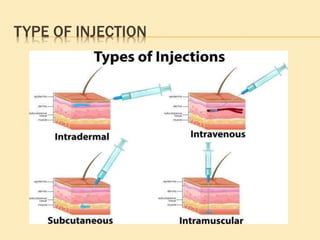
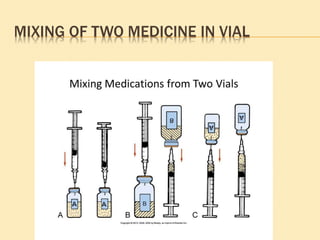
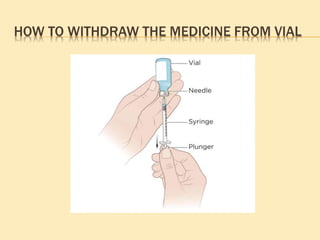
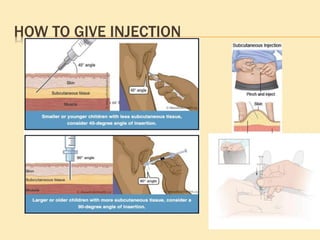
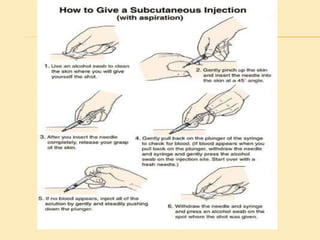
This document outlines the procedure for administering subcutaneous injections, detailing the preparation, identification of the patient, injection techniques, and post-procedure care. It emphasizes the importance of aseptic technique, proper disposal of materials, and precautions regarding multi-use versus single-use devices. Additionally, it provides guidelines for evaluating patient responses and ensuring safety during the procedure.







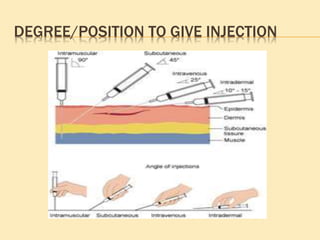
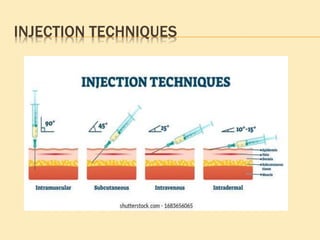
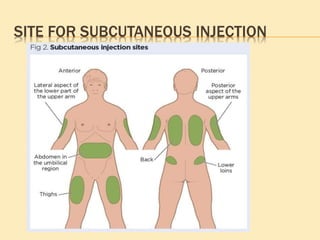
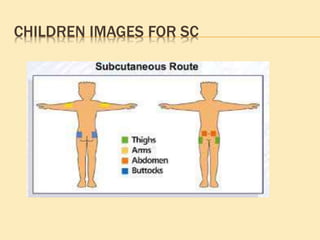










![SINGLE-USE (DISPOSABLE) DEVICES
What is a single-use device?
According to the Food and Drug Administration’s
(FDA’s) guidance entitled Labeling
Recommendations for Single-Use Devices
Reprocessed by Third Parties and Hospital sexternal
icon, “a single-use device, also referred to as a
disposable device, [is] intended for use on one
patient during a single procedure. It is not intended to
be reprocessed (cleaned, disinfected/sterilized) and
used on another patient.
The labeling may or may not identify the device as
single-use or disposable and does not include
instructions for reprocessing.”](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/subcutaneousinjectionaspernabhppt-221006120849-9fb7a653/85/SUBCUTANEOUS-INJECTION-AS-PER-NABH-PPT-pptx-27-320.jpg)



![REFERENCES
CDC. Basic Expectations for Safe Care Training
Module 6 – Safe Injection Practices. Available
at: https://www.cdc.gov/oralhealth/infectioncontr
ol/safe-care-modules.htm. Accessed May 8,
2018.
CDC. Summary of Infection Prevention
Practices in Dental Settings: Basic Expectations
for Safe Care. Available
at: https://www.cdc.gov/oralhealth/infectioncontr
ol/pdf/safe-care2.pdf pdf icon[PDF – 834 KB].
Accessed March 31, 2016.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/subcutaneousinjectionaspernabhppt-221006120849-9fb7a653/85/SUBCUTANEOUS-INJECTION-AS-PER-NABH-PPT-pptx-31-320.jpg)