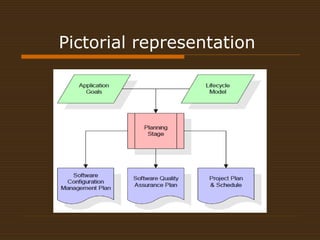
The document discusses the system development life cycle (SDLC), which is a process used by systems analysts to develop information systems. It describes the main phases of the SDLC as planning, requirements definition, design, development, integration and testing, operations and maintenance, and implementation and evaluation. Each phase is discussed in detail, with definitions and pictorial representations provided. The document also covers the merits and demerits of following the SDLC process.