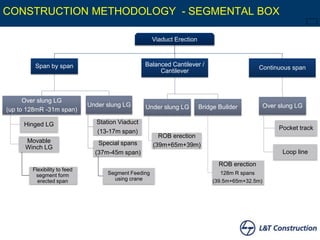
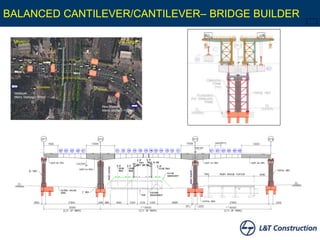
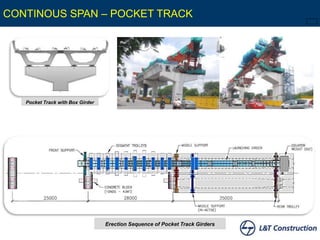
This document discusses sustainable construction techniques used for the Hyderabad Metro Rail project in India. It focuses on the use of precast segmental construction methods for the viaduct that reduced disturbance to traffic during construction. Over 99,000 precast concrete segments were produced in two large casting yards and erected using various launching girder techniques, including hinged, movable winch, underslung, balanced cantilever, cantilever, and continuous span methods. This allowed for the fast, flexible, and high quality construction of the 71 kilometer elevated viaduct structure with 66 stations.