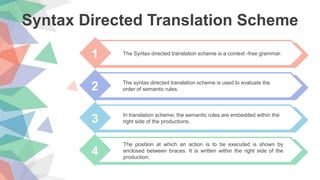
The document discusses syntax-directed translation (SDT) which is a method of compiler implementation where source language translation is driven by the parser. SDT uses an augmented context-free grammar called an attribute grammar to control semantic analysis and translation. SDT translates a string into a sequence of actions by attaching actions to each rule of the grammar. The parsing process and parse trees are used to direct semantic analysis and translation of the source program according to the order specified by the semantic rules embedded in the grammar.