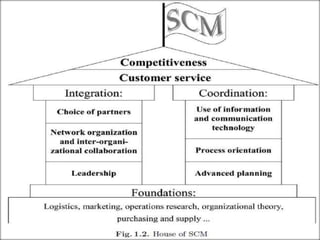
Logistics connects supply sources with demand and fills the gap between the two. It is an information-based process of moving goods from one place to another. Supply chain management integrates supplier, distributor, and customer logistics requirements into a single process. Logistics refers to the movement of materials within and between organizations, while supply chain management acknowledges all traditional logistics activities as well as marketing, finance, and customer service. The goal of logistics and supply chain management is to deliver the right product to the right place at the right time at the lowest cost.