Embed presentation
Downloaded 10 times

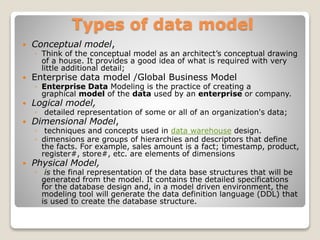


The document discusses data modeling and outlines its purpose as a graphical documentation method for understanding data requirements and defining database design specifications. It details various types of data models, including conceptual, enterprise, logical, dimensional, and physical models, each with unique characteristics and applications in database design. The physical model represents the final database structure and includes detailed specifications for implementation.



