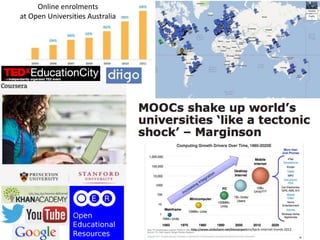
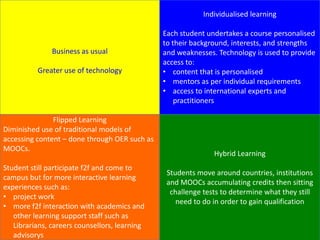
The document discusses trends in online education including the rise of MOOCs and how they are impacting traditional models of learning. It notes that MOOC learners tend to be professionals looking to develop skills for their jobs. The UTS model of learning emphasizes professional practice, global engagement, and research-inspired education. It also outlines new learning spaces and technologies being used at UTS to support collaborative and interactive learning experiences.