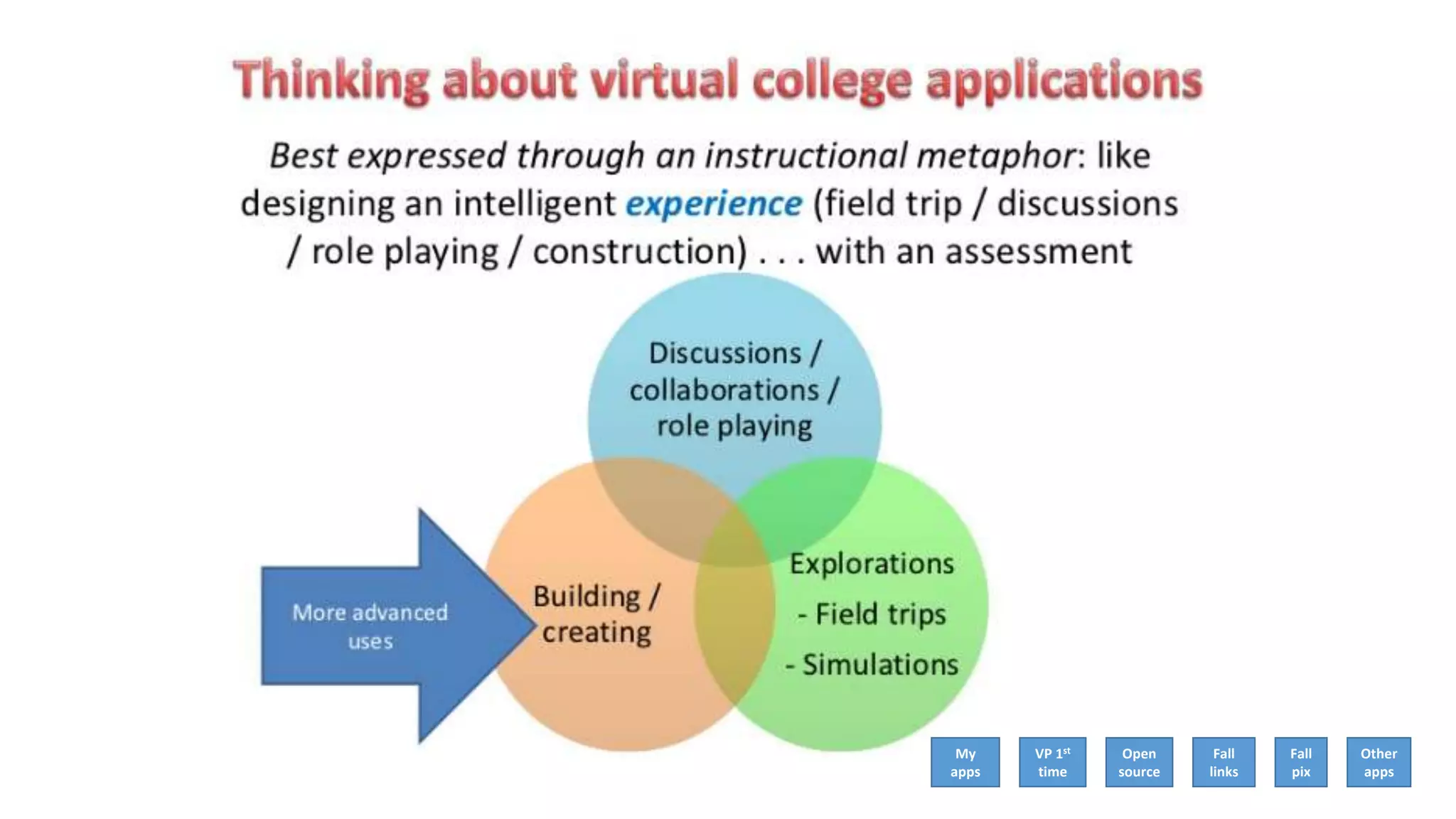
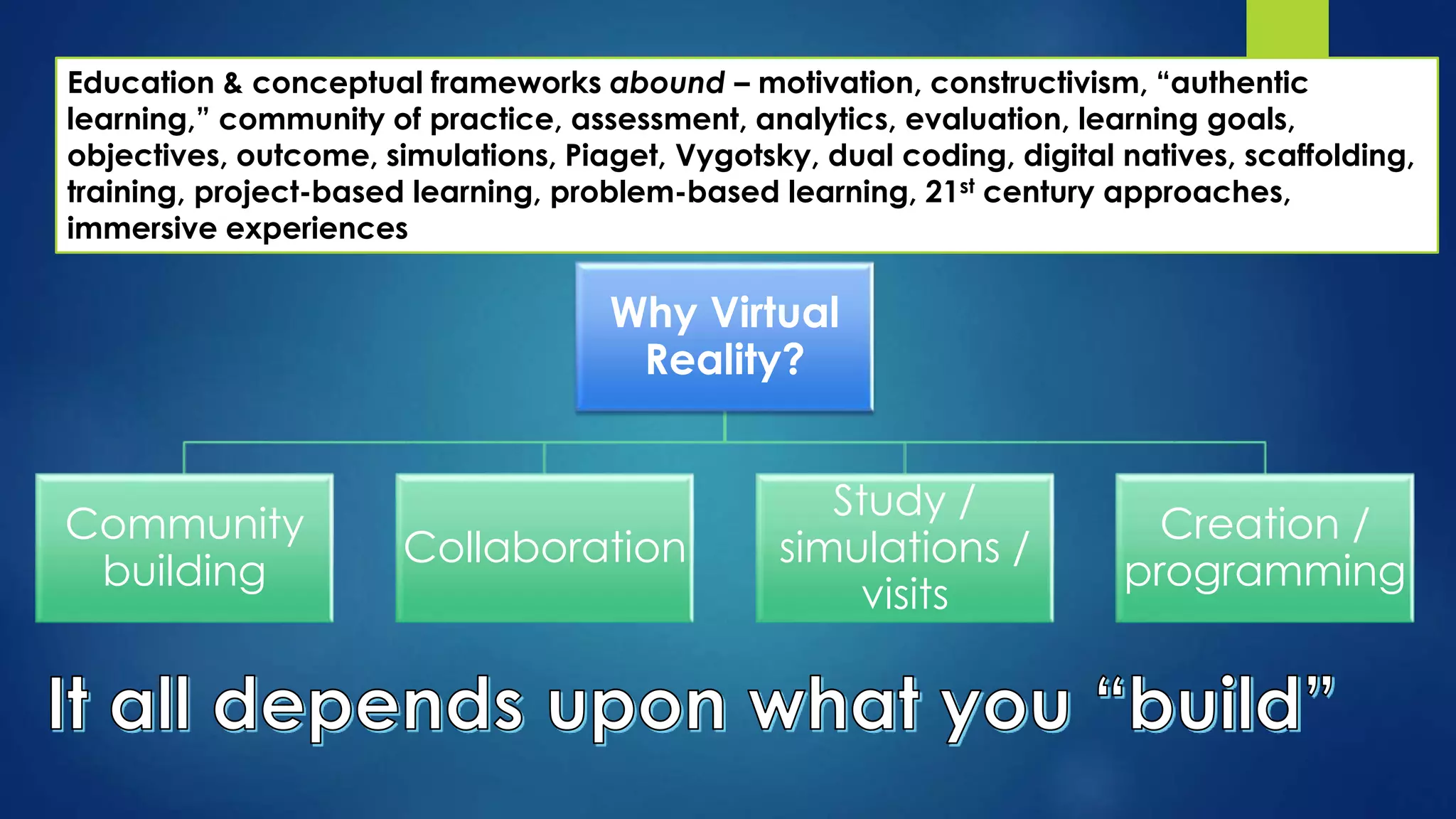
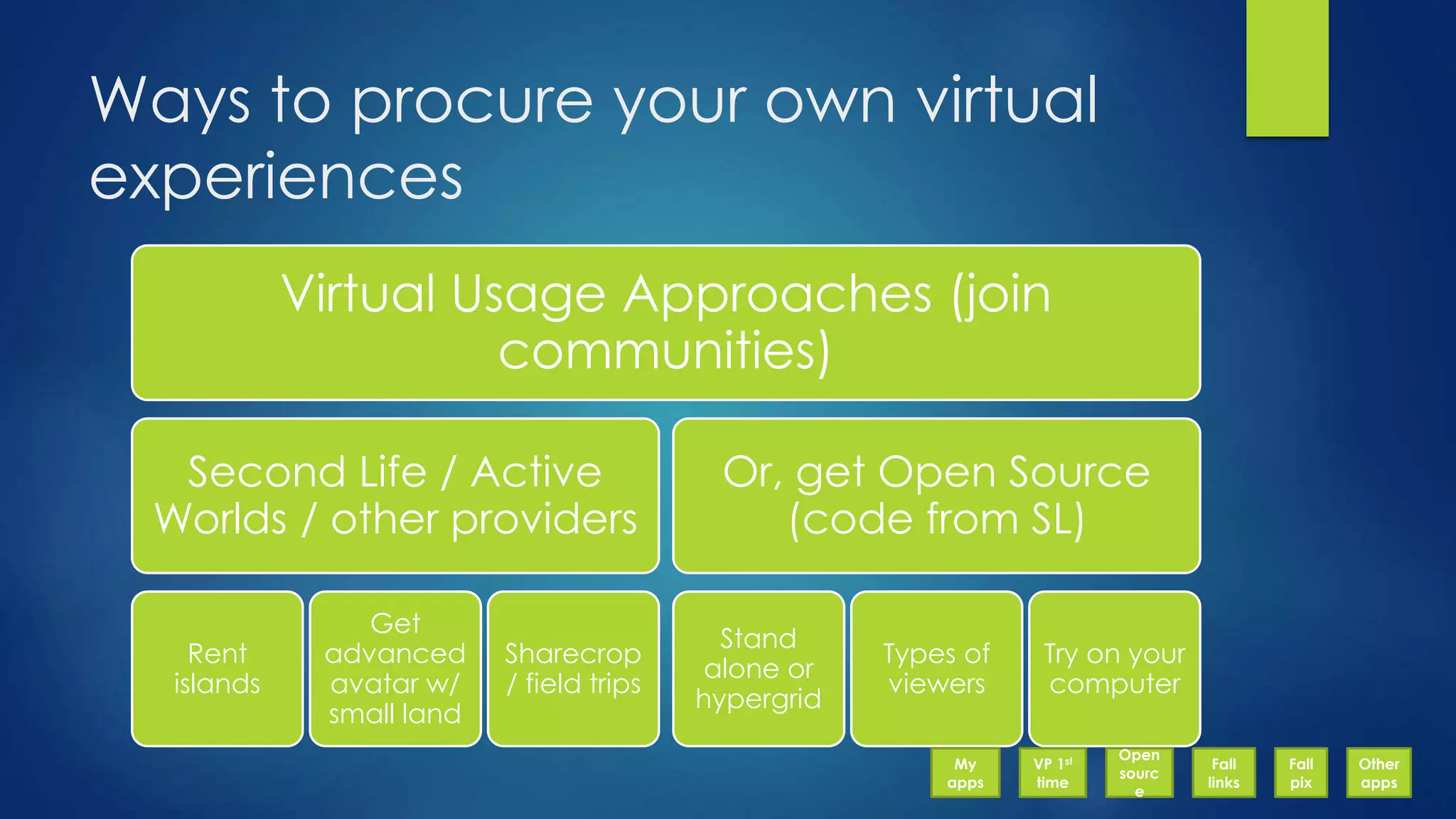
