Embed presentation
Downloaded 10 times


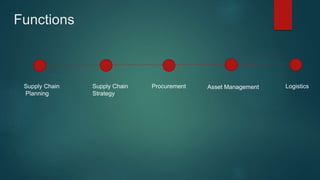






This document discusses retail supply chain management. It defines supply chain management and lists its key functions as supply chain planning, strategy, procurement, asset management, and logistics. The document also outlines key supply chain processes and the objectives and functions of logistics in moving inventory from origin to point of sale. Finally, it lists some common supply chain and logistics problems and their solutions.







