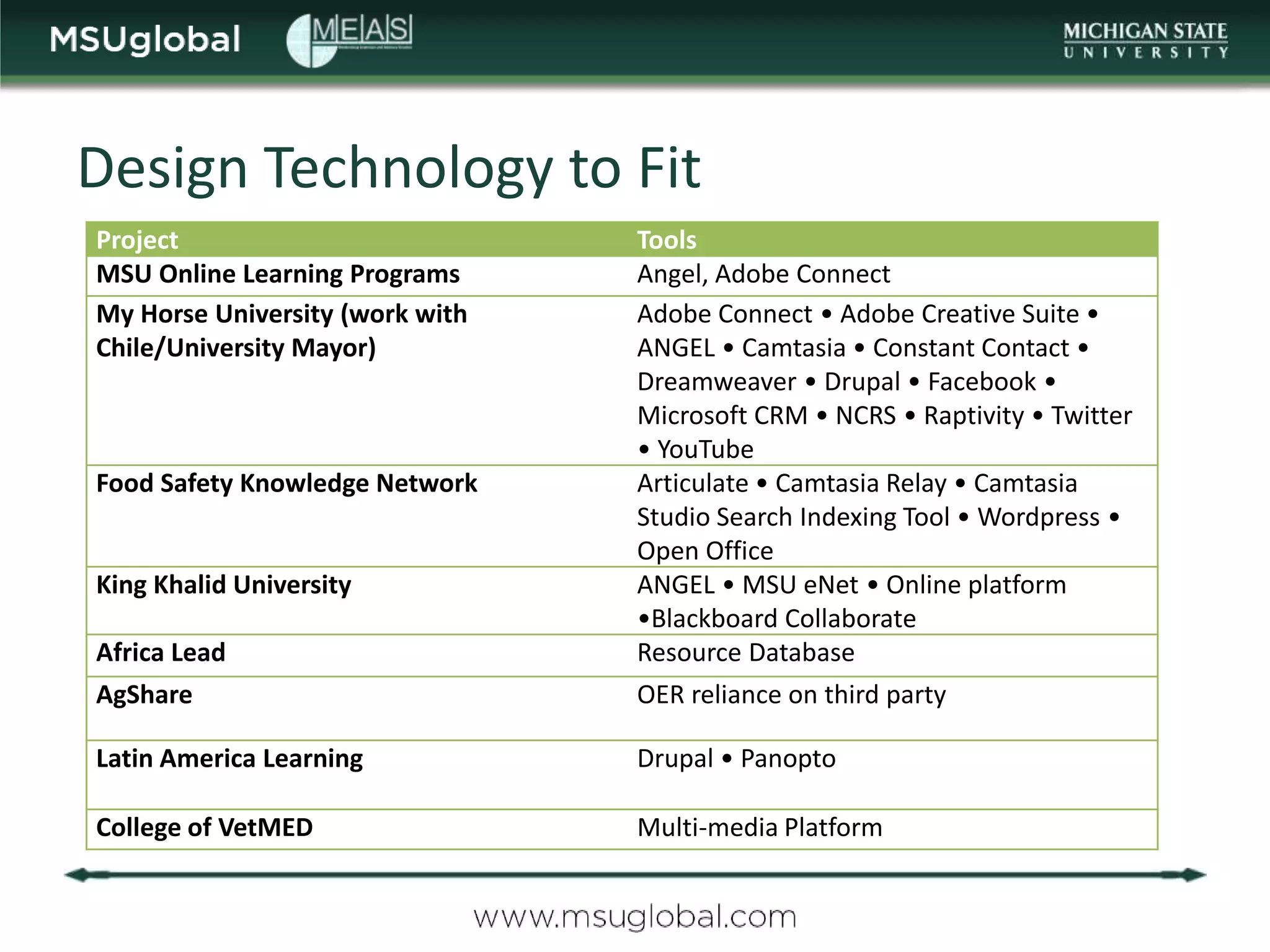
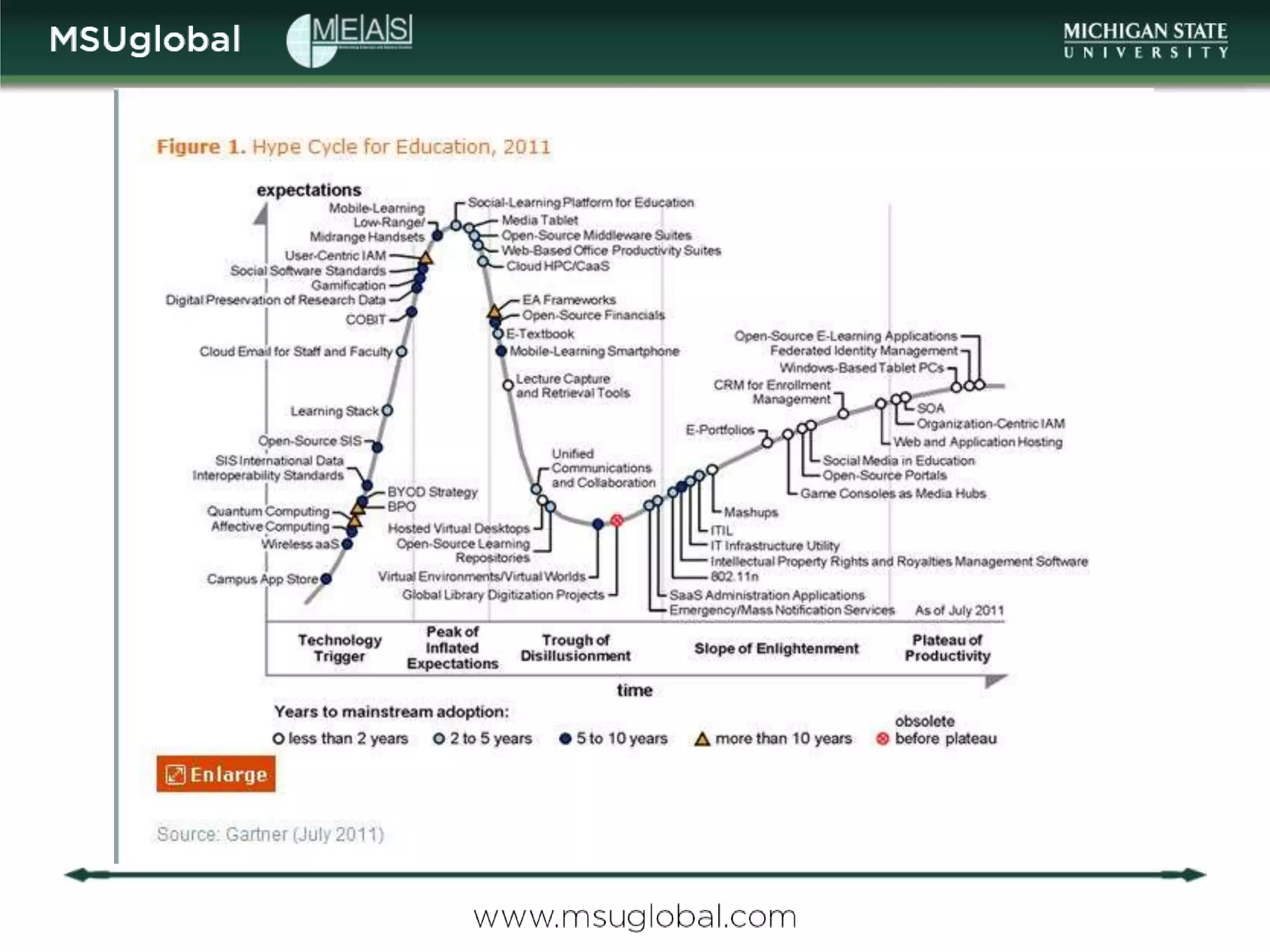
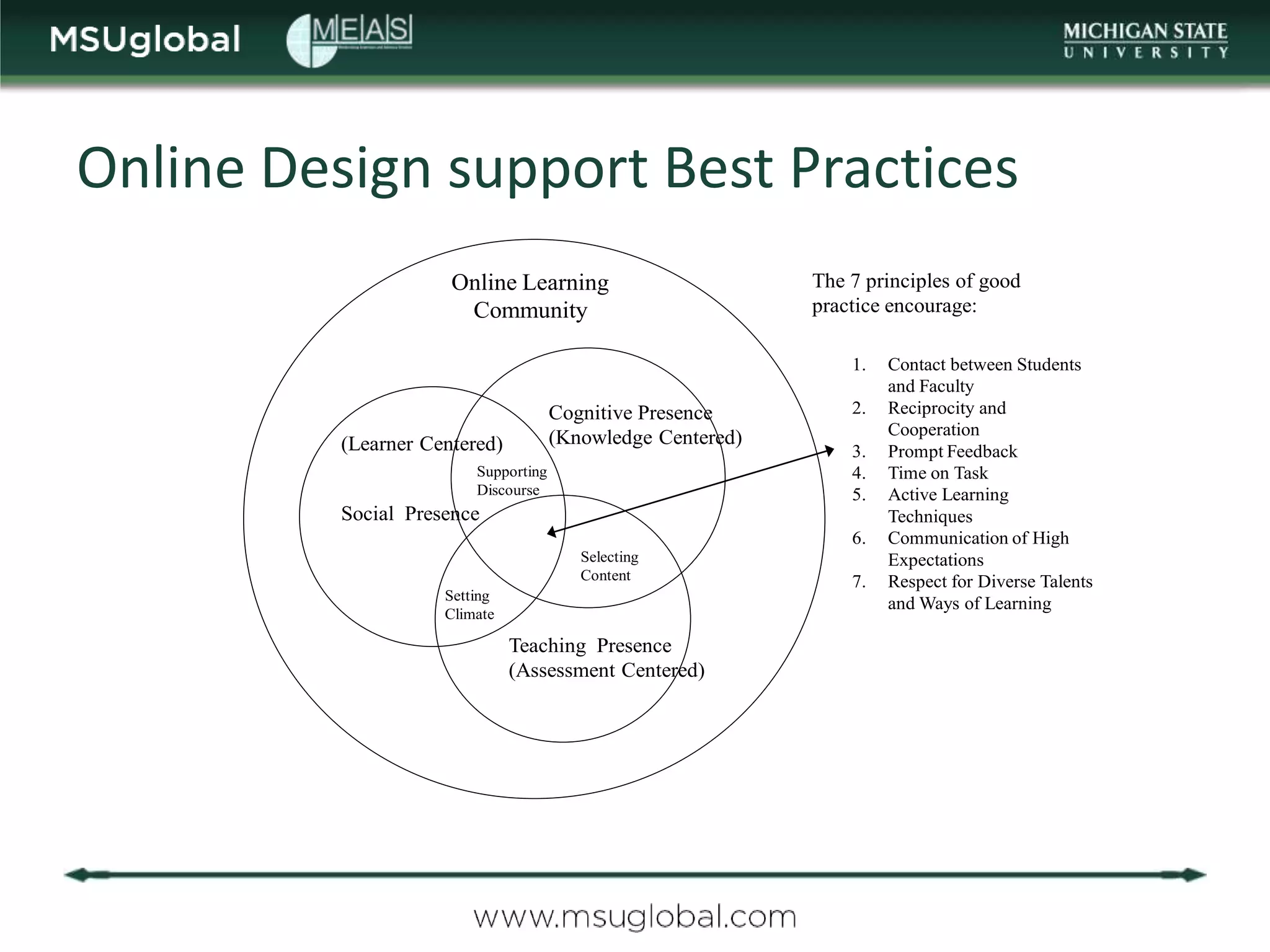
