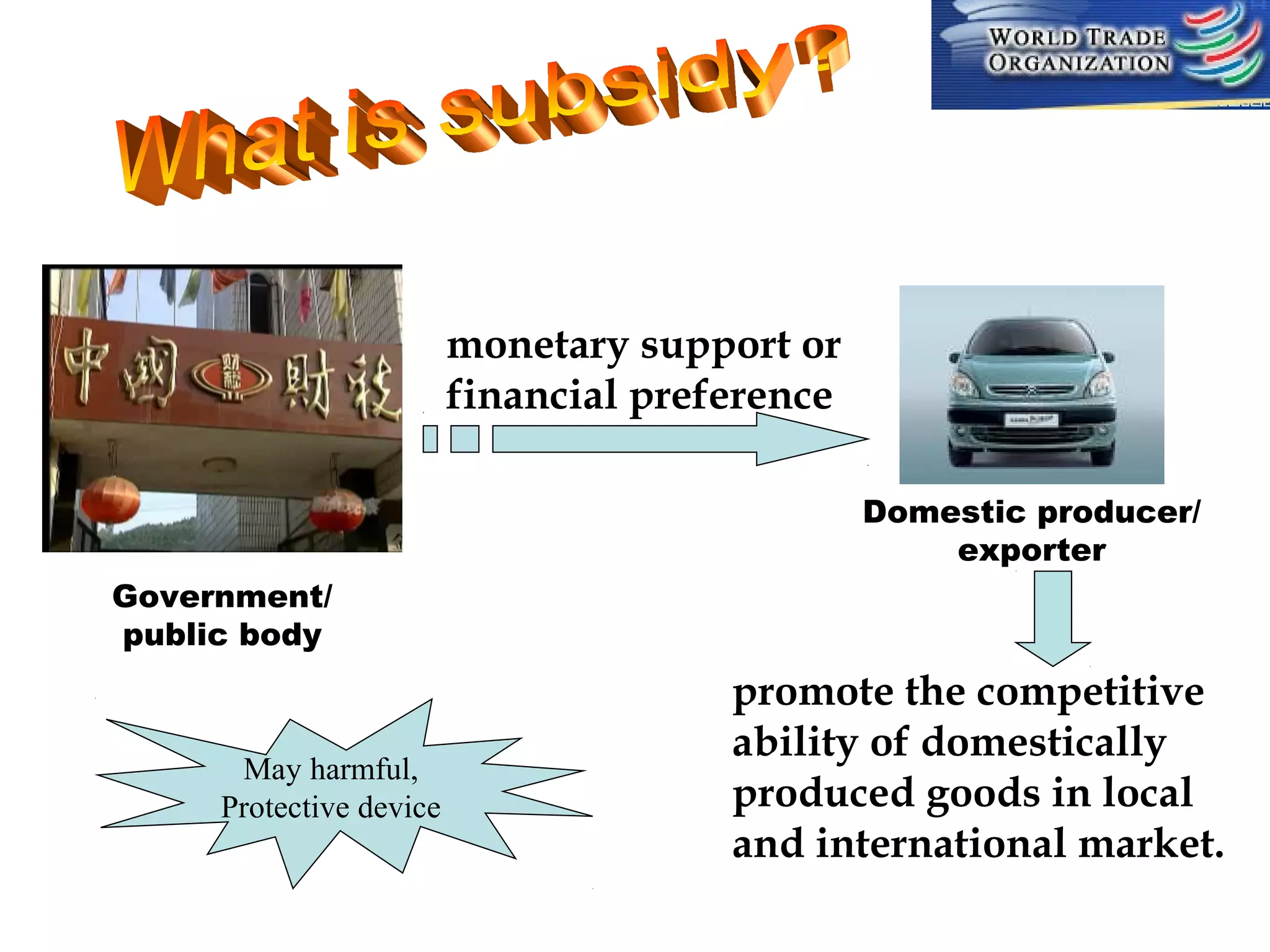
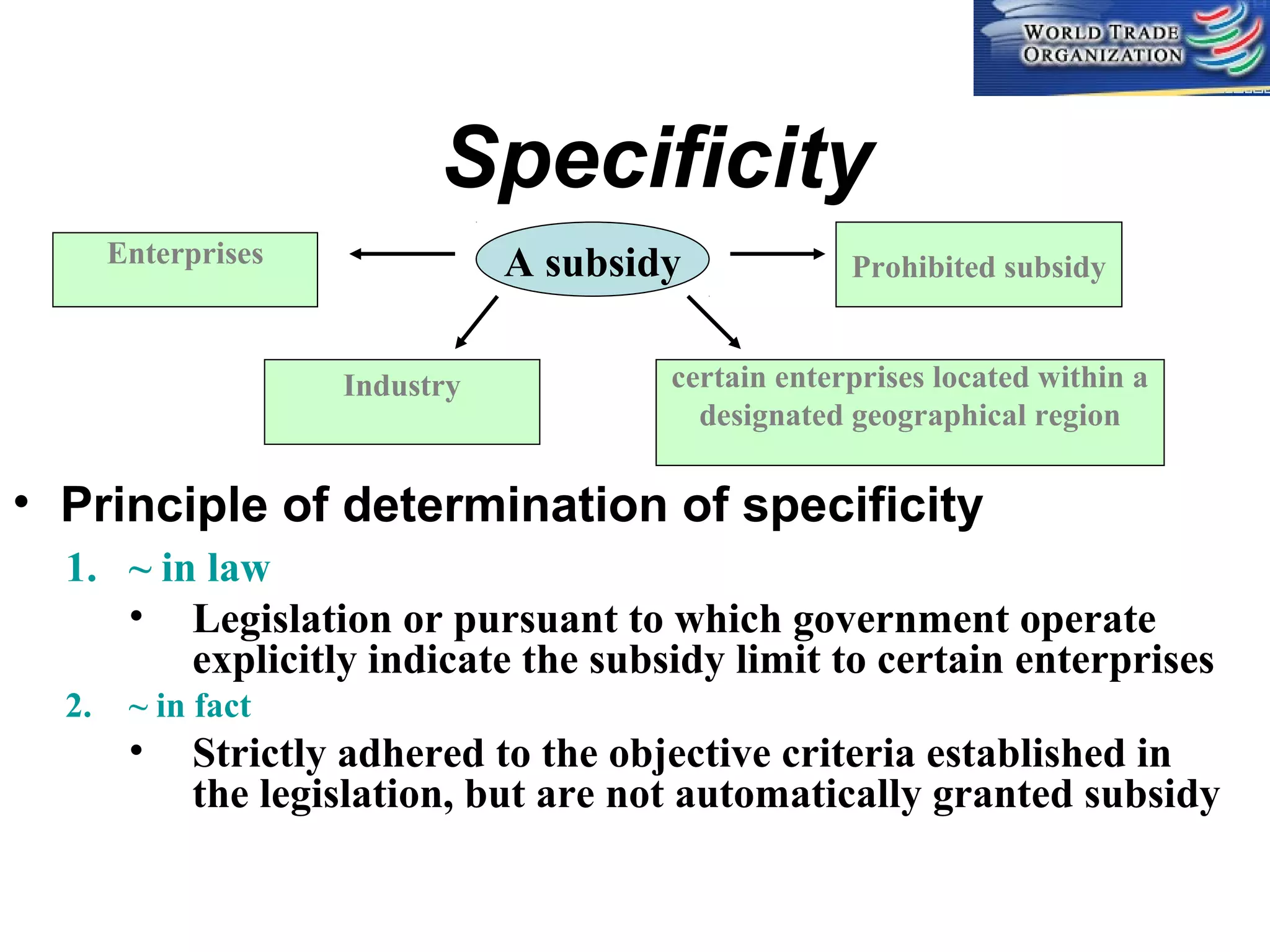
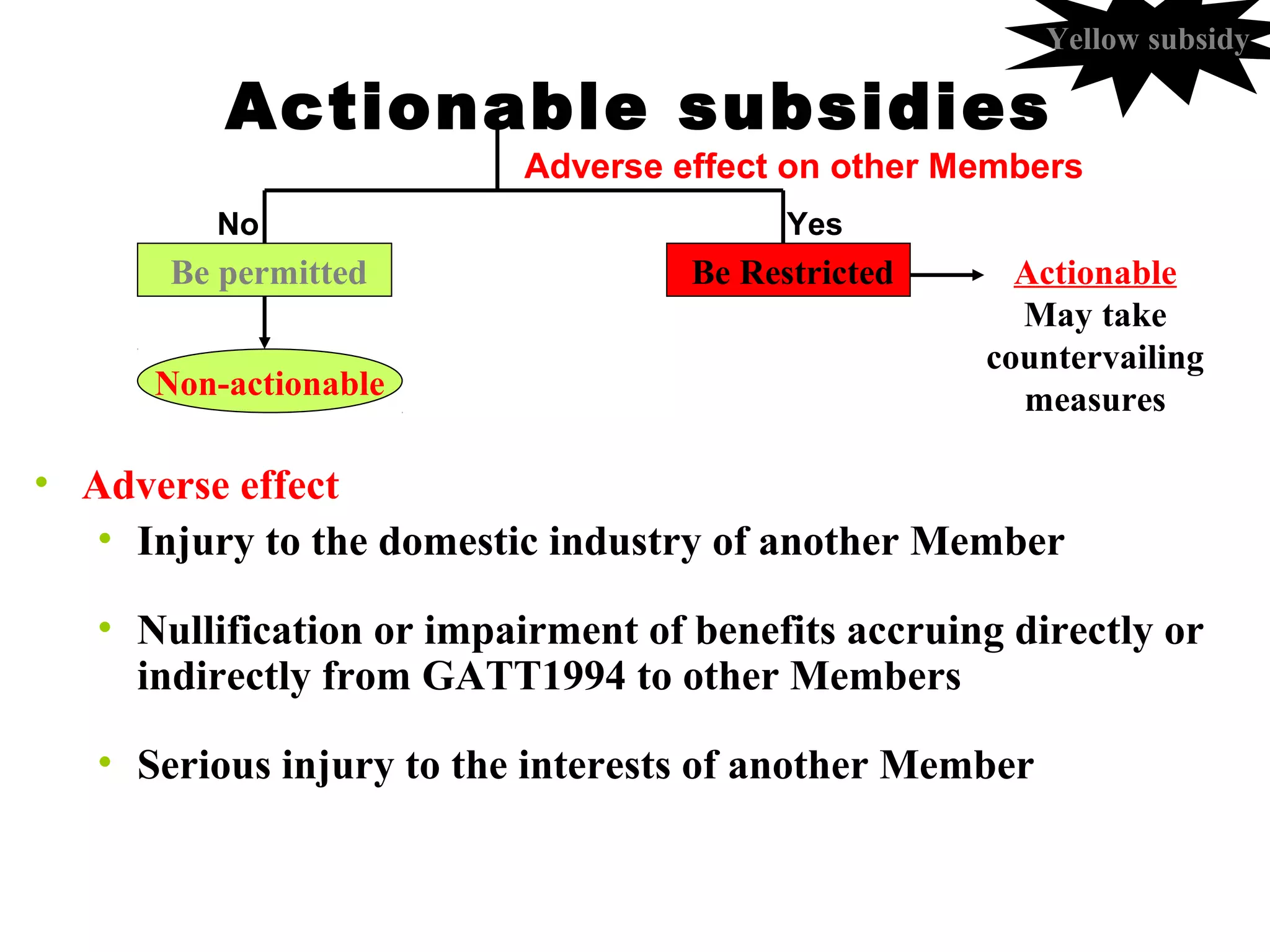
