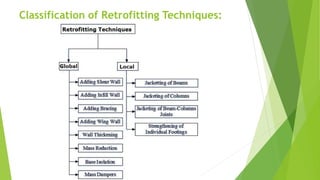
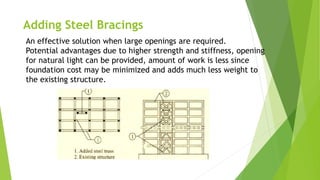
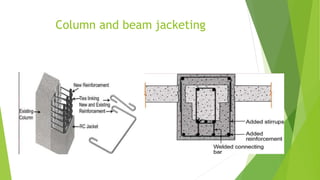
This document discusses various techniques for retrofitting concrete structures to make them more resistant to seismic activity and other natural hazards. It defines retrofitting as modifying existing structures to increase resistance. Key techniques mentioned include adding new shear walls, steel bracing, column and beam jacketing with steel or concrete, base isolation using seismic isolators, mass reduction by removing floors, and wall thickening. The document also discusses challenges in retrofitting and standards from Indian codes for earthquake-resistant design. The conclusion emphasizes that retrofitting has matured but expertise is still lacking, and optimization is needed to determine the most cost-effective technique for a given structure.