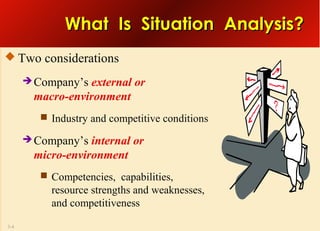
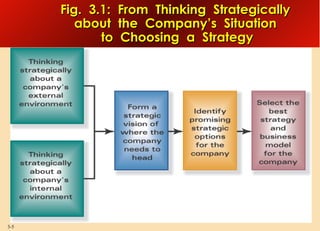
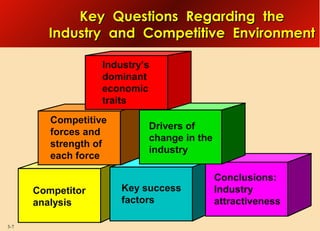
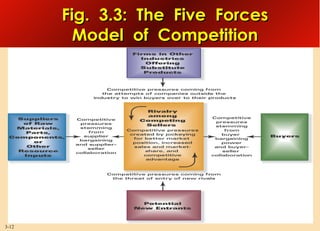
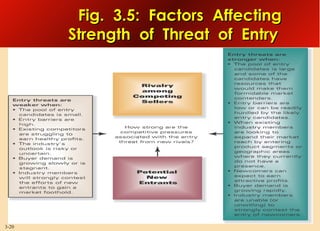
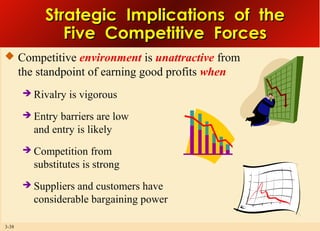
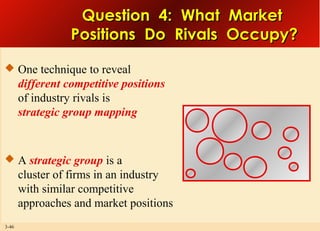
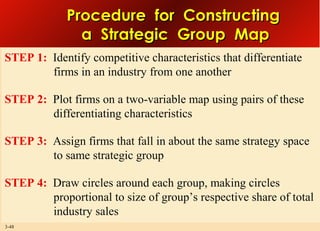
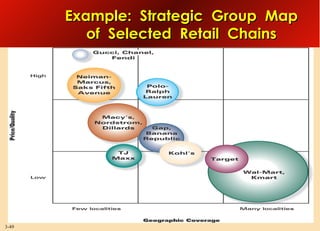
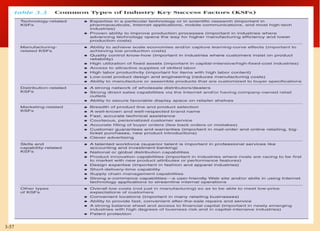
This document provides an overview of analyzing a company's external environment from a strategic perspective. It discusses the key components of situational analysis including the macroenvironment and microenvironment. It outlines seven questions to consider when analyzing an industry's competitive environment, including the dominant economic traits, competitive forces, drivers of change, success factors, and attractiveness. Several models are presented for assessing the five competitive forces of rivalry, potential entry, substitutes, supplier power, and buyer power. Factors that influence the strength of each competitive force are also discussed.