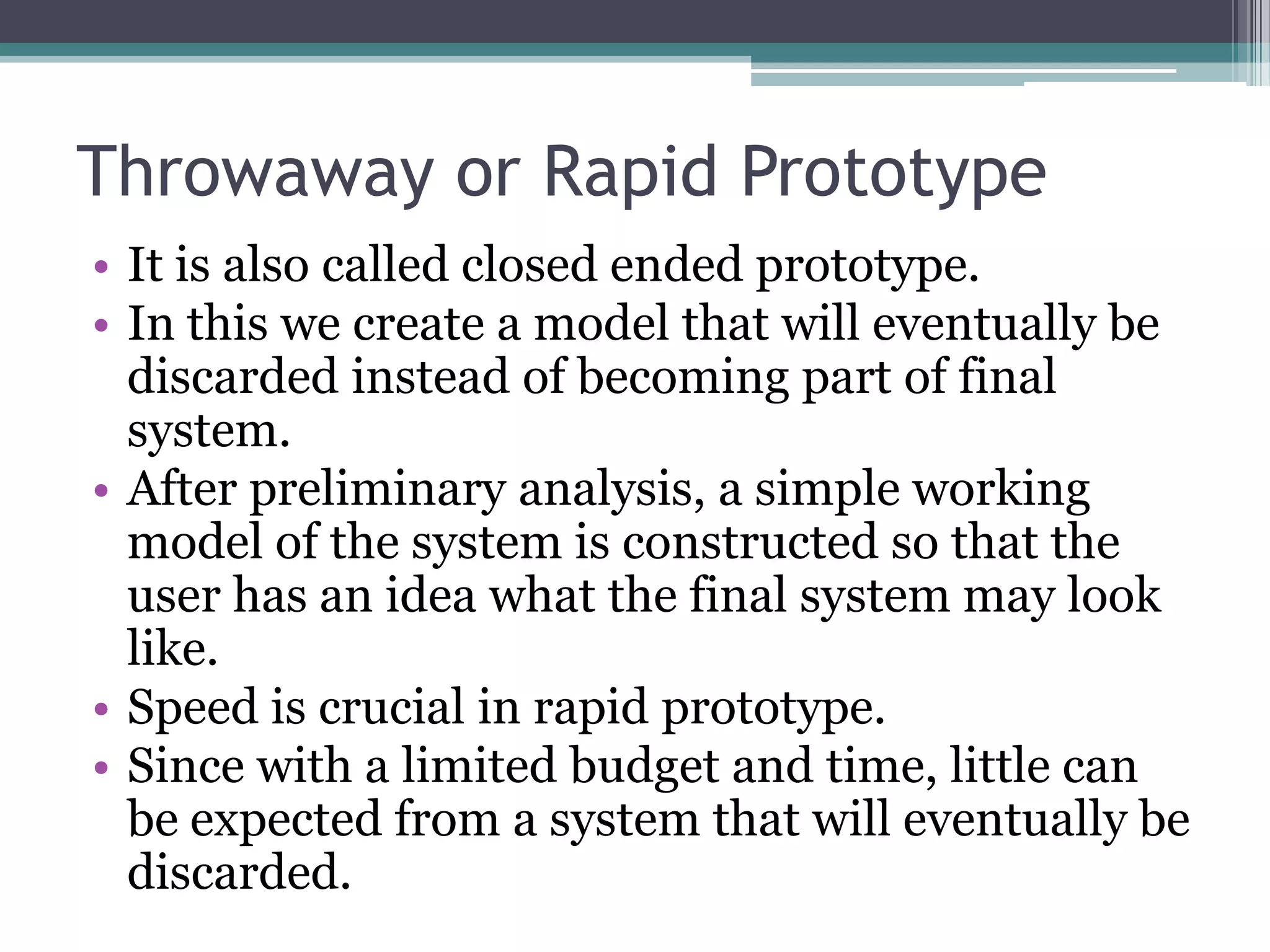
The document discusses the system development life cycle (SDLC), which describes the stages of an information system development project. It outlines the typical stages: recognition of need, feasibility study, analysis, design, implementation, post-implementation, maintenance, and prototyping. The feasibility study assesses the economic, technical, and behavioral factors. Analysis involves gathering requirements through tools like interviews and documentation. Design defines technical specifications and system flow. Implementation deploys the system. Prototyping allows refining the system through iterative testing and user feedback before final implementation.