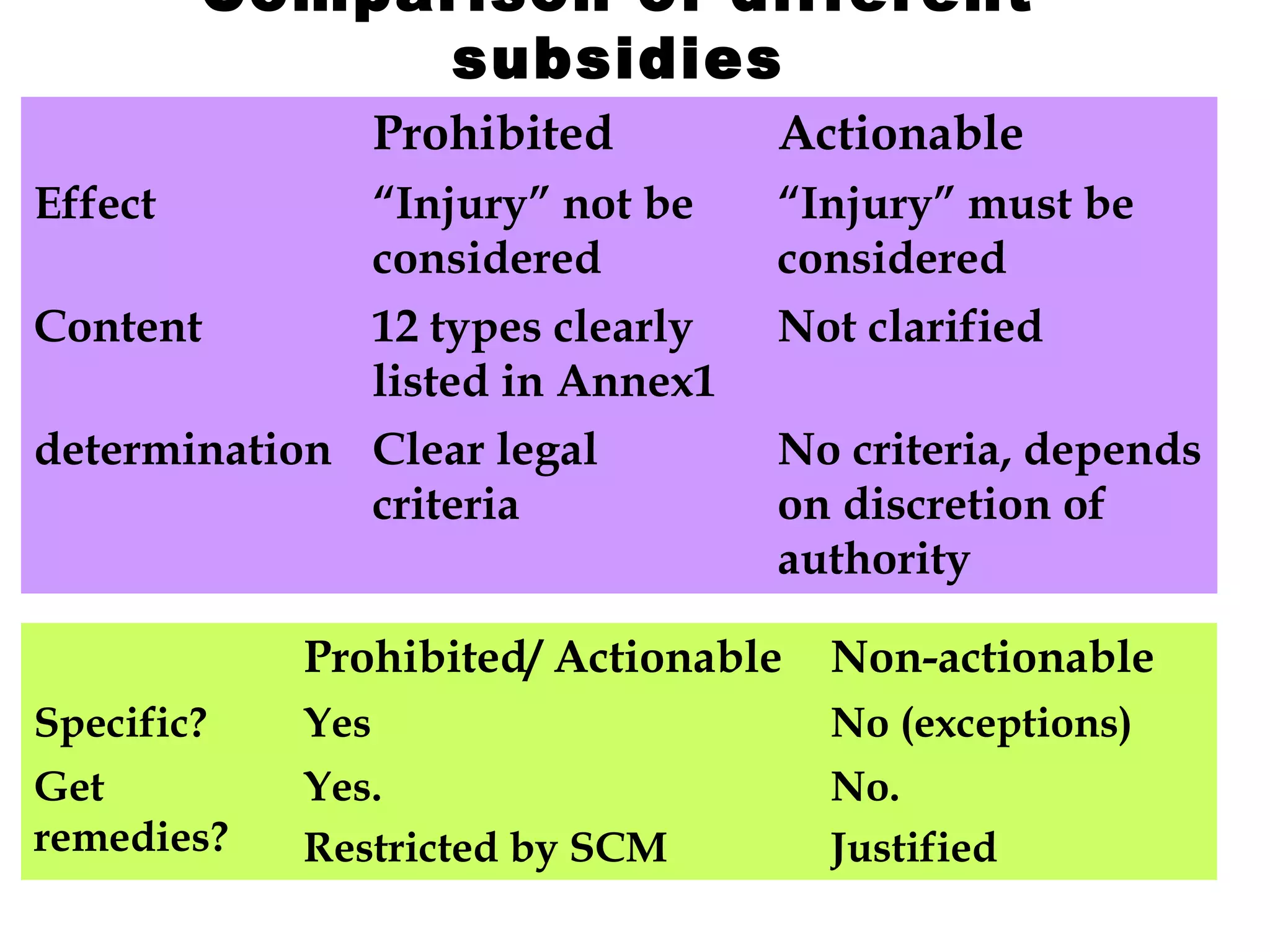
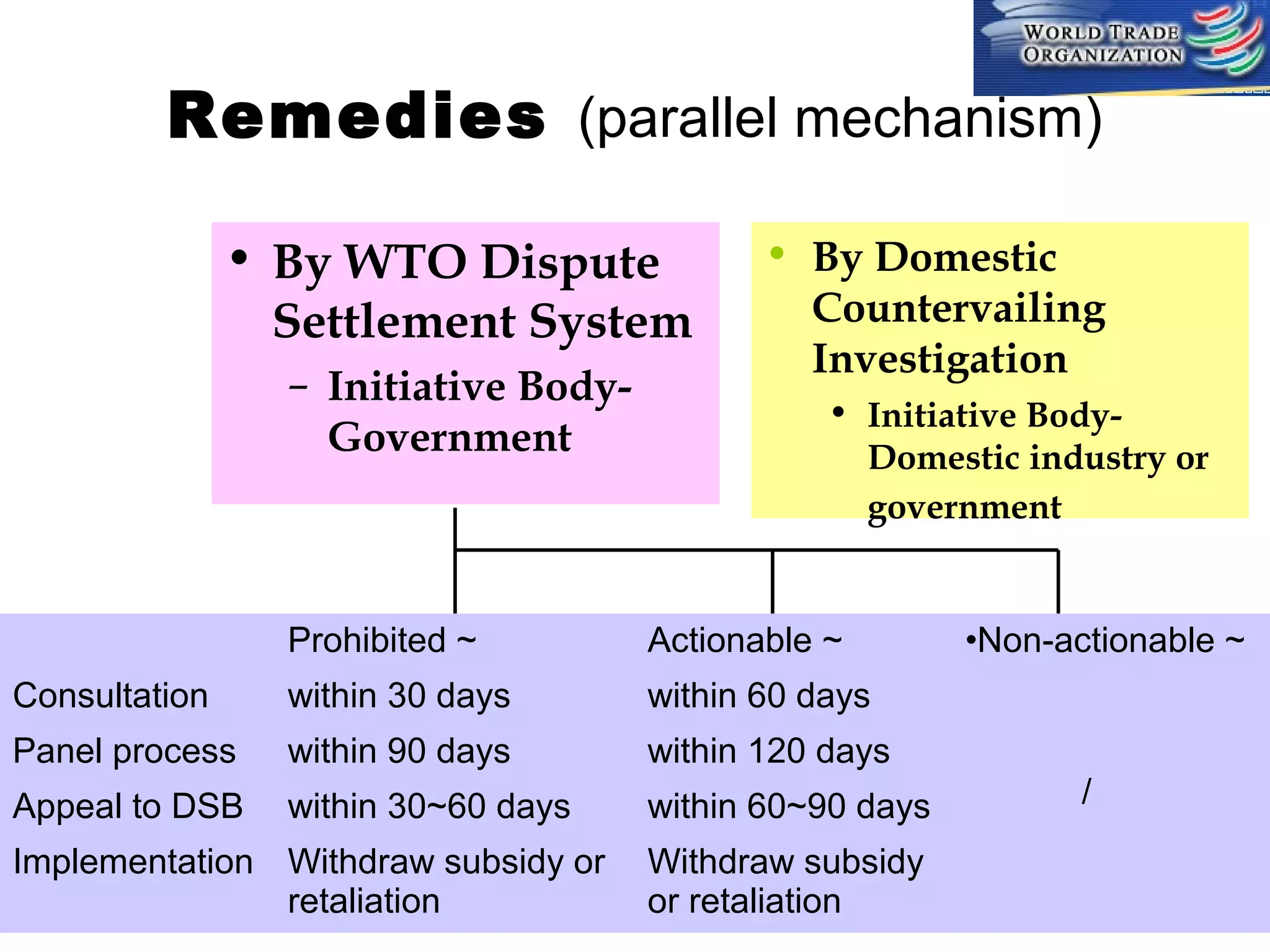
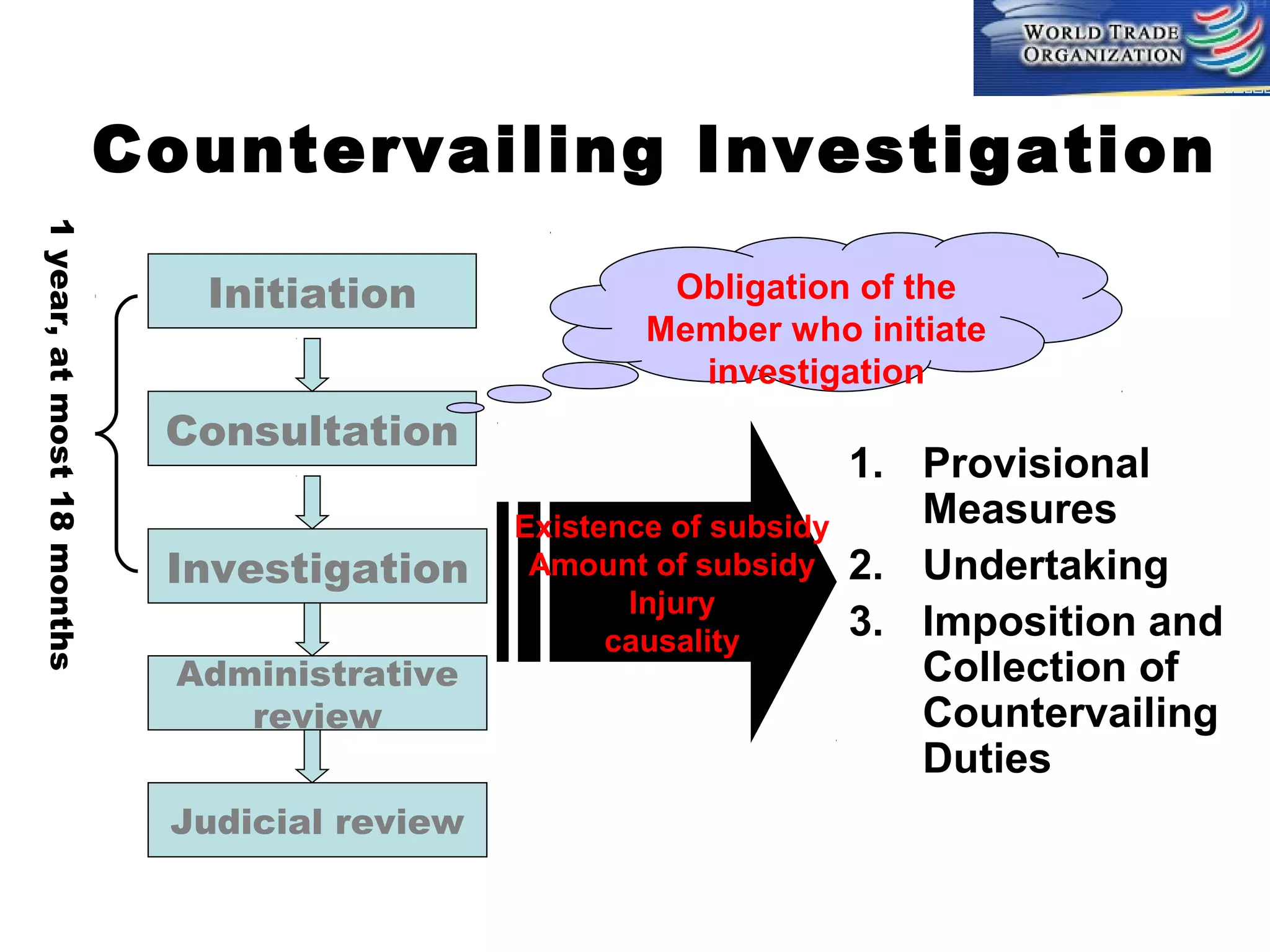
