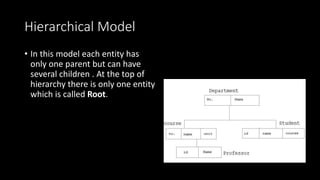
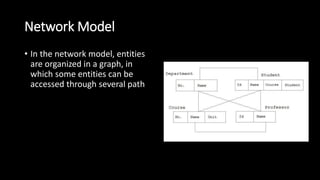
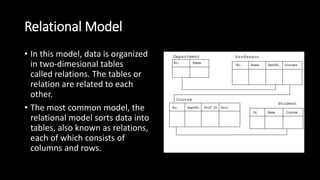
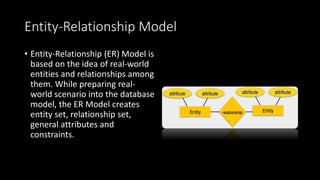
This document presents an overview of data models. It defines a data model as how the logical structure of a database is modeled, introducing abstraction in a DBMS. Several types of data models are described, including hierarchical, network, relational, entity-relationship, object-oriented, document, entity-attribute-value, star schema, and object-relational models. The entity-relationship model is explained in more detail, noting that it is based on entities, attributes, and relationships between entities. Entities represent real-world objects and are described by attributes, while relationships define associations between entities.