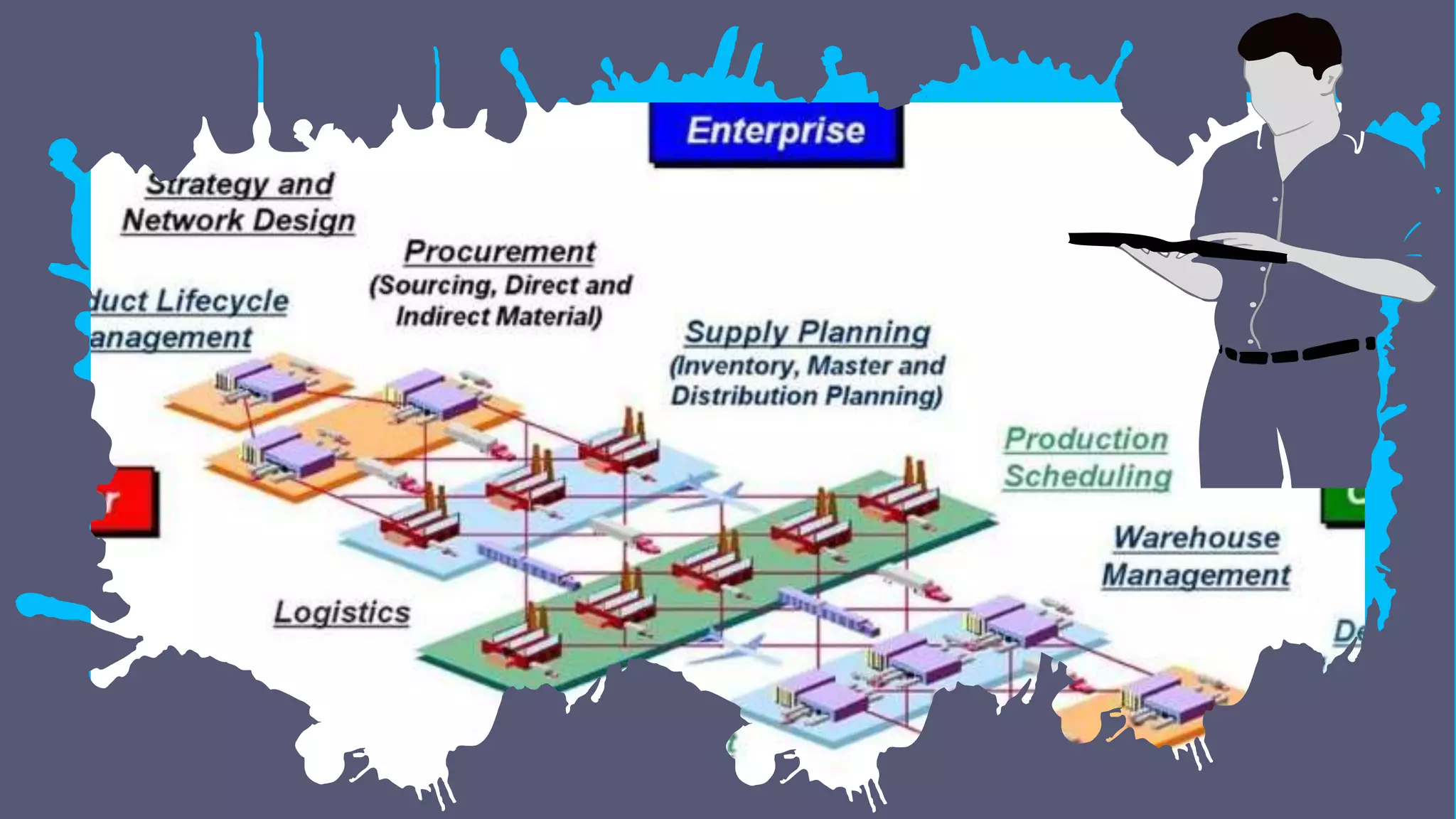
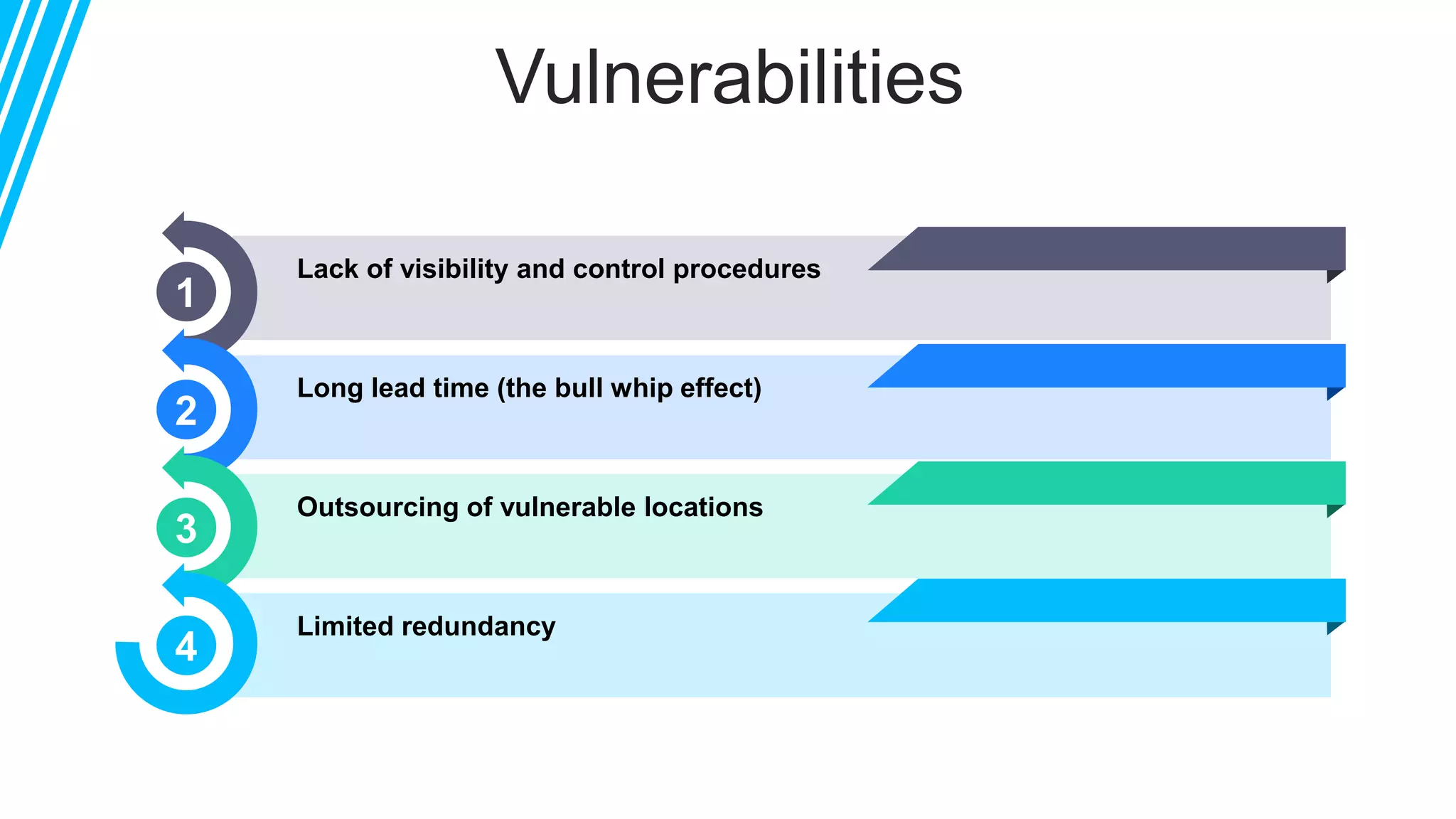
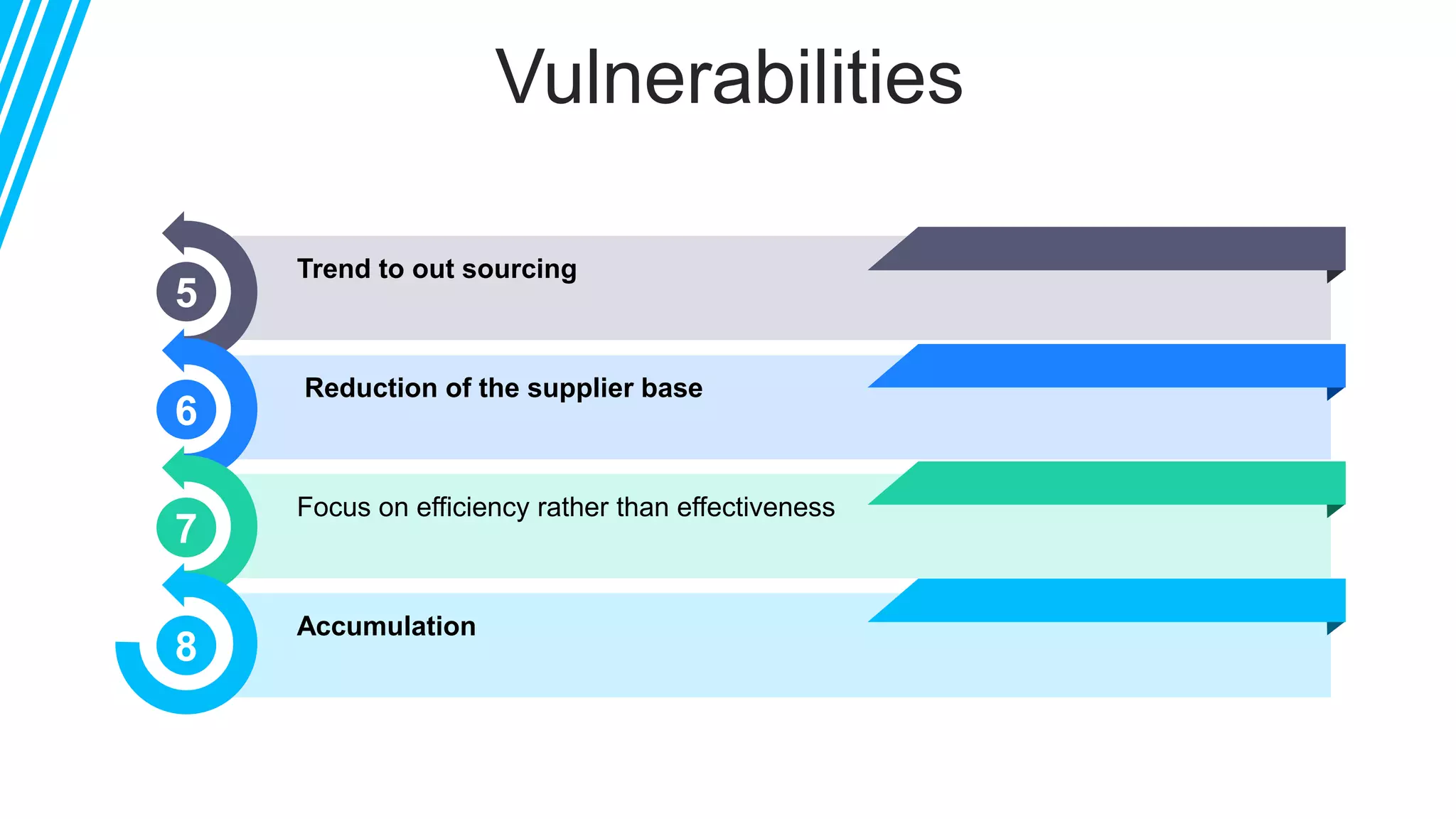
