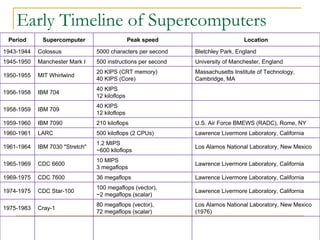
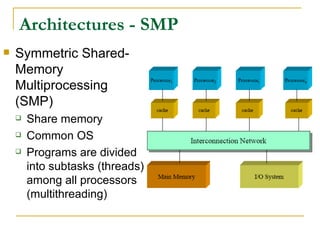
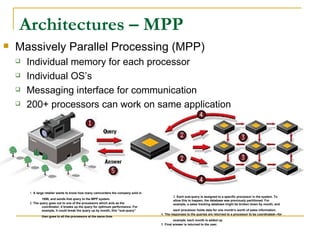
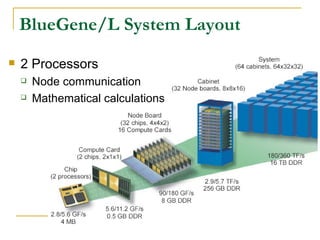
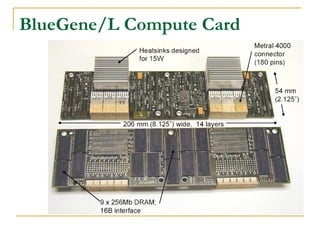
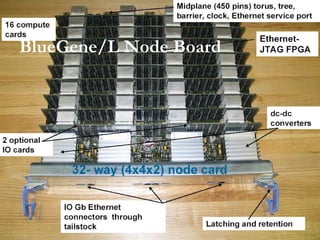
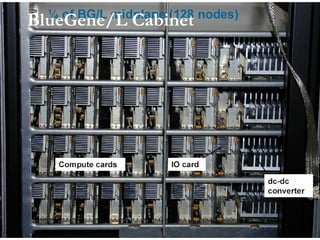
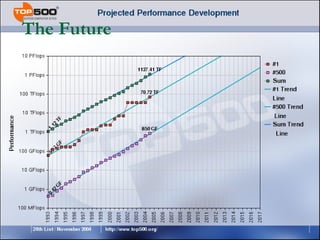
This document provides an overview of supercomputers including their uses, history, architectures, and key systems. Supercomputers are the most powerful and expensive computers available designed to solve complex problems quickly. They are used for tasks like weather forecasting, nuclear simulation, and cryptography. They differ from personal computers in cost, environment, programming languages, and lack of common peripherals. Major early systems included the CDC 6600 and Cray-1. Current systems use clustering, symmetric multiprocessing, or massively parallel processing architectures. The top systems include BlueGene/L, Columbia, and Earth Simulator.