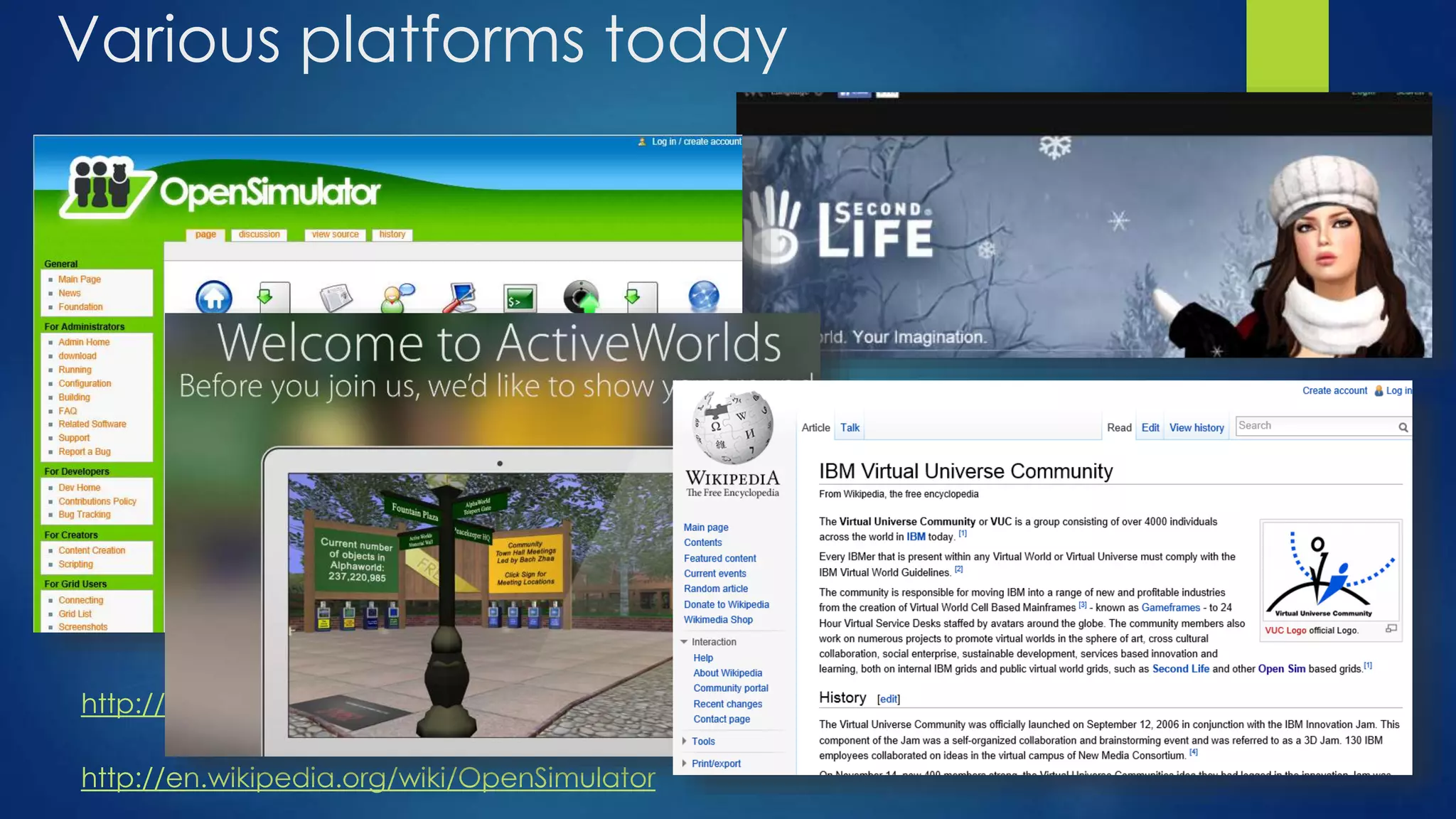
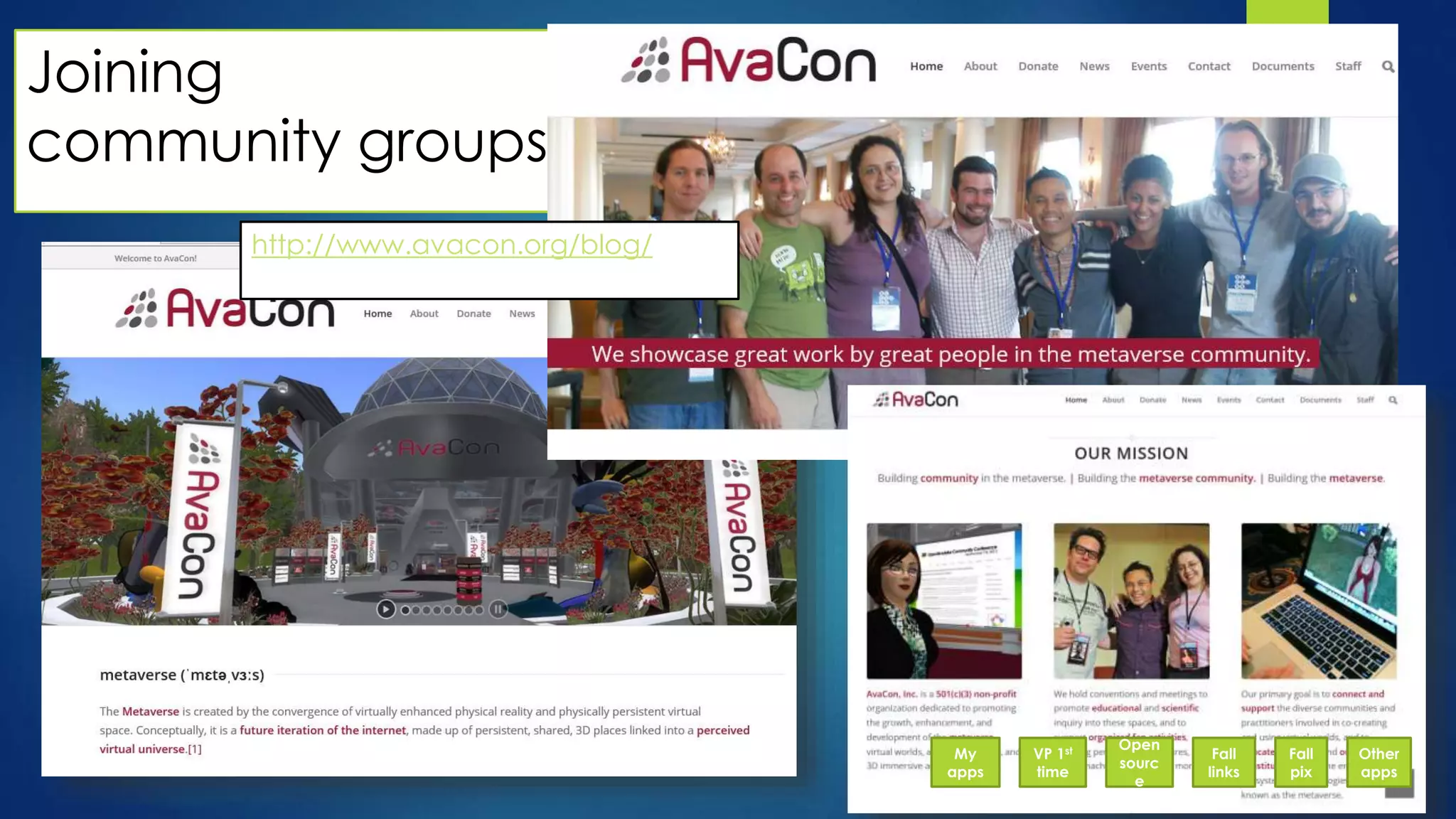
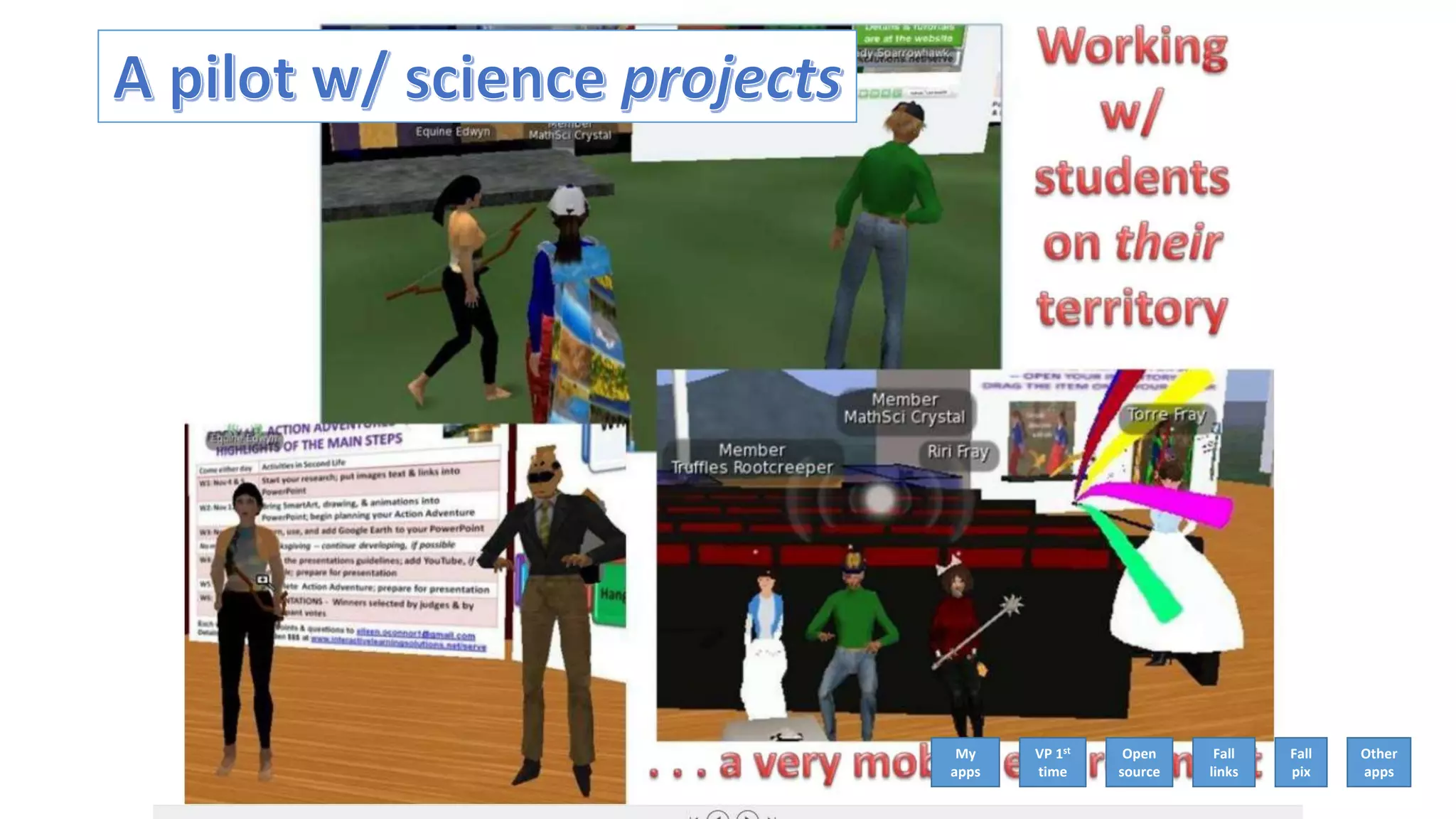