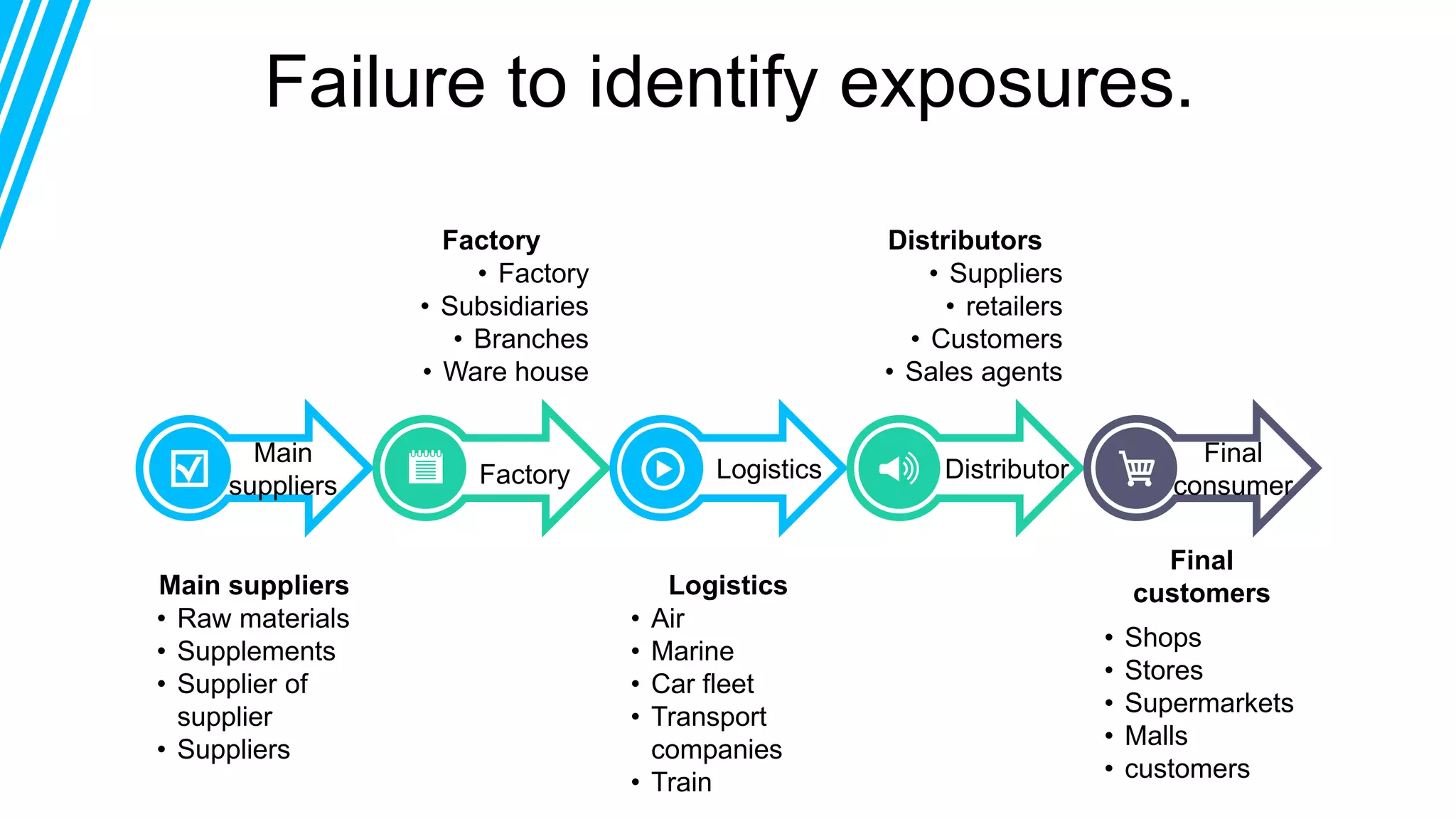
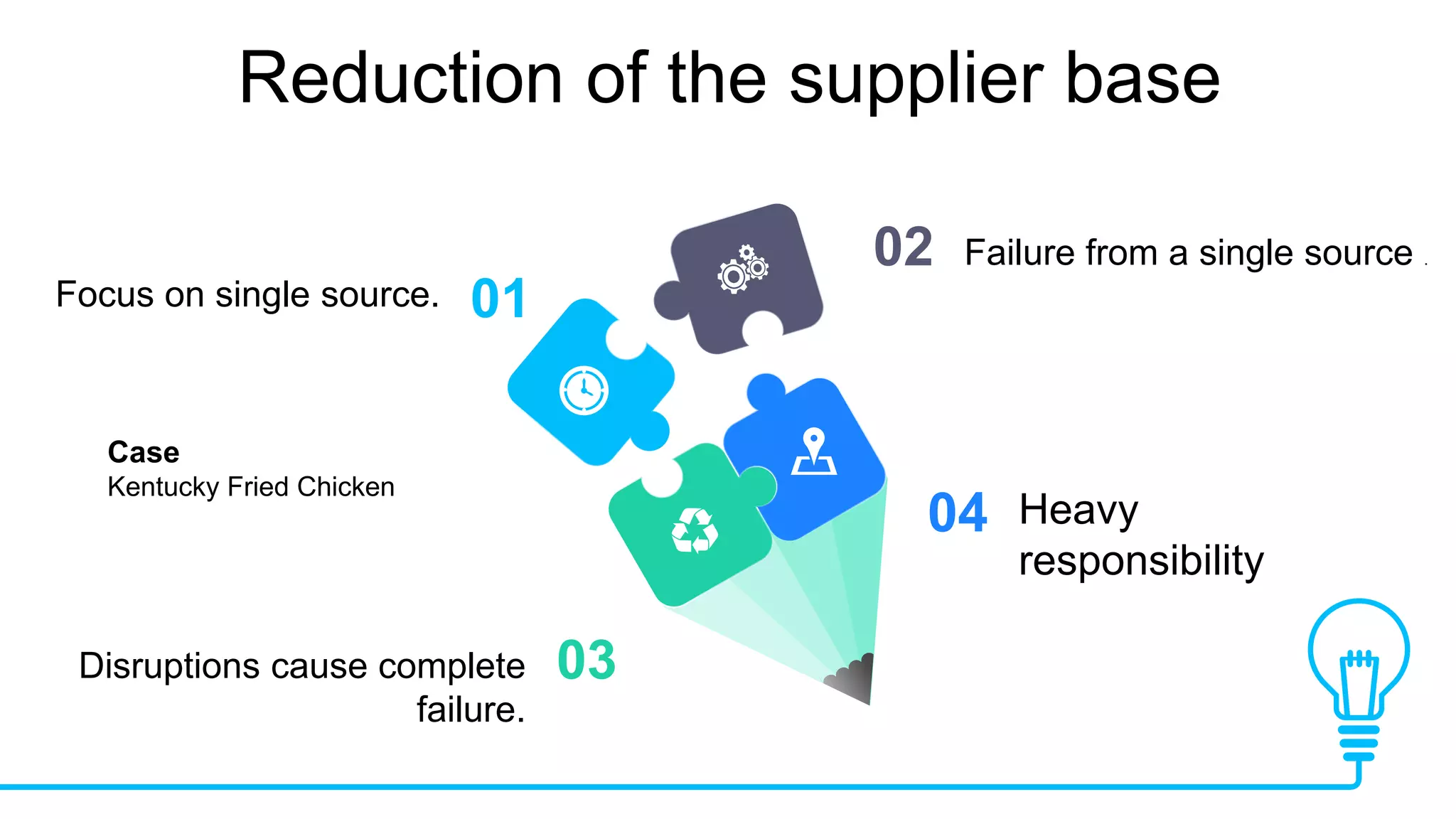
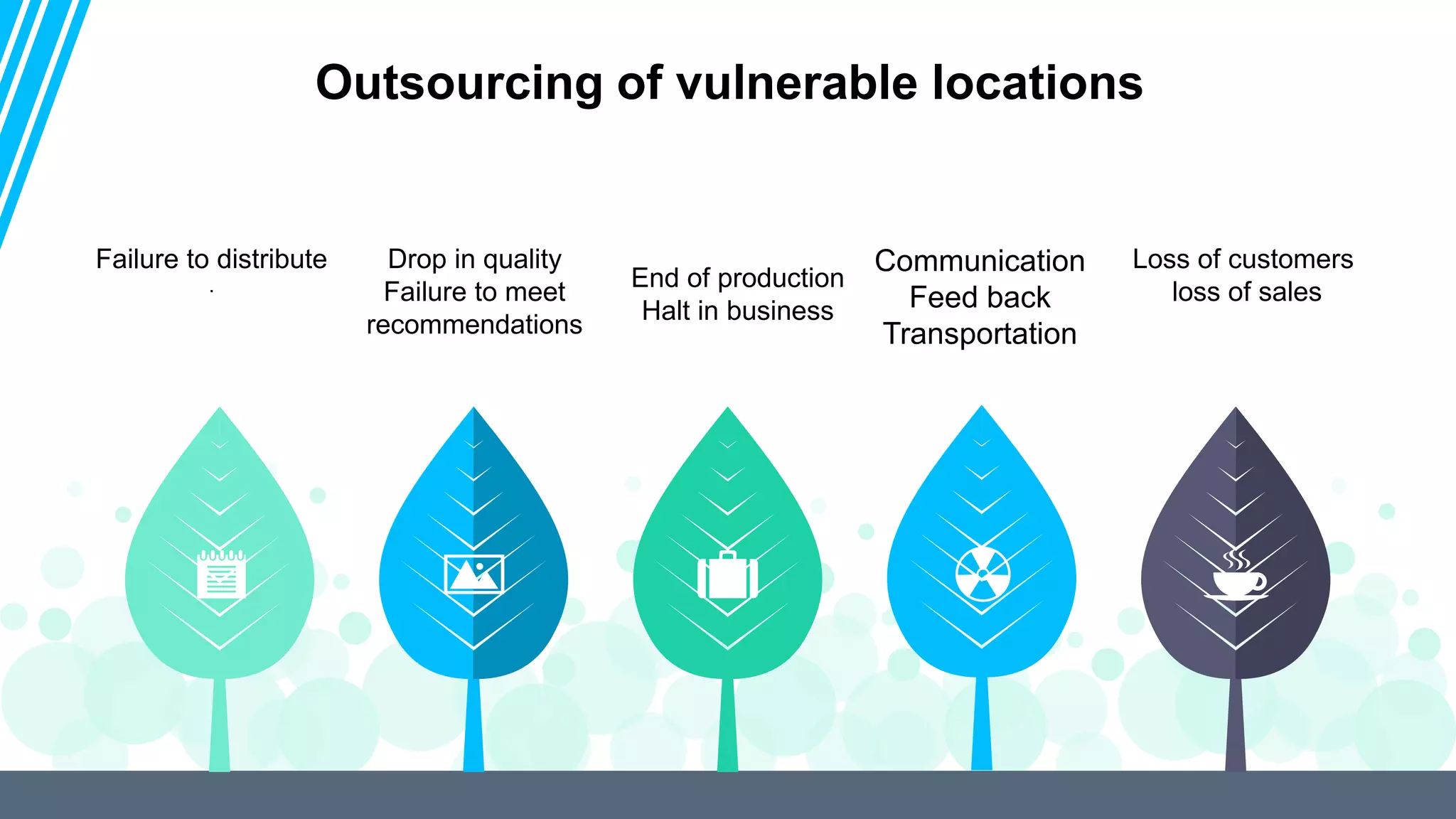
