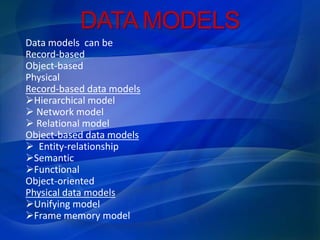
Data models can be record-based (hierarchical, network, relational), object-based (entity-relationship, semantic, functional, object-oriented), or physical (unifying frame memory). The entity-relationship model is a method to visualize data logically and independently of hardware. It facilitates database design by allowing specification of entity types, relationships between entities, and attributes of entities. The main concepts are entities, relationships between entities, and attributes of entities.