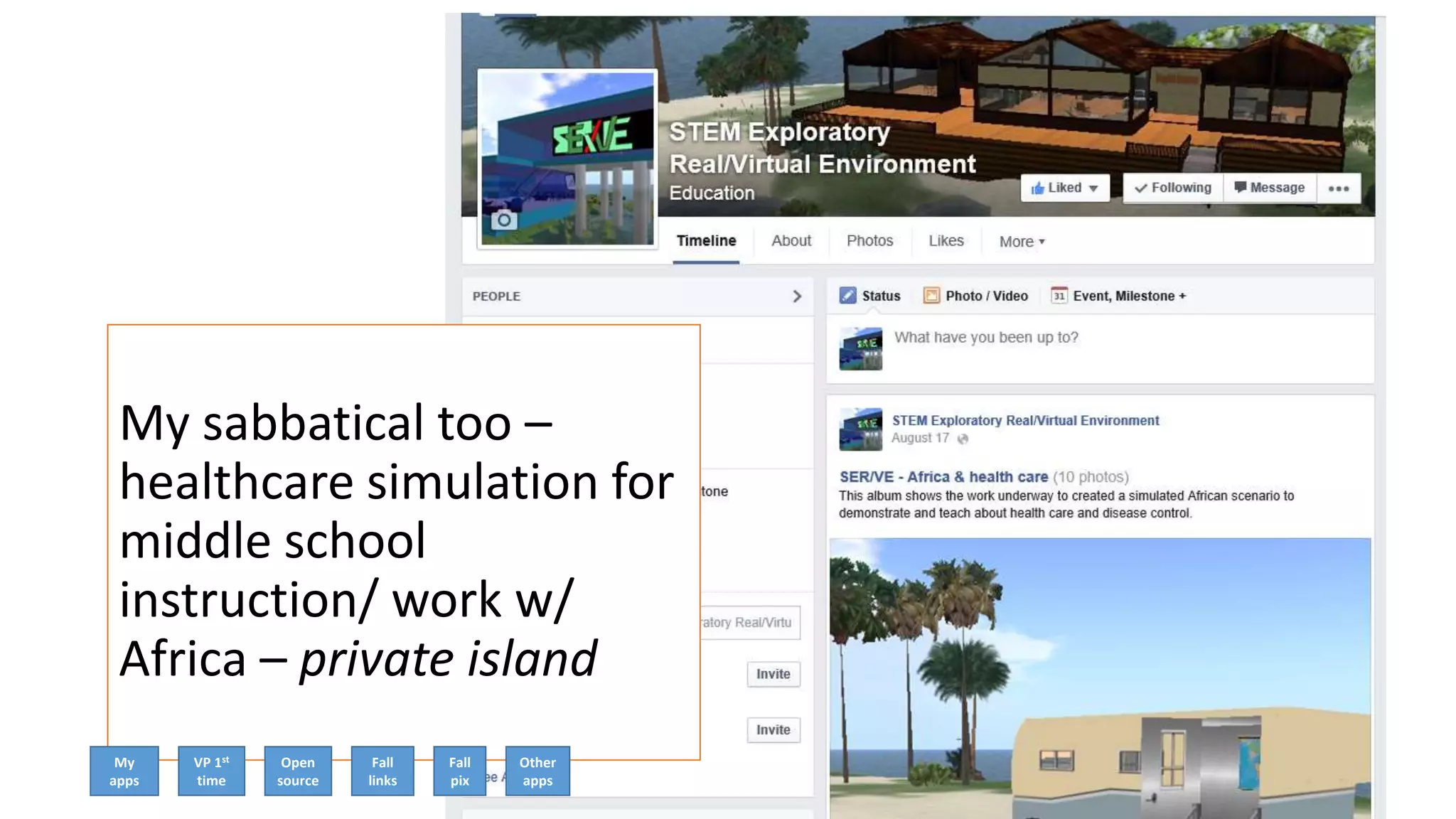
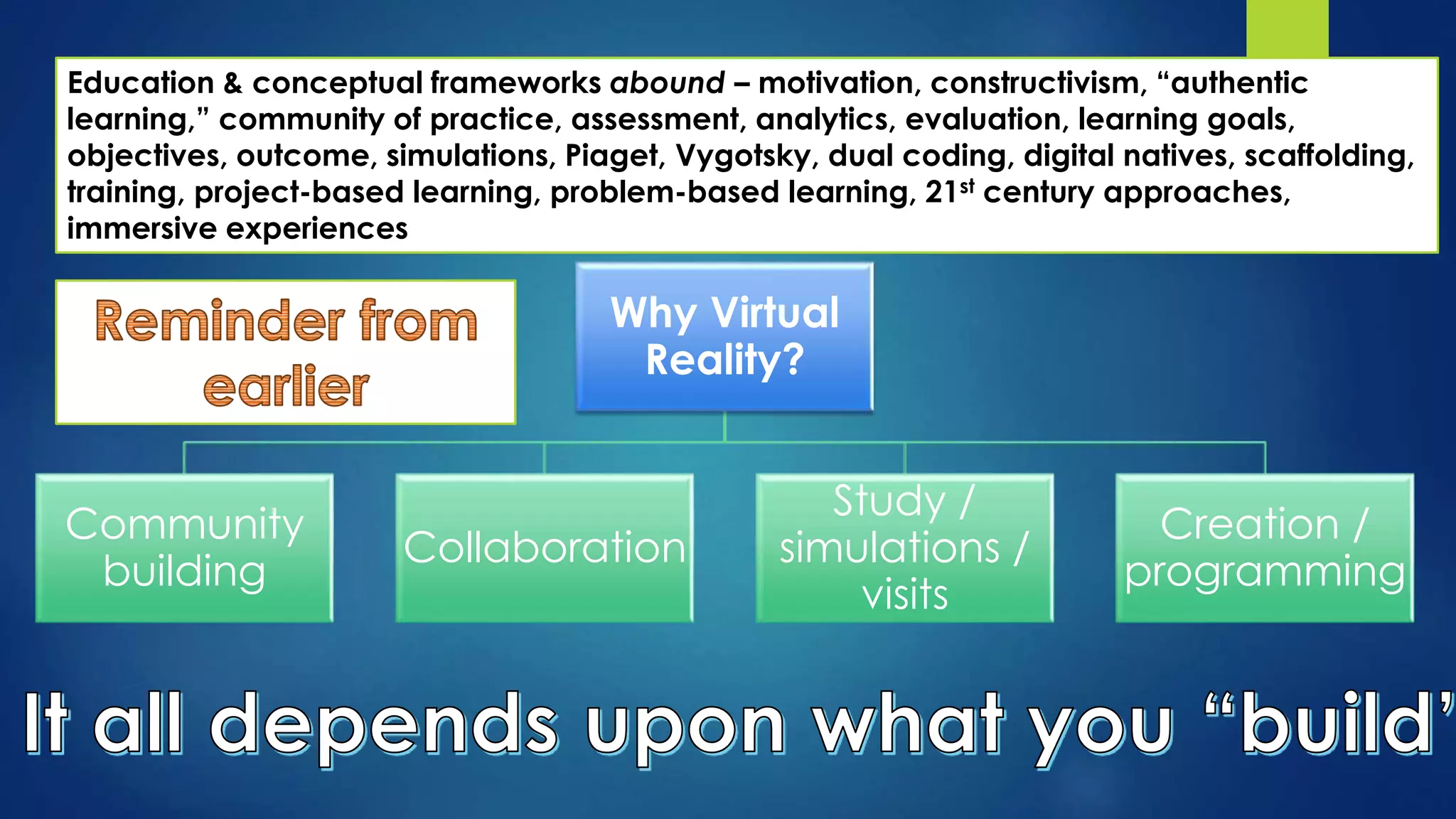
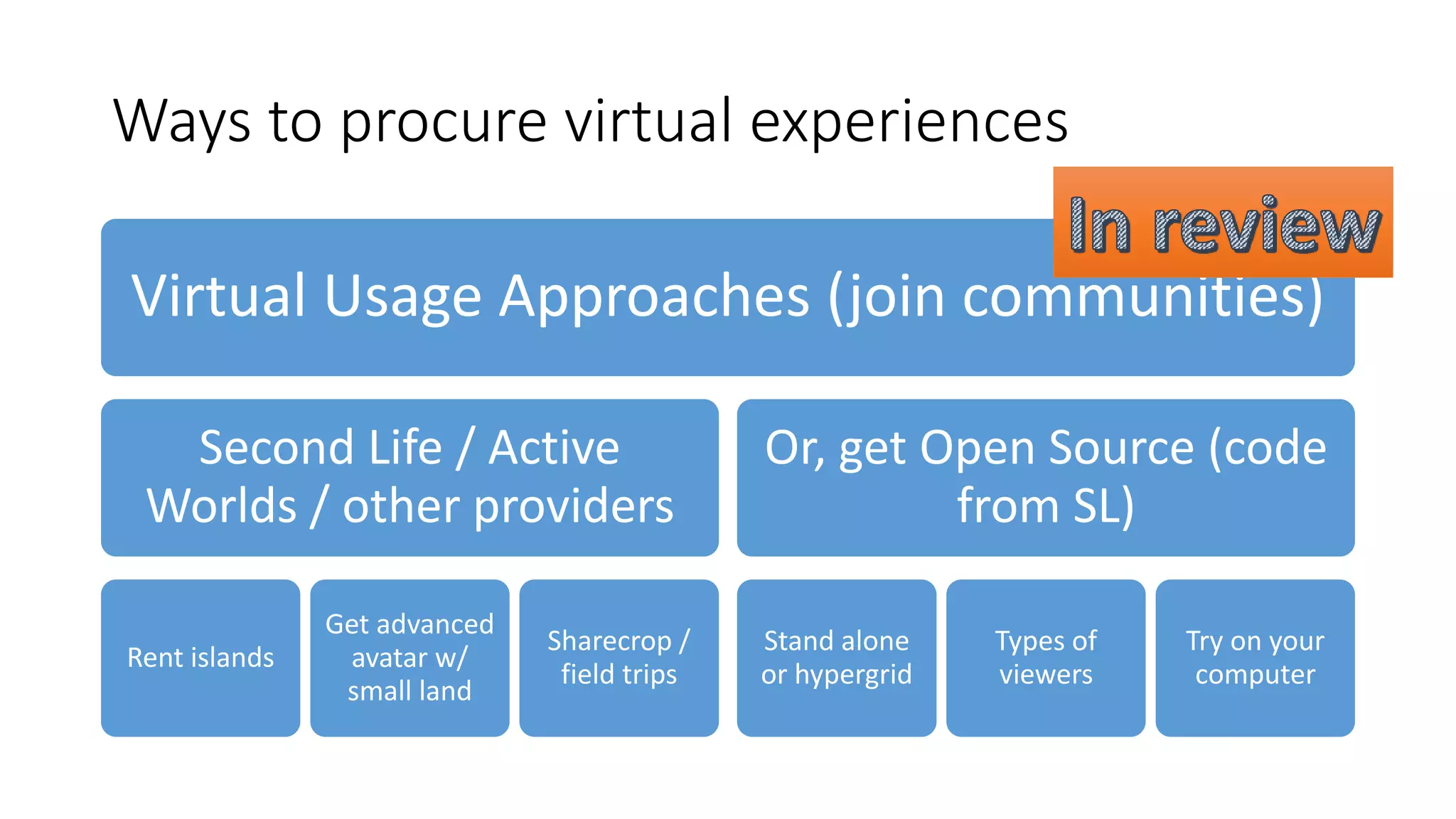
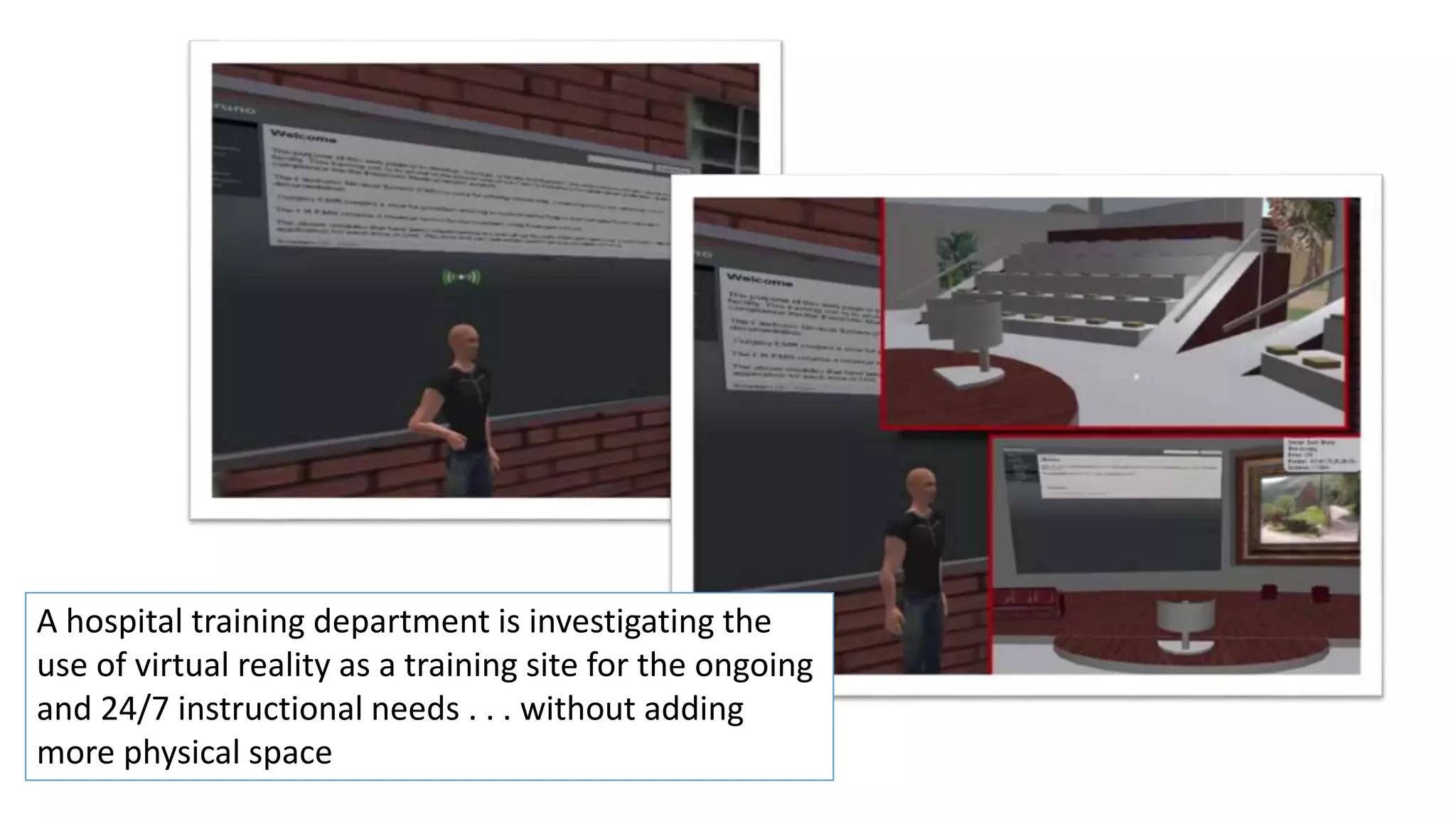
