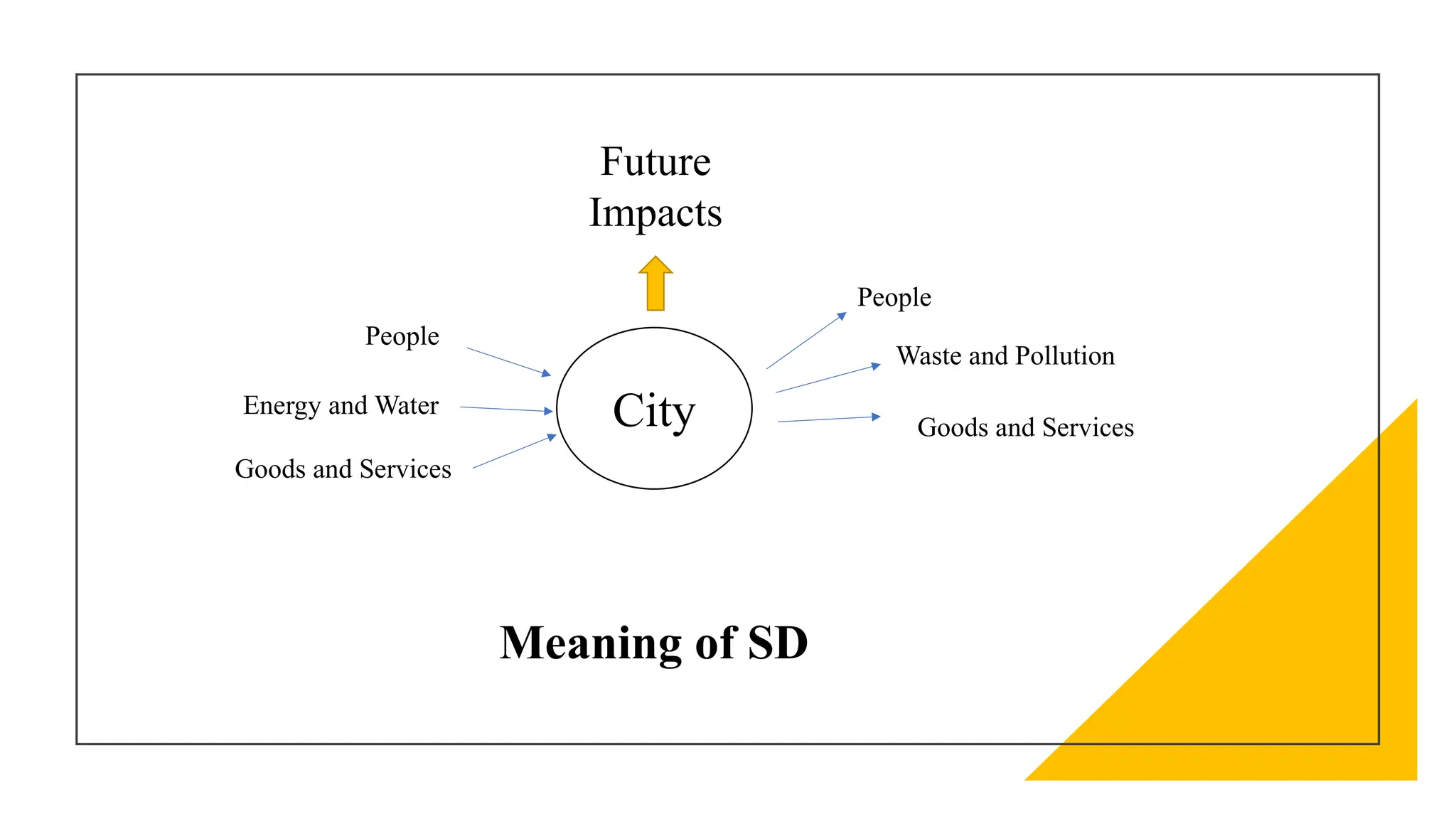
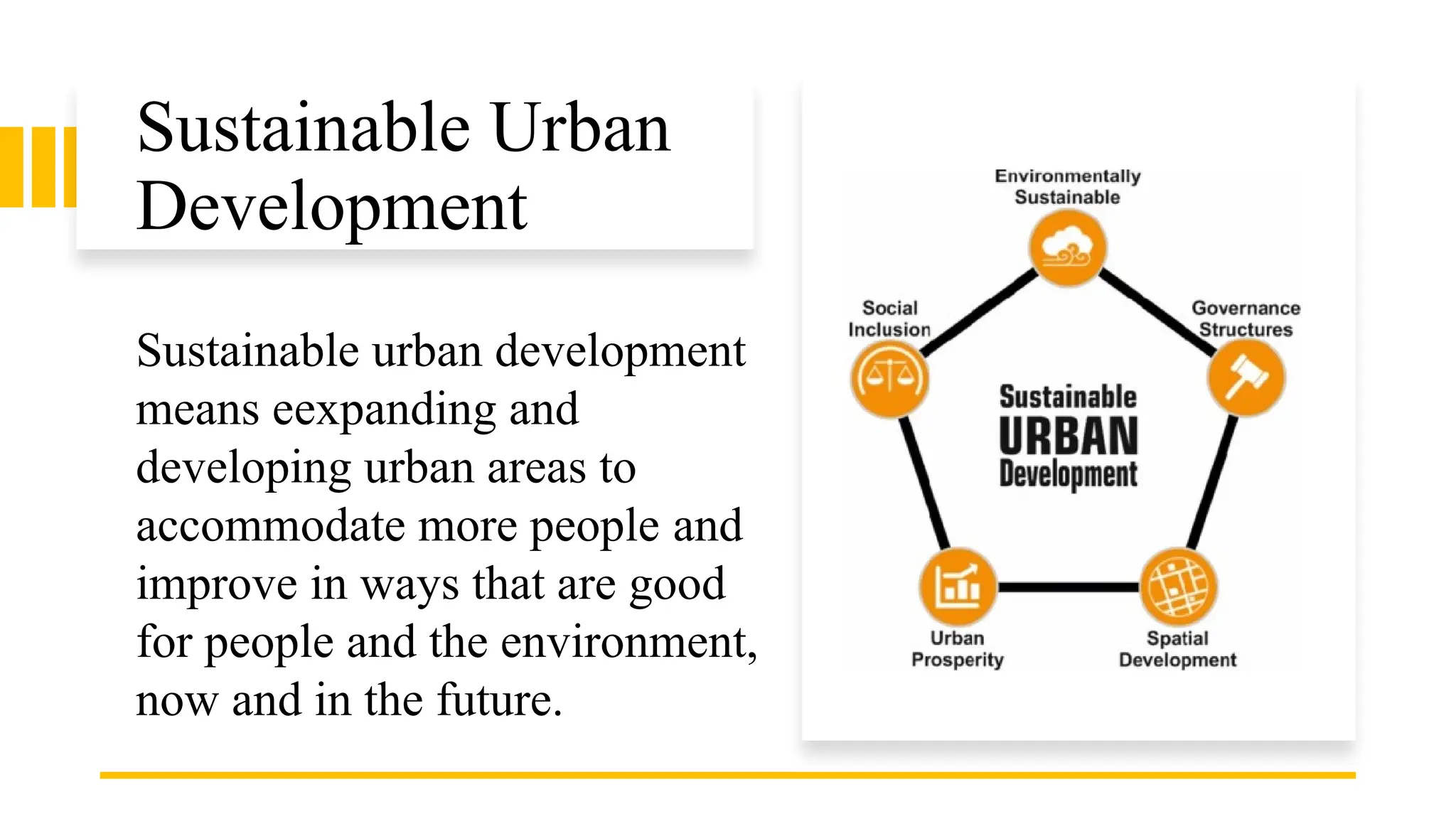
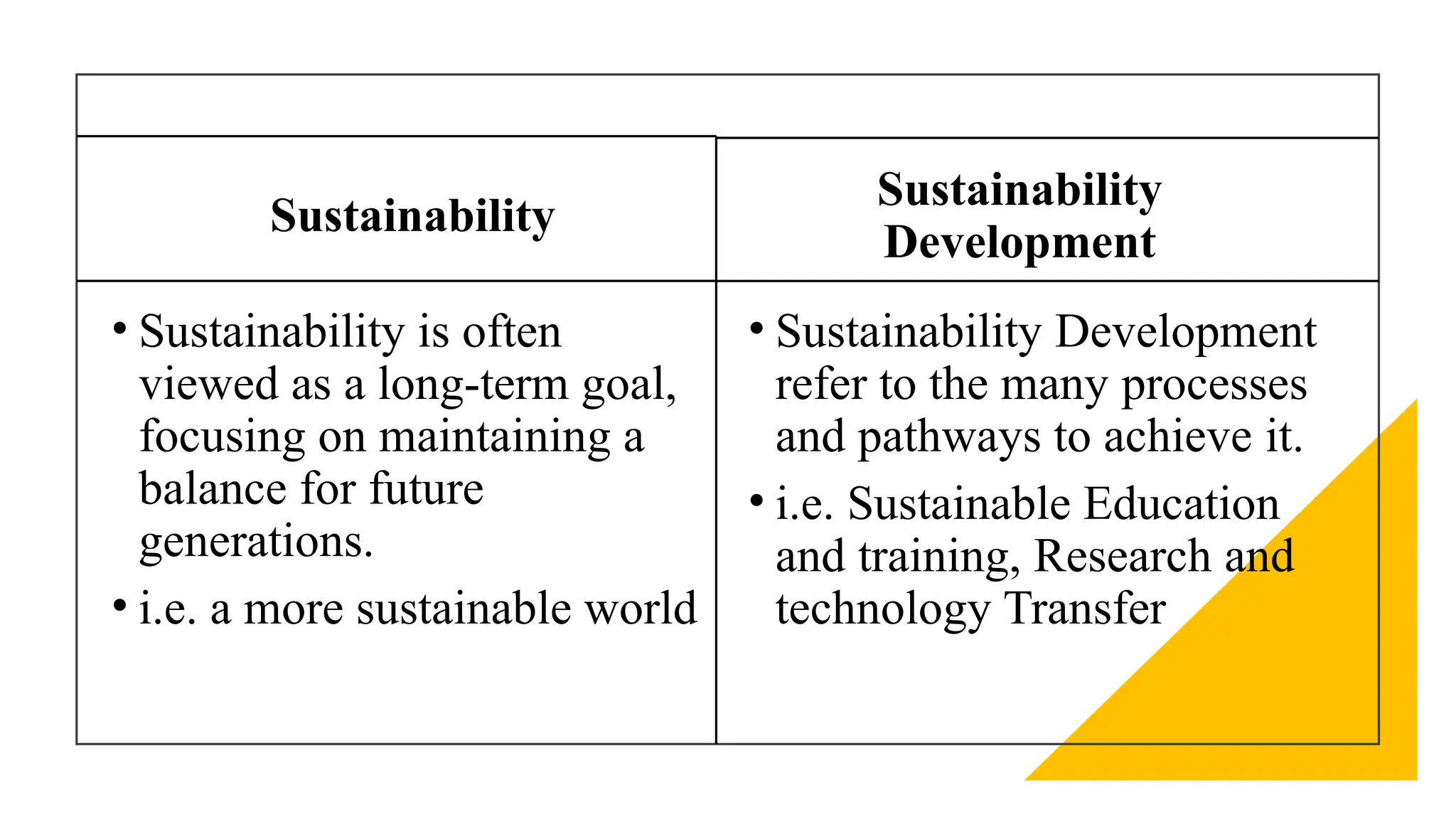
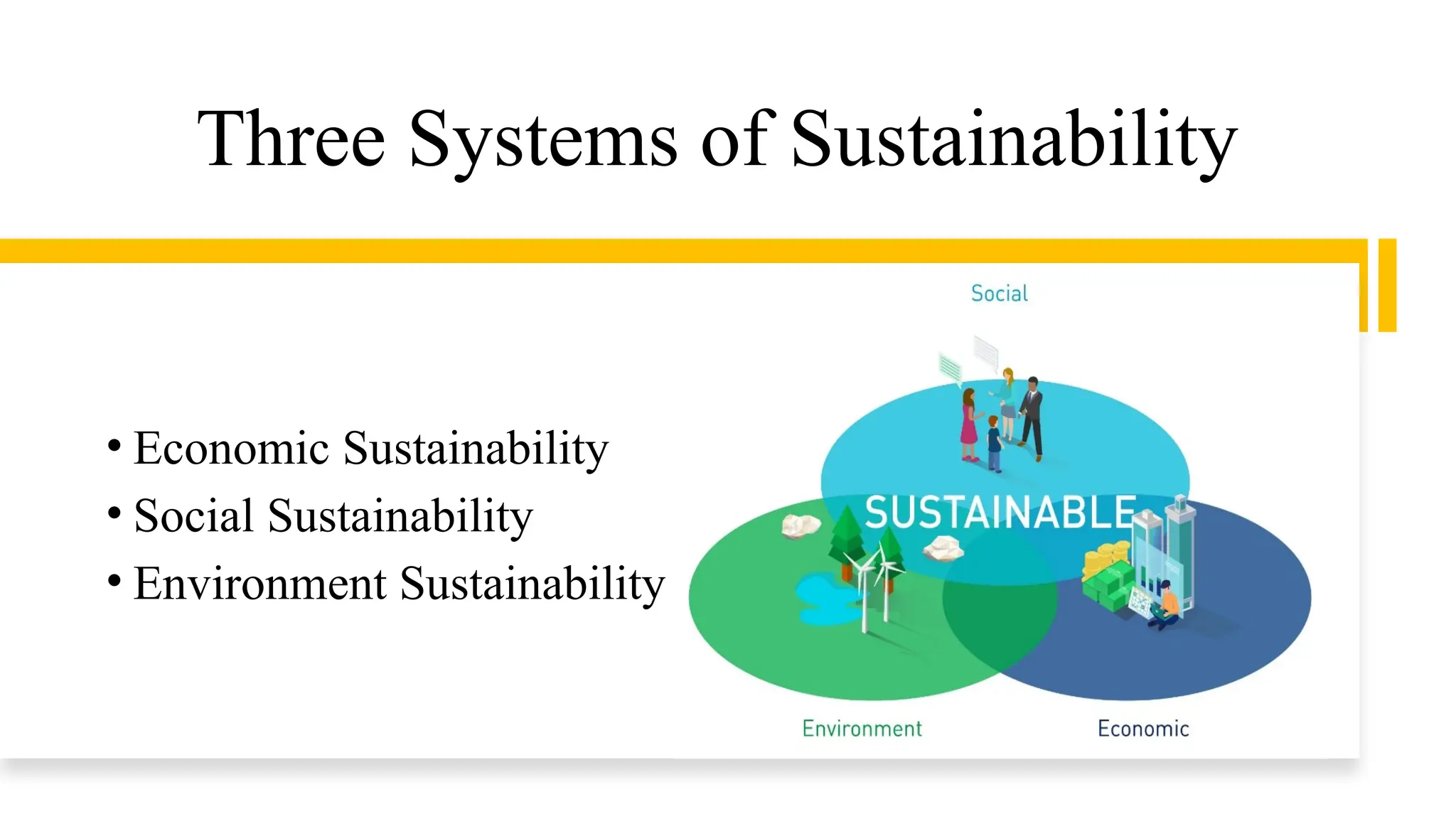
