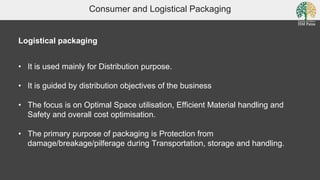
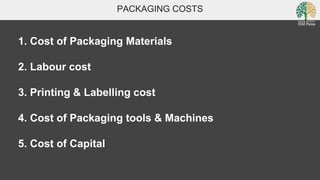
This document discusses packaging from a logistical perspective. It defines packaging as protecting, containing, identifying, promoting, and facilitating transportation and use of a product. Logistical packaging focuses on distribution objectives like optimal space utilization, efficient material handling, and cost optimization for transportation, storage, and handling. Logistical packaging functions include protection, warehousing, transportation, material handling, and providing information. Packaging can be at the primary, secondary, or tertiary level. Common packaging materials include plastic, paper, wood, metal, glass, jute and cotton. Costs associated with packaging include materials, labor, printing, tools/machinery, and capital.