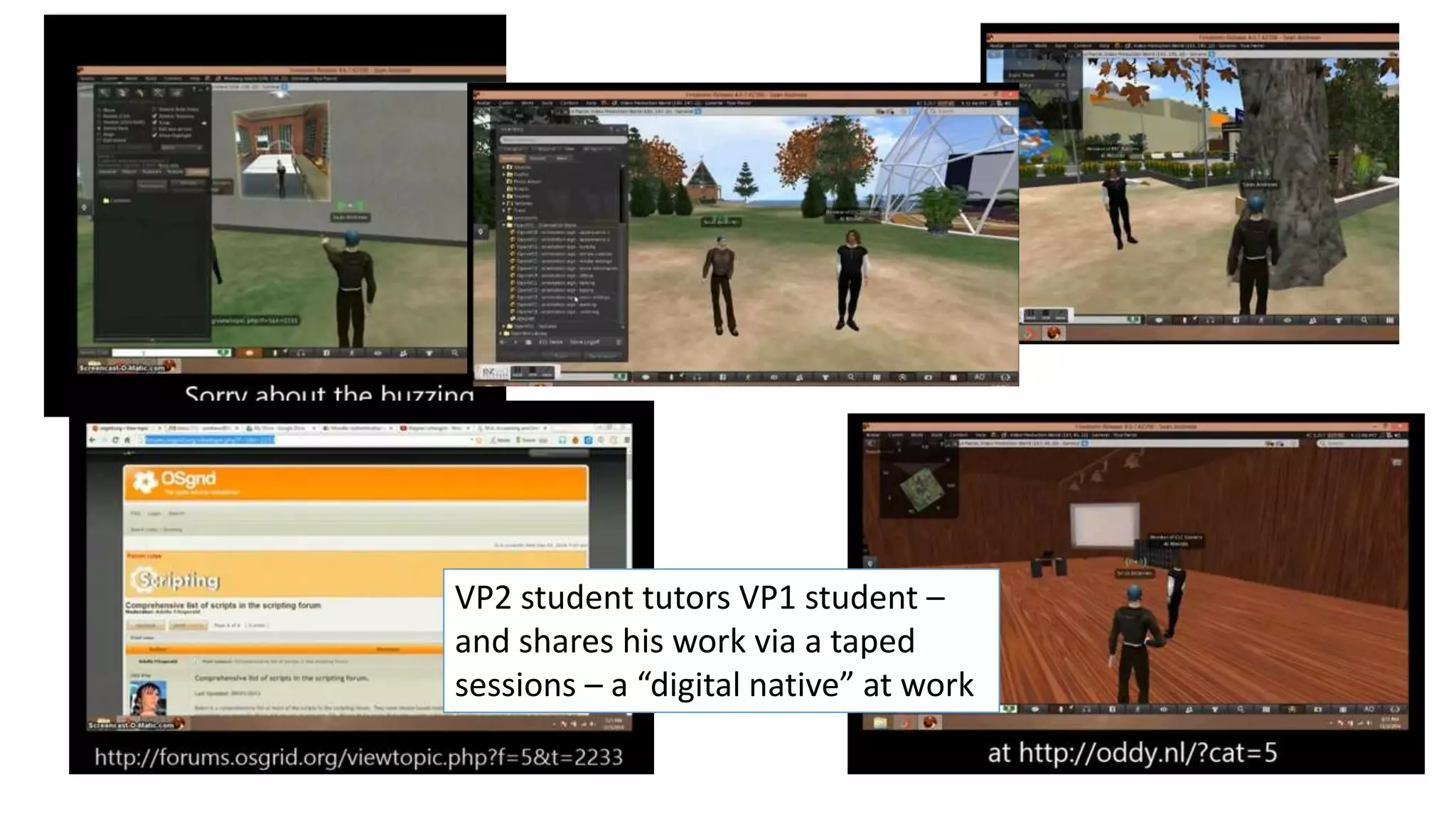
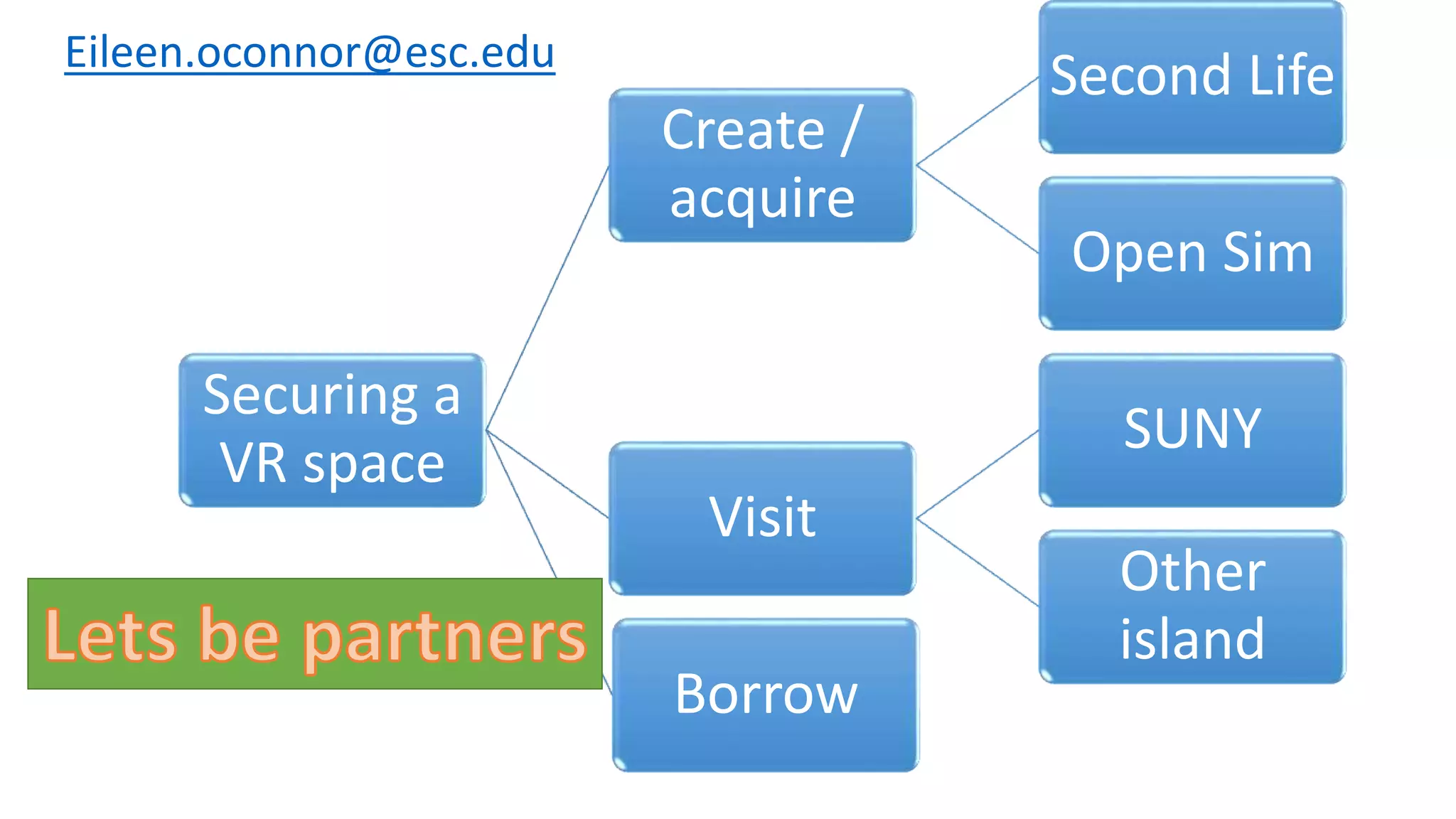
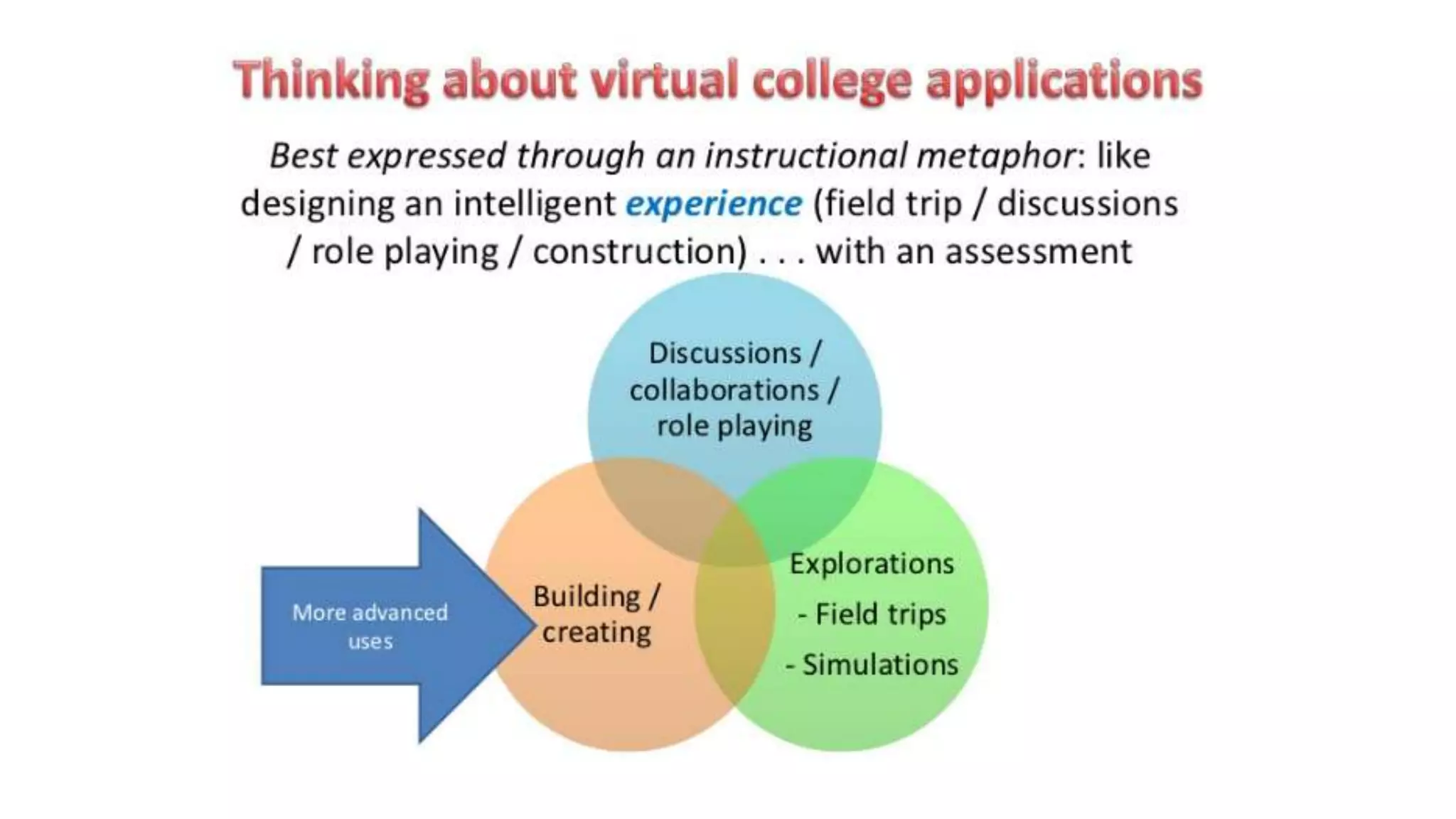
The document discusses the use of virtual reality (VR) in creating engaging learning environments and online communities, highlighting the instructor's experiences from Second Life to open-source platforms. It covers various applications in education, including teacher training and K-12 STEM, and emphasizes community building, collaboration, and project-based learning. Additionally, it outlines how open-source VR allows for greater creativity and ownership in student projects, facilitating immersive educational experiences.