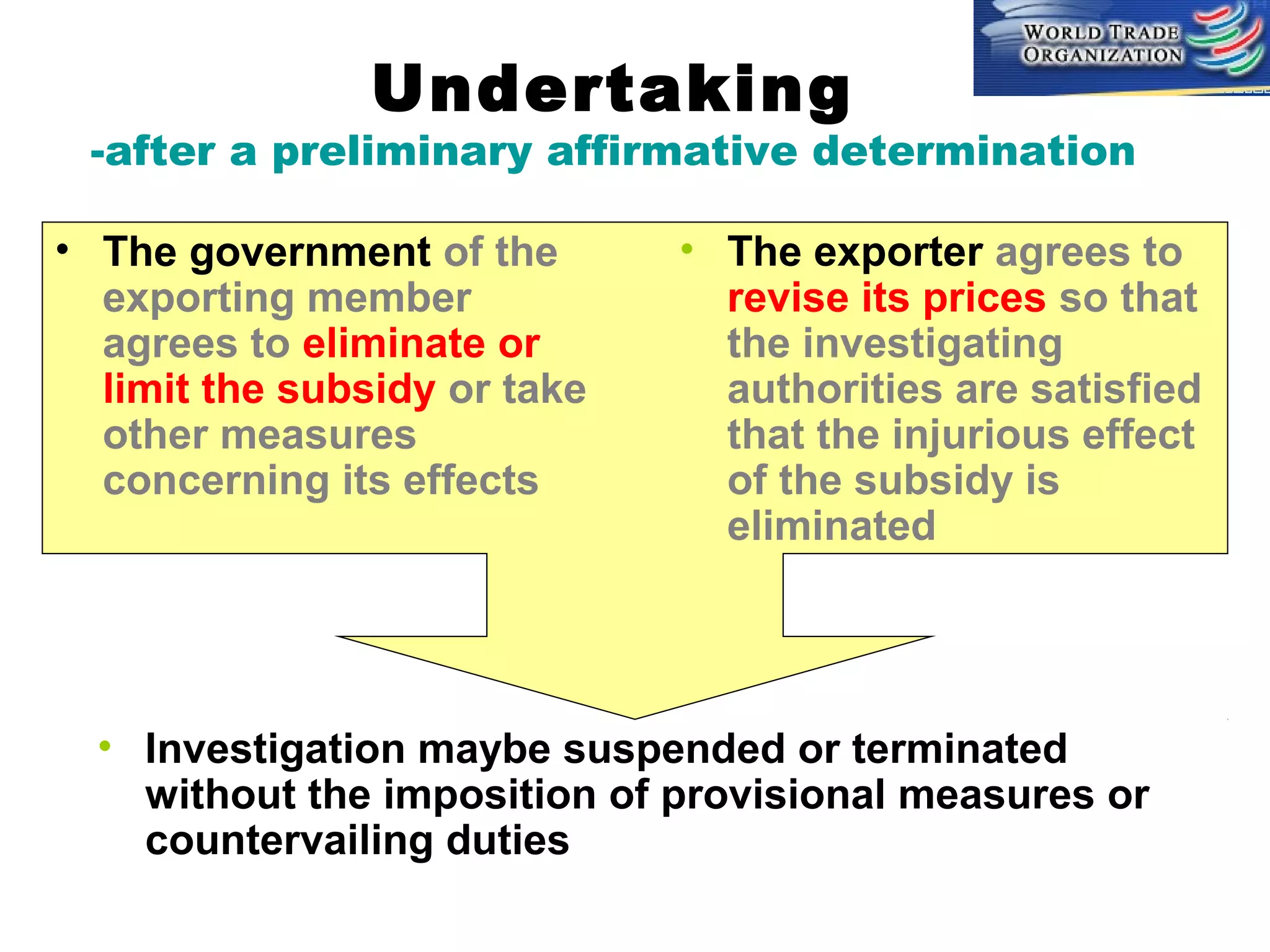
This document discusses subsidies and countervailing measures in international trade. It begins by defining subsidies as monetary support provided by a government or public body to domestic producers or exporters. It then outlines international rules on subsidies from GATT/WTO agreements. Subsidies are categorized as prohibited, actionable, or non-actionable depending on their trade effects. Remedies for different subsidy types include disputes at the WTO or domestic countervailing investigations and duties.