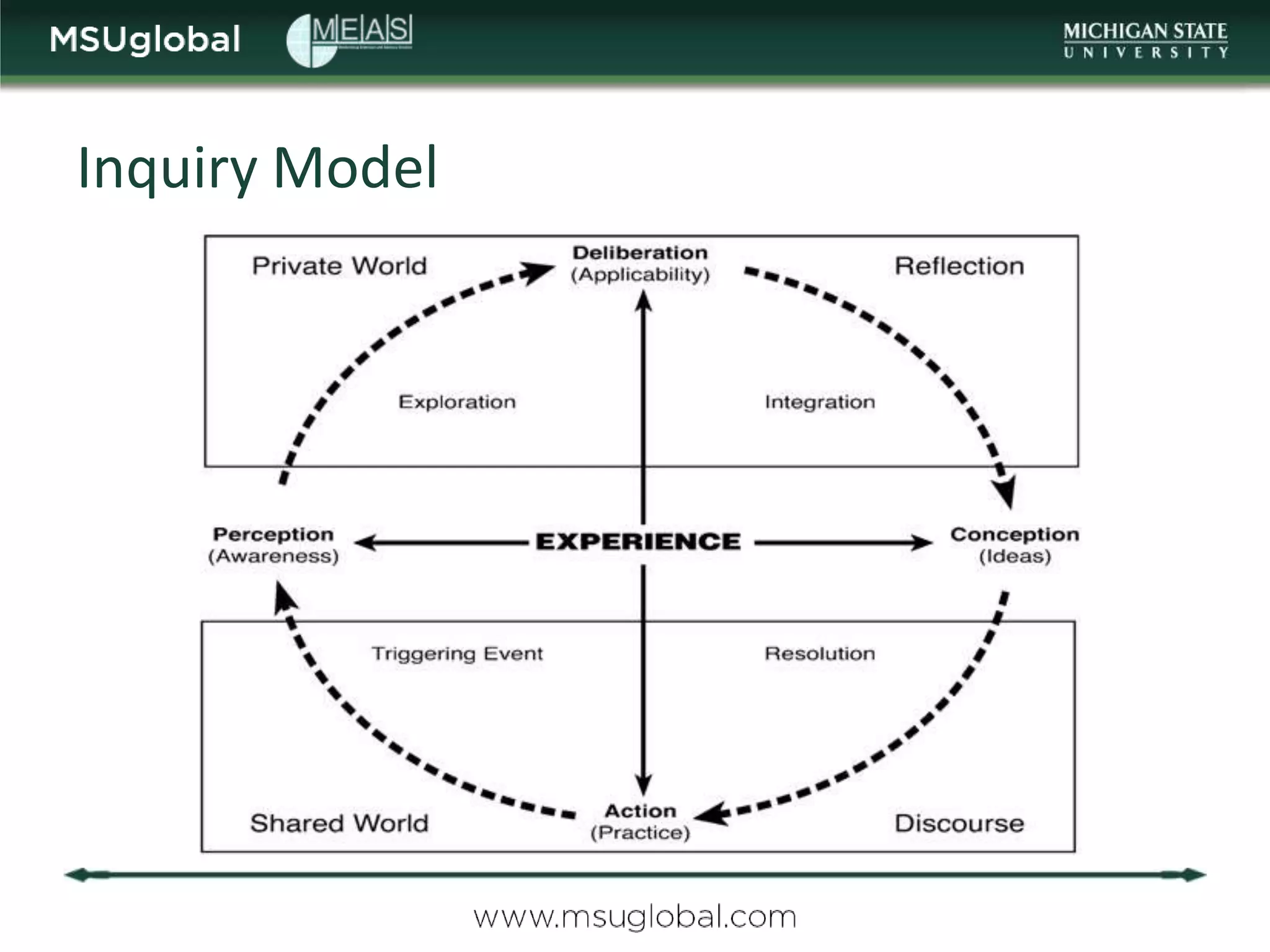
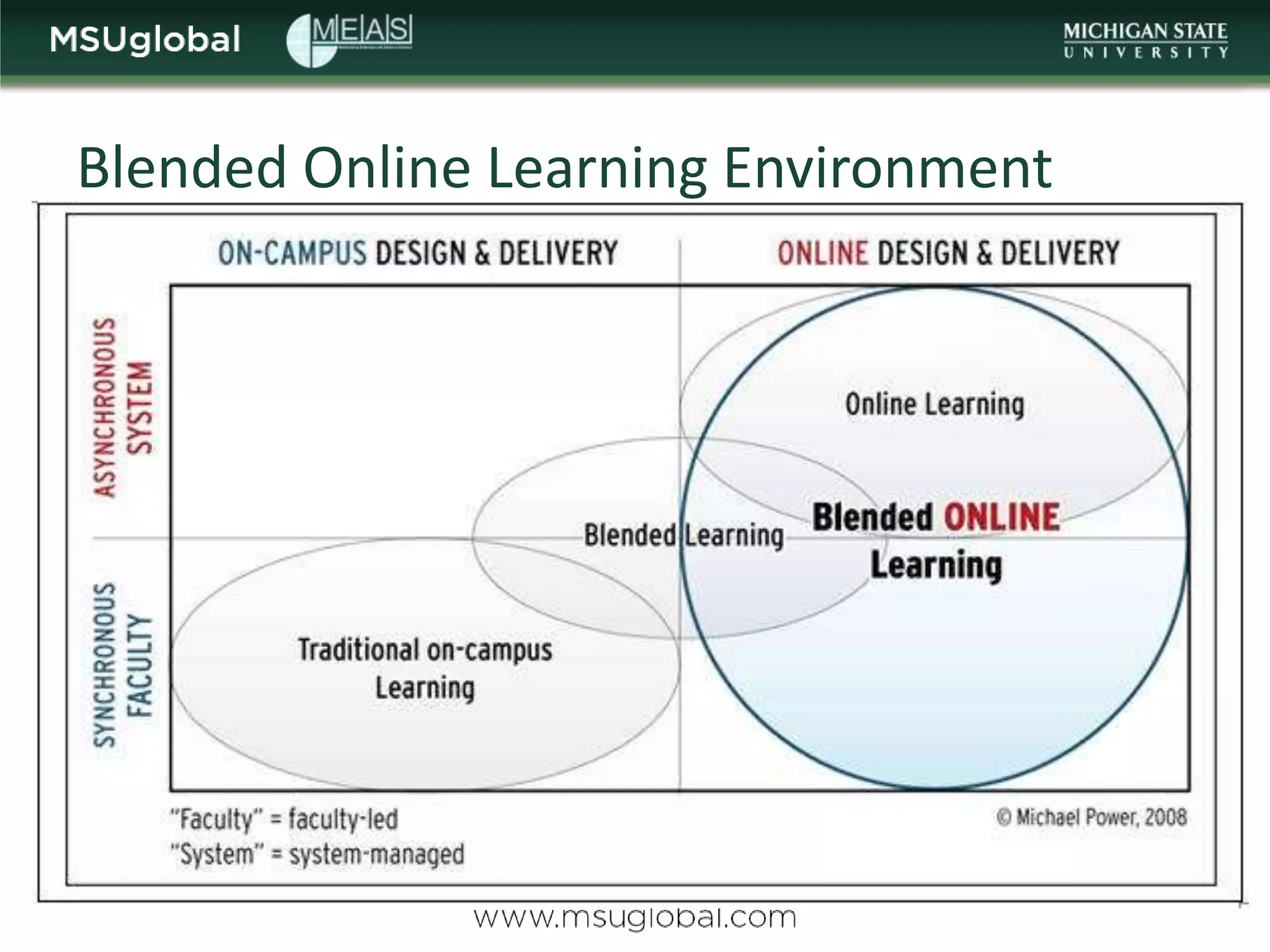
