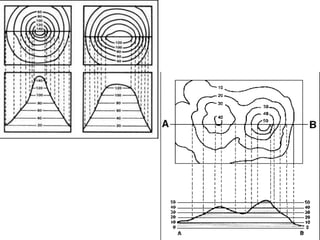
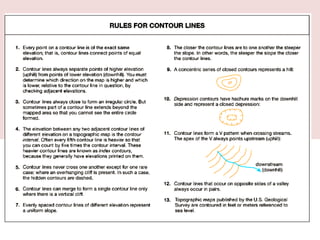
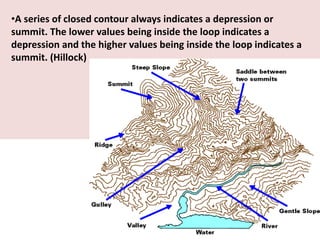
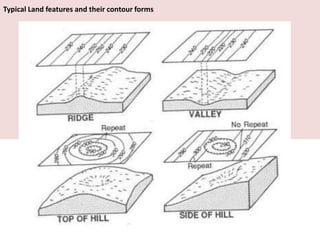
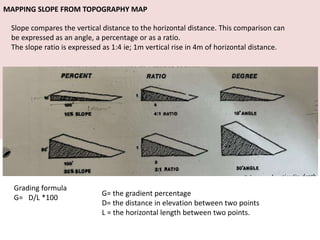
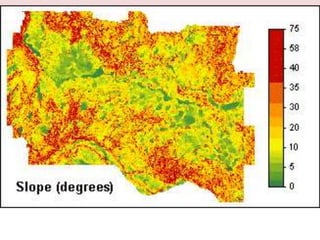
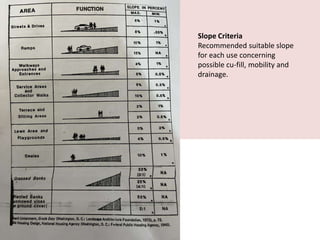
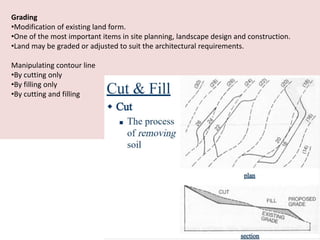
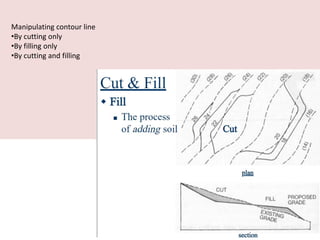
This document discusses the study of topography and contour maps. It defines topography as the study of land surfaces and their features. Contour maps represent elevation data through a series of contour lines that connect points of equal elevation. Characteristics of contour lines such as spacing and shape can indicate features of the landscape like slopes, hills, and depressions. Contour maps are useful for engineering projects, route planning, and understanding the drainage of an area. Slope can be measured from contour maps by comparing vertical and horizontal distances between points. Land can be graded by modifying contours through cutting, filling, or both.