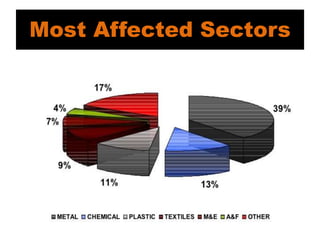
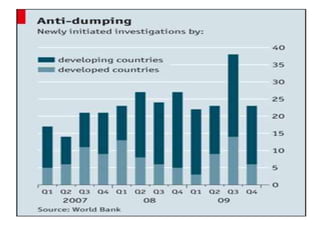
The document outlines the concept of anti-dumping as a measure to combat international price discrimination where products are sold at lower prices in the importing country than their domestic market. It discusses the reasons for dumping, its effects on local industries, and the legal framework governing anti-dumping measures, including historical context. Anti-dumping duties are imposed to protect domestic industries from unfair competition, exemplified by India's recent action against Chinese telecom equipment imports.