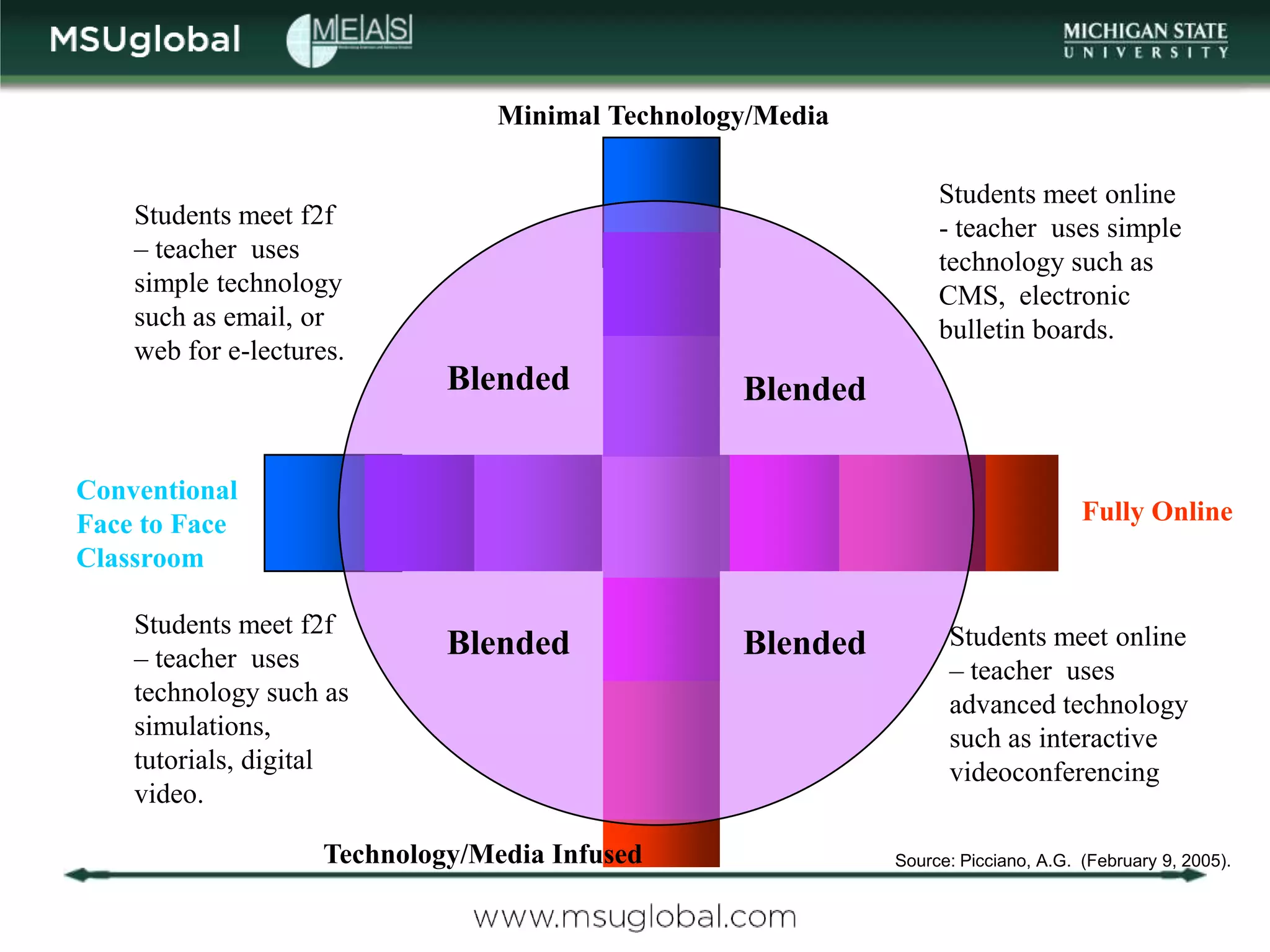
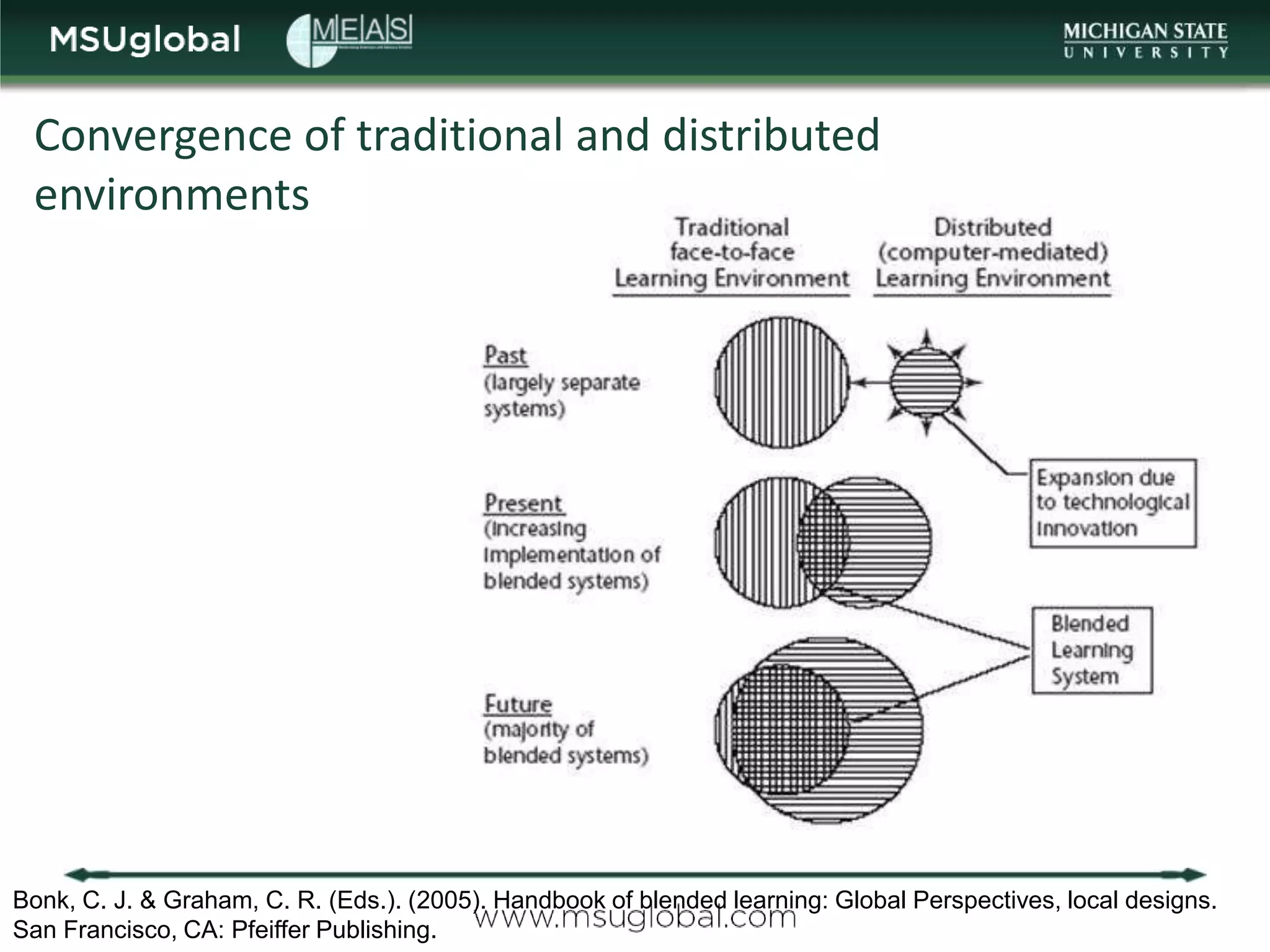
The document by Karen Vignare from Michigan State University provides an overview of online learning, blended learning, and open educational resources (OER). It emphasizes the importance of technology in education, the characteristics of online and blended learning, and the benefits of OER in making educational materials accessible and adaptable. It outlines best practices for online course design and highlights trends in e-learning that facilitate learning experiences.