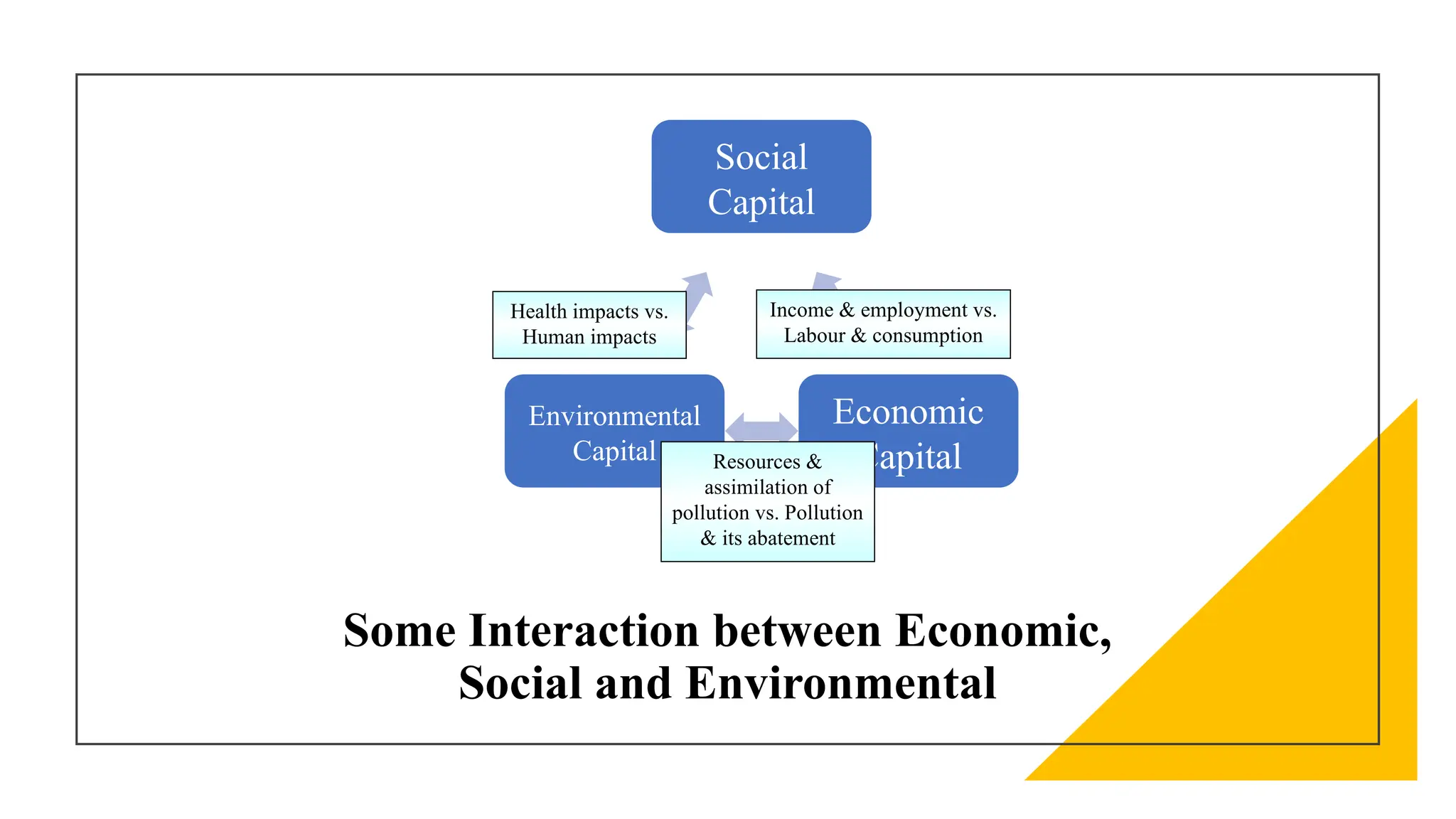
The document discusses sustainable urban development, emphasizing the need for a balanced approach to meet today's needs without compromising future generations. It outlines the key aspects of sustainability, including economic, social, environmental, and political dimensions, and highlights common urban issues related to pollution, green spaces, and resource management. Copenhagen is presented as an exemplary model of sustainable urban development, showcasing initiatives such as biking infrastructure, green spaces, and clean energy utilization.