Strut and Tie Model for Pile Cap
•
5 likes•2,741 views
Peer review presentation for the strut and tie method as an analysis and design approach for the mat on piles foundations of the primary separation cell (vessel).
Report
Share
Report
Share
Recommended
ETABS Modelling

The aim of this manual is to give the design application of the basic requirements of EC8 for new concrete and steel buildings using ETABS. This book can be used by users of ETABS modeler. Is not cover all the steps that you have to carry during designing model using ETABS but is a good manual for those who using Eurocodes.
Dynamic Response

Seminar on Design of Tall Buildings: Trends and Advancements for Structural Performance, November 2016
CSI ETABS & SAFE MANUAL: Slab Analysis and Design to EC2

CSI ETABS & SAFE MANUAL: Slab Analysis and Design to EC2Eur Ing Valentinos Neophytou BEng (Hons), MSc, CEng MICE
This document presents an example of analysis design of slab using ETABS. This example examines a simple single story building, which is regular in plan and elevation. It is examining and compares the calculated ultimate moment from CSI ETABS & SAFE with hand calculation. Moment coefficients were used to calculate the ultimate moment. However it is good practice that such hand analysis methods are used to verify the output of more sophisticated methods.
Also, this document contains simple procedure (step-by-step) of how to design solid slab according to Eurocode 2.The process of designing elements will not be revolutionised as a result of using Eurocode 2. Due to time constraints and knowledge, I may not be able to address the whole issues.
CE 72.32 (January 2016 Semester) Lecture 3 - Design Criteria 

CE 72.32 (January 2016 Semester) Lecture 3 - Design Criteria
Recommended
ETABS Modelling

The aim of this manual is to give the design application of the basic requirements of EC8 for new concrete and steel buildings using ETABS. This book can be used by users of ETABS modeler. Is not cover all the steps that you have to carry during designing model using ETABS but is a good manual for those who using Eurocodes.
Dynamic Response

Seminar on Design of Tall Buildings: Trends and Advancements for Structural Performance, November 2016
CSI ETABS & SAFE MANUAL: Slab Analysis and Design to EC2

CSI ETABS & SAFE MANUAL: Slab Analysis and Design to EC2Eur Ing Valentinos Neophytou BEng (Hons), MSc, CEng MICE
This document presents an example of analysis design of slab using ETABS. This example examines a simple single story building, which is regular in plan and elevation. It is examining and compares the calculated ultimate moment from CSI ETABS & SAFE with hand calculation. Moment coefficients were used to calculate the ultimate moment. However it is good practice that such hand analysis methods are used to verify the output of more sophisticated methods.
Also, this document contains simple procedure (step-by-step) of how to design solid slab according to Eurocode 2.The process of designing elements will not be revolutionised as a result of using Eurocode 2. Due to time constraints and knowledge, I may not be able to address the whole issues.
CE 72.32 (January 2016 Semester) Lecture 3 - Design Criteria 

CE 72.32 (January 2016 Semester) Lecture 3 - Design Criteria
CE 72.32 (January 2016 Semester) Lecture 8 - Structural Analysis for Lateral ...

CE 72.32 (January 2016 Semester) Lecture 8 - Structural Analysis for Lateral Loads
Column design.ppt

Civil Engineering, Column Design
Structure Engineering, Combined loading, axial loading, bending,
short column, column design criteria, short column design, RCC Column design
CE72.52 - Lecture 3b - Section Behavior - Shear and Torsion

CE72.52 - Advanced Concrete Structures - Lecture 3b - Section Behavior - Shear and Torsion
Design Procedure of Singly,Doubly & T-Beam(As Per ACI code)

Content:
-USD(Ultimate Strength Design)
-Classification of beam with respect to design system
-Assumptions
-Evolution of design parameters
-Moment Factors Kn,
-Balanced Reinforcement Ratio b
-Calculating Strength Reduction Factor
-Calculating
-Design procedure for Singly Reinforced Beam
-Design procedure for Doubly Reinforced Beam
-Design procedure for T-Beam
-Appendix
Prestress loss due to friction & anchorage take up

This document provides a detailed procedure for calculating prestress loss due to anchorage take-up. Prestress Loss due to friction is also discussed in detail.
Comparision of Design Codes ACI 318-11, IS 456 2000 and Eurocode II

