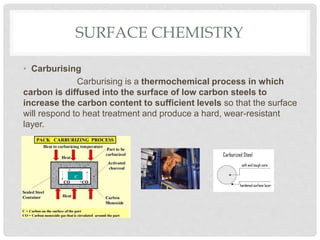
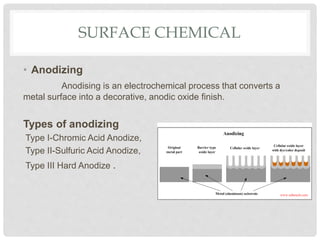
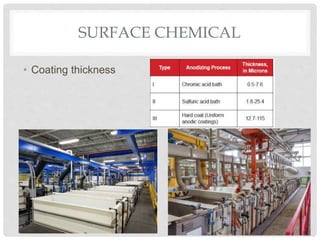
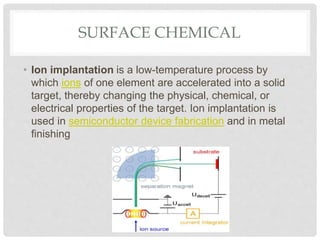
This document discusses different types of surface treatment processes. Surface treatment involves modifying the surface of a material to improve properties like corrosion and wear resistance or appearance. There are two main types: surface metallurgy and surface chemistry. Surface metallurgy changes the microstructure only on the surface through processes like surface hardening, laser melting, and shot peening. Surface chemistry involves diffusion processes like carburizing, nitriding, anodizing, carbonitriding, and chromizing to add elements to the surface and create a hardened casing. Ion implantation is also discussed as a low-temperature process to modify surface properties.