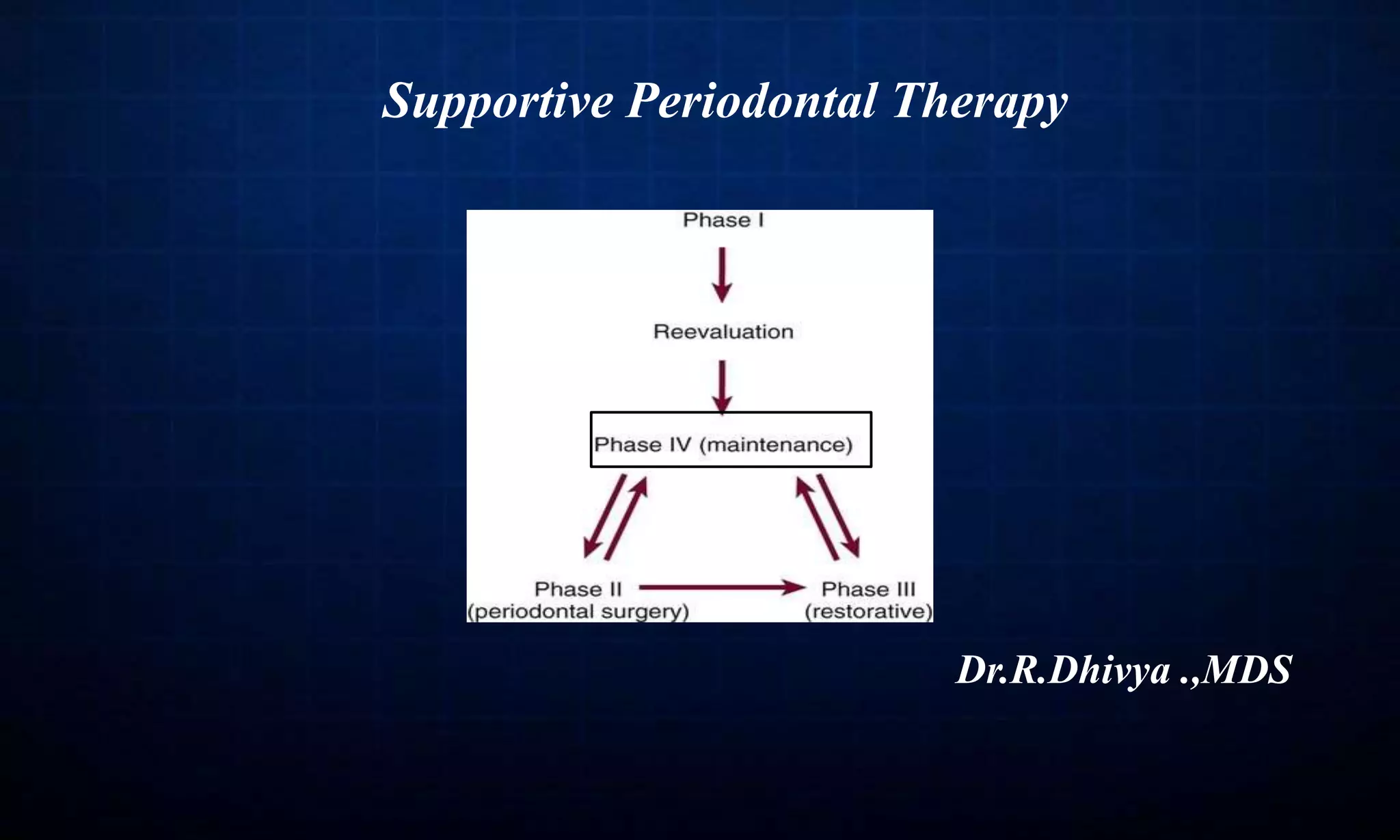
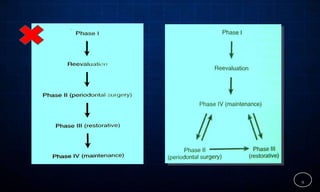
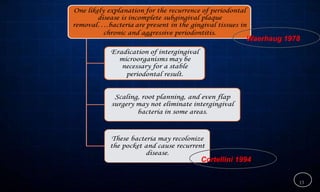
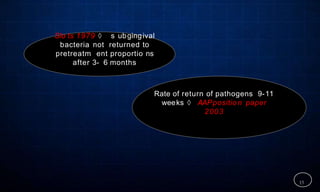
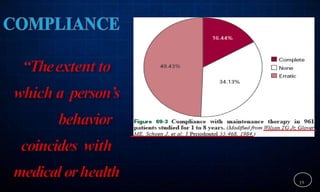
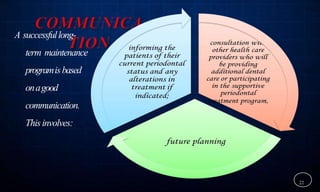
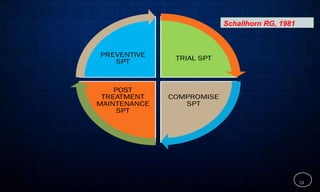
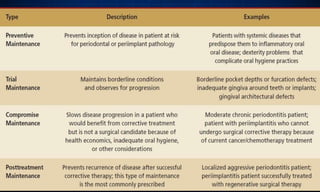
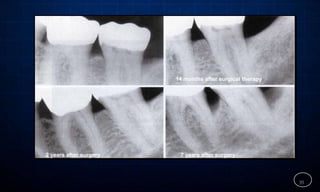
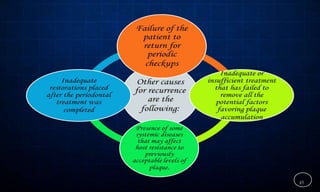
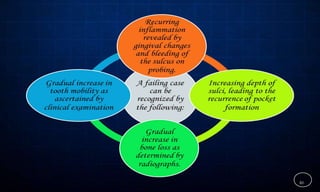
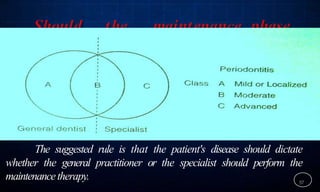
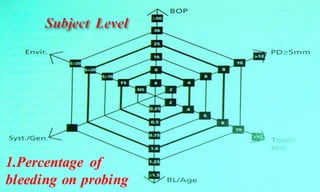
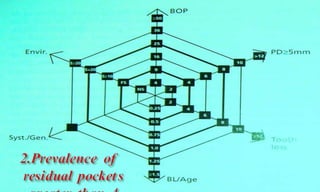
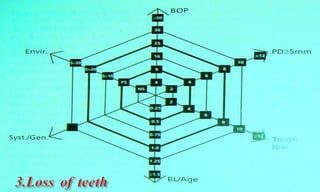
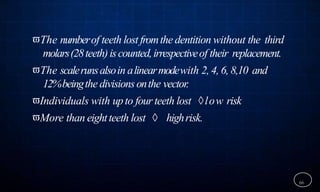
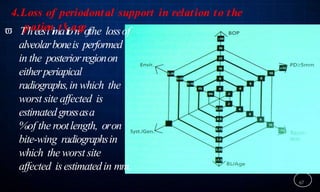
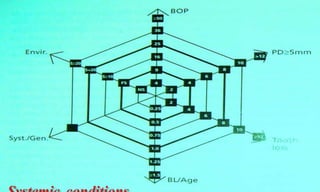
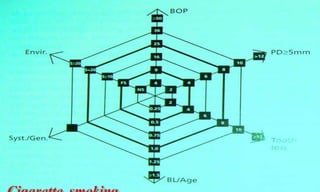
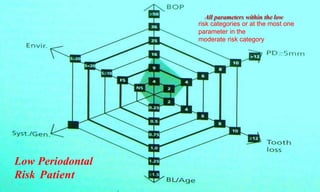
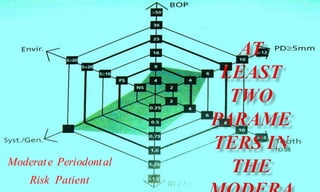
