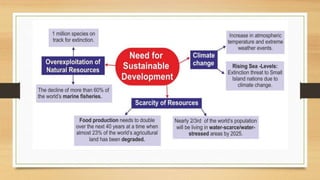
The document provides an overview of a seminar presentation on sustainable development goals and Agenda 2030. It defines sustainable development, discusses the three pillars of sustainability - environmental, economic, and social. It outlines the 17 UN sustainable development goals, global issues related to sustainable development like climate change, inequality, and challenges in achieving the goals. It concludes that sustainable development ensures resources are available for future generations through eco-friendly practices.