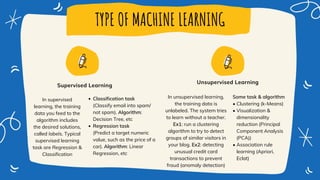
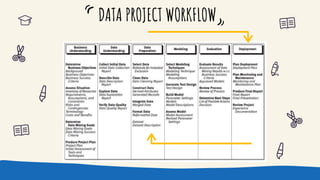
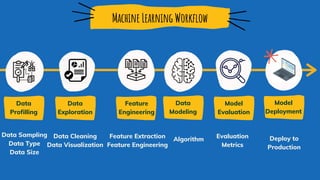
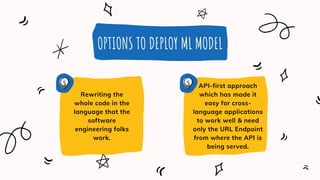
This document discusses machine learning and model deployment. It provides an overview of machine learning, including the types of problems it can be applied to and common machine learning techniques. It then discusses the typical machine learning workflow, including data profiling, exploration, feature engineering, modeling, evaluation, and deployment. It also covers the two main types of machine learning - supervised and unsupervised learning. Finally, it discusses options for deploying machine learning models, including rewriting code in a different language or using an API-first approach. It provides steps for creating a machine learning API using the Python framework Flask.