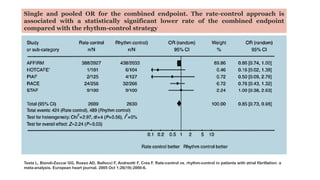
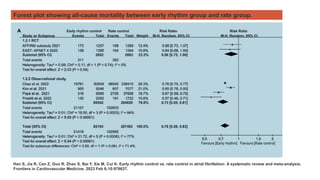
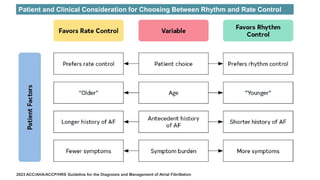
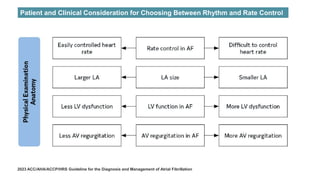
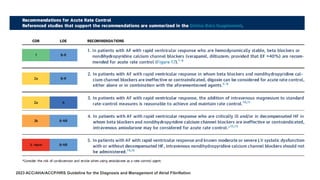
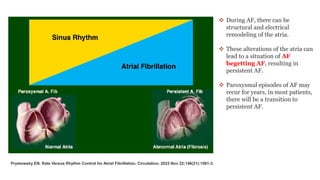
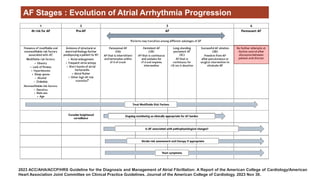
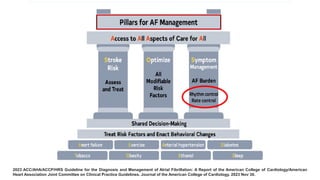
The document reviews studies on atrial fibrillation (AF), comparing rhythm control to rate control in terms of their effectiveness on mortality and quality of life. It finds no significant differences in outcomes between strategies in most trials reviewed, with rhythm control often leading to increased hospitalizations. Recent guidelines suggest early rhythm control may reduce AF burden and improve clinical outcomes, although more research is needed to clarify these findings.


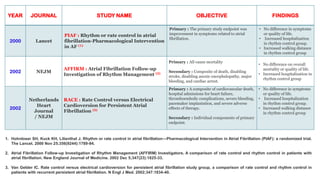

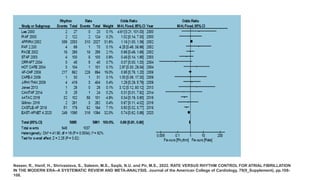
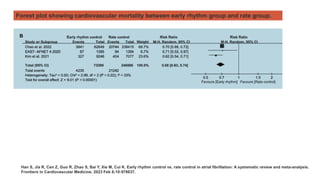
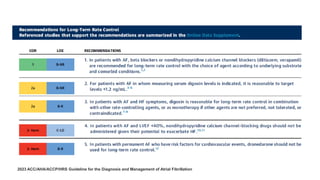
![YEAR JOURNAL STUDY NAME OBJECTIVE FINDINGS
2005
European
Heart
Journal
Rate-control vs. rhythm-control in
patients with atrial fibrillation: A Meta-
Analysis
• RACE
• AFFIRM
• PIAF
• STAF
• HOT CAFÉ
Systematically assess the risk/benefit
ratio of a rate-control strategy vs. a
rhythm-control strategy in patients with
first or recurrent atrial fibrillation (AF)
• 5239 patients with AF
compared rate-control vs.
rhythm-control.
• Average follow-up ranged
from 1 to 3.5 years.
• A rate-control strategy
compared with a rhythm-
control approach was
associated with a
significantly reduced risk
of CEP [OR 0.84 (0.73,
0.98), P ¼ 0.02], and with
a trend towards a reduced
risk of death [OR 0.87
(0.74, 1.02), P ¼ 0.09]
and thromboembolic
stroke [OR 0.80 (0.6,
1.07), P ¼ 0.14].
• There was no significant
difference in the risk of
major bleeds [OR 1.14
(0.9, 1.45), P ¼ 0.28] and
systemic embolism [OR
0.93 (0.43, 2.02), P ¼
0.90].
Testa L, Biondi-Zoccai GG, Russo AD, Bellocci F, Andreotti F, Crea F. Rate-control vs. rhythm-control in patients with atrial fibrillation: a meta-analysis.
European heart journal. 2005 Oct 1;26(19):2000-6.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ratevsrhythmcontrolforafib-250115072055-efbfe01b/85/Rate-vs-Rhythm-control-for-Atrial-Fibrillation-8-320.jpg)