National building codes have been formulated in different countries to lay down guidelines for the design and construction of structures. The codes have been evolved from the collective wisdom of expert structural engineers, gained over the years. These codes are periodically revised to bring them in line with current research, and often current trends. The main function of the design codes is to ensure adequate structural safety, by specifying certain essential minimum reinforcement for design. They render the task of the designer relatively easy and simple, results are often formulated in formulas or charts. The codes ensure a certain degree of consistency among different designers. Finally, they have some legal validity in that they protect the structural designer from any liability due to structural failures that are caused by inadequate supervision and or faulty material and construction. The aim of this project is to compare the design codes of IS 456-2007, ACI 318-11code and Eurocode II. The broad design criteria like stress strain block parameters, L D ratio, load combinations, formula will be compared along with the area of steel for the major structural members like beams, slab, columns, footing to get an over view how the codes fair in comparison with each other. The emphasis will be to put the results in tabular and graphical representation so as to get a better clarity and comparative analysis. Iqbal Rasool Dar "Comparision of Design Codes ACI 318-11, IS 456:2000 and Eurocode II" Published in International Journal of Trend in Scientific Research and Development (ijtsrd), ISSN: 2456-6470, Volume-3 | Issue-1 , December 2018, URL: http://www.ijtsrd.com/papers/ijtsrd18949.pdf
http://www.ijtsrd.com/engineering/civil-engineering/18949/comparision-of-design-codes-aci-318-11-is-4562000-and-eurocode-ii/iqbal-rasool-dar
Surface Structures, including SAP2000

The lecture is in support of:
(1) The Design of Building Structures (Vol.1, Vol. 2), rev. ed., PDF eBook by Wolfgang Schueller, 2016
(2) Building Support Structures, Analysis and Design with SAP2000 Software, 2nd ed., eBook by Wolfgang Schueller,
The SAP2000V15 Examples and Problems SDB files are available on the Computers & Structures, Inc. (CSI) website: http://www.csiamerica.com/go/schueller
Calulation of deflection and crack width according to is 456 2000

Calculation of Deflection and Crack
Eurocode 2 design of composite concrete

Abstract (Dutch)
Samengestelde betonnen liggers vervaardigd van prefab voorgespannen- en/of gewapende elementen zijn zeer populair in de huidige praktijk van de civiele techniek. Twee betonnen, samengestelde delen van de ligger worden gestort op verschillende tijdstippen. Verschillende elasticiteitsmoduli, opeenvolgende belastingaanbrenging, en verschillend krimp en kruip veroorzaken een herverdeling van de normaalspanning en ongelijke rekken en spanningen in twee aansluitende vezels in het aansluitvlak.
Dit seminar richt zich op de berekening volgens de EN 1992-1-1 en EN 1992-2. De aannames met betrekking tot de berekening en de controle van de gewapende en/of voorgespannen samengestelde liggers en doorsnedes zal worden toegelicht.
Ook wordt er ingegaan op:
• De spanning/rek respons van de doorsnede belast door normaalkracht en buigende momenten,
• De principes van het gebruik van de “initiële toestand” in berekeningen van de uiterste grenstoestand en de bruikbaarheidsgrenstoestand,
• De controle van dwarskracht en wringing,
• De interactie tussen alle snedekrachten,
• De principes van de controles van de spanningbeperking,
• De achtergrond van de scheurwijdtecontrole
Speciale aandacht zal er worden gegeven aan de berekening van de schuifspanning in het aansluitvlak, en de beschouwing van de invloed van de verschillende leeftijd van de betonnen delen met betrekking tot de schuifspanningen. Een alternatieve berekeningsmethode ten opzichte van de Eurocode 2 zal worden voorgesteld en worden getest.
De praktische voorbeelden volgens de Eurocode 2 zullen worden uitgevoerd met behulp van de IDEA StatiCa software.
CE72.52 - Lecture 3a - Section Behavior - Flexure

CE72.52 - Advanced Concrete Structures - Lecture 3a - Section Behavior - Flexure
Lec12 Continuous Beams and One Way Slabs(2) Columns (Reinforced Concrete Desi...

Lec12 Continuous Beams and One Way Slabs(2) Columns (Reinforced Concrete Design I & Prof. Abdelhamid Charif)
Beam design

Basic of reinforced concrete designs and singly,doubly reinforced beam design according to bs 8110
Paper " STRUT-AND-TIE MODEL AND 3-D NONLINEAR FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS FOR THE...