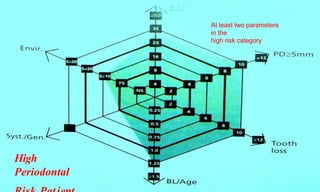
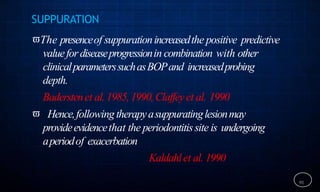
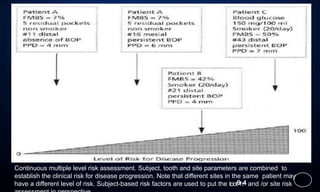
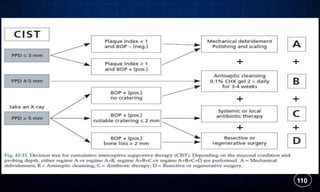
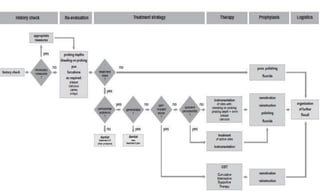
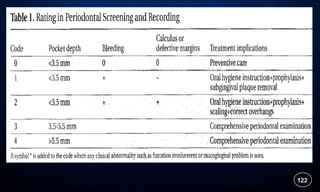
This document discusses supportive periodontal therapy (SPT), including its objectives, components, efficacy, and role in daily practice. SPT involves regular patient monitoring after active periodontal treatment to prevent reinfection and continued disease progression. Key aspects of SPT include patient motivation and reinstruction, treatment of reinfected sites, polishing and fluoride application, and determining the appropriate recall interval. The success of long-term SPT relies on effective communication and compliance. SPT can help maintain bone height and attachment levels if performed regularly.