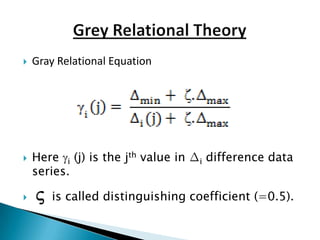
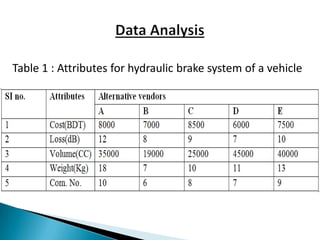
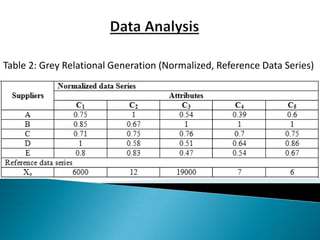
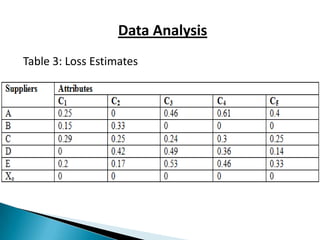
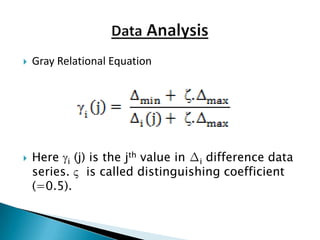
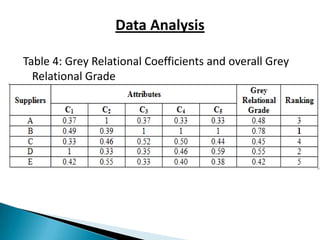
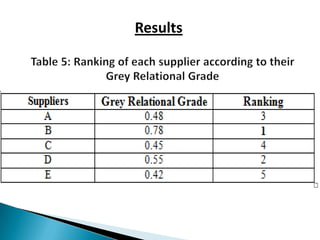
This document discusses supplier selection using grey relational theory. It involves choosing suppliers based on multiple qualitative and quantitative criteria. Several methods are analyzed, including fuzzy logic, analytical hierarchical process, and multi-criteria decision making. An example is presented to illustrate grey relational analysis for selecting a brake system supplier based on attributes like cost, quality, and delivery time. The results show grey relational theory provides an effective way to evaluate suppliers that considers both subjective and objective factors.