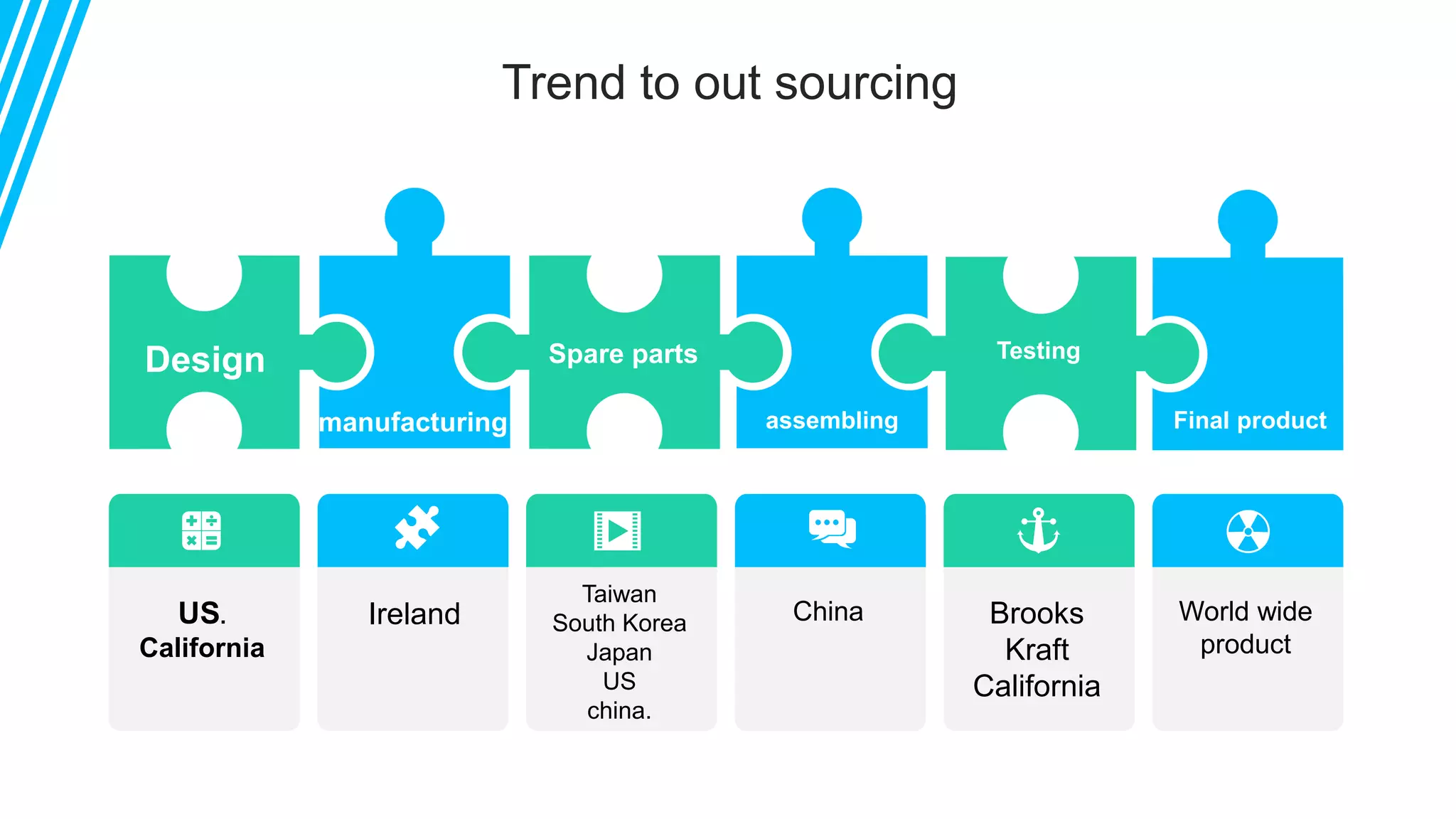
The document discusses global supply chain management, emphasizing the distribution of goods and services to optimize profit and mitigate risks. It highlights vulnerabilities such as lack of visibility, long lead times, and outsourcing that can lead to significant operational failures, exemplified by case studies like KFC and Apple. The presentation also underscores the importance of effective logistics, supplier management, and the impact of technology and globalization on supply chain complexities.