Paper " STRUT-AND-TIE MODEL AND 3-D NONLINEAR FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS FOR THE...Waleed E. El-Demerdash
More Related Content
What's hot
CE 72.32 (January 2016 Semester) Lecture 8 - Structural Analysis for Lateral ...

CE 72.32 (January 2016 Semester) Lecture 8 - Structural Analysis for Lateral Loads
Column design.ppt

Civil Engineering, Column Design
Structure Engineering, Combined loading, axial loading, bending,
short column, column design criteria, short column design, RCC Column design
CE72.52 - Lecture 3b - Section Behavior - Shear and Torsion

CE72.52 - Advanced Concrete Structures - Lecture 3b - Section Behavior - Shear and Torsion
Design Procedure of Singly,Doubly & T-Beam(As Per ACI code)

Content:
-USD(Ultimate Strength Design)
-Classification of beam with respect to design system
-Assumptions
-Evolution of design parameters
-Moment Factors Kn,
-Balanced Reinforcement Ratio b
-Calculating Strength Reduction Factor
-Calculating
-Design procedure for Singly Reinforced Beam
-Design procedure for Doubly Reinforced Beam
-Design procedure for T-Beam
-Appendix
Prestress loss due to friction & anchorage take up

This document provides a detailed procedure for calculating prestress loss due to anchorage take-up. Prestress Loss due to friction is also discussed in detail.
Comparision of Design Codes ACI 318-11, IS 456 2000 and Eurocode II

National building codes have been formulated in different countries to lay down guidelines for the design and construction of structures. The codes have been evolved from the collective wisdom of expert structural engineers, gained over the years. These codes are periodically revised to bring them in line with current research, and often current trends. The main function of the design codes is to ensure adequate structural safety, by specifying certain essential minimum reinforcement for design. They render the task of the designer relatively easy and simple, results are often formulated in formulas or charts. The codes ensure a certain degree of consistency among different designers. Finally, they have some legal validity in that they protect the structural designer from any liability due to structural failures that are caused by inadequate supervision and or faulty material and construction. The aim of this project is to compare the design codes of IS 456-2007, ACI 318-11code and Eurocode II. The broad design criteria like stress strain block parameters, L D ratio, load combinations, formula will be compared along with the area of steel for the major structural members like beams, slab, columns, footing to get an over view how the codes fair in comparison with each other. The emphasis will be to put the results in tabular and graphical representation so as to get a better clarity and comparative analysis. Iqbal Rasool Dar "Comparision of Design Codes ACI 318-11, IS 456:2000 and Eurocode II" Published in International Journal of Trend in Scientific Research and Development (ijtsrd), ISSN: 2456-6470, Volume-3 | Issue-1 , December 2018, URL: http://www.ijtsrd.com/papers/ijtsrd18949.pdf
http://www.ijtsrd.com/engineering/civil-engineering/18949/comparision-of-design-codes-aci-318-11-is-4562000-and-eurocode-ii/iqbal-rasool-dar
Surface Structures, including SAP2000

The lecture is in support of:
(1) The Design of Building Structures (Vol.1, Vol. 2), rev. ed., PDF eBook by Wolfgang Schueller, 2016
(2) Building Support Structures, Analysis and Design with SAP2000 Software, 2nd ed., eBook by Wolfgang Schueller,
The SAP2000V15 Examples and Problems SDB files are available on the Computers & Structures, Inc. (CSI) website: http://www.csiamerica.com/go/schueller
Calulation of deflection and crack width according to is 456 2000

Calculation of Deflection and Crack
Eurocode 2 design of composite concrete

Abstract (Dutch)
Samengestelde betonnen liggers vervaardigd van prefab voorgespannen- en/of gewapende elementen zijn zeer populair in de huidige praktijk van de civiele techniek. Twee betonnen, samengestelde delen van de ligger worden gestort op verschillende tijdstippen. Verschillende elasticiteitsmoduli, opeenvolgende belastingaanbrenging, en verschillend krimp en kruip veroorzaken een herverdeling van de normaalspanning en ongelijke rekken en spanningen in twee aansluitende vezels in het aansluitvlak.
Dit seminar richt zich op de berekening volgens de EN 1992-1-1 en EN 1992-2. De aannames met betrekking tot de berekening en de controle van de gewapende en/of voorgespannen samengestelde liggers en doorsnedes zal worden toegelicht.
Ook wordt er ingegaan op:
• De spanning/rek respons van de doorsnede belast door normaalkracht en buigende momenten,
• De principes van het gebruik van de “initiële toestand” in berekeningen van de uiterste grenstoestand en de bruikbaarheidsgrenstoestand,
• De controle van dwarskracht en wringing,
• De interactie tussen alle snedekrachten,
• De principes van de controles van de spanningbeperking,
• De achtergrond van de scheurwijdtecontrole
Speciale aandacht zal er worden gegeven aan de berekening van de schuifspanning in het aansluitvlak, en de beschouwing van de invloed van de verschillende leeftijd van de betonnen delen met betrekking tot de schuifspanningen. Een alternatieve berekeningsmethode ten opzichte van de Eurocode 2 zal worden voorgesteld en worden getest.
De praktische voorbeelden volgens de Eurocode 2 zullen worden uitgevoerd met behulp van de IDEA StatiCa software.
CE72.52 - Lecture 3a - Section Behavior - Flexure

CE72.52 - Advanced Concrete Structures - Lecture 3a - Section Behavior - Flexure
Lec12 Continuous Beams and One Way Slabs(2) Columns (Reinforced Concrete Desi...

Lec12 Continuous Beams and One Way Slabs(2) Columns (Reinforced Concrete Design I & Prof. Abdelhamid Charif)
Beam design

Basic of reinforced concrete designs and singly,doubly reinforced beam design according to bs 8110
What's hot (20)
CE 72.32 (January 2016 Semester) Lecture 8 - Structural Analysis for Lateral ...

CE 72.32 (January 2016 Semester) Lecture 8 - Structural Analysis for Lateral ...
CE72.52 - Lecture 3b - Section Behavior - Shear and Torsion

CE72.52 - Lecture 3b - Section Behavior - Shear and Torsion
Design Procedure of Singly,Doubly & T-Beam(As Per ACI code)

Design Procedure of Singly,Doubly & T-Beam(As Per ACI code)
Prestress loss due to friction & anchorage take up

Prestress loss due to friction & anchorage take up
Comparision of Design Codes ACI 318-11, IS 456 2000 and Eurocode II

Comparision of Design Codes ACI 318-11, IS 456 2000 and Eurocode II
Calulation of deflection and crack width according to is 456 2000

Calulation of deflection and crack width according to is 456 2000
Lec12 Continuous Beams and One Way Slabs(2) Columns (Reinforced Concrete Desi...

Lec12 Continuous Beams and One Way Slabs(2) Columns (Reinforced Concrete Desi...
Similar to Strut and Tie Model for Pile Cap
Paper " STRUT-AND-TIE MODEL AND 3-D NONLINEAR FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS FOR THE...

Paper " STRUT-AND-TIE MODEL AND 3-D NONLINEAR FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS FOR THE...Waleed E. El-Demerdash
Lec11 Continuous Beams and One Way Slabs(1) (Reinforced Concrete Design I & P...

Lec11 Continuous Beams and One Way Slabs(1) (Reinforced Concrete Design I & Prof. Abdelhamid Charif)
Behavior of RC Shallow and Deep Beams with Openings Via the Strut-and-Tie Mod...

Behavior of RC Shallow and Deep Beams with Openings Via the Strut-and-Tie Mod...Waleed E. El-Demerdash
Paper
Arabian Journal for Science and Engineering
By:
Waleed E. El-Demerdash, Salah E. ElMetwally, Mohamed E. El-Zoughiby & Ahmed A. Ghaleb
Tensegrity structure

A tensegrity structure is a combination of compression members and tension cables. I have already discussed the advantages and disadvantages of this structure based on some reputed journals.
Similar to Strut and Tie Model for Pile Cap (20)
Paper " STRUT-AND-TIE MODEL AND 3-D NONLINEAR FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS FOR THE...

Paper " STRUT-AND-TIE MODEL AND 3-D NONLINEAR FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS FOR THE...
Deflections in PT elements pt structure for all pt slabs in civil industry.pdf

Deflections in PT elements pt structure for all pt slabs in civil industry.pdf
Lec11 Continuous Beams and One Way Slabs(1) (Reinforced Concrete Design I & P...

Lec11 Continuous Beams and One Way Slabs(1) (Reinforced Concrete Design I & P...
Behavior of RC Shallow and Deep Beams with Openings Via the Strut-and-Tie Mod...

Behavior of RC Shallow and Deep Beams with Openings Via the Strut-and-Tie Mod...
Recently uploaded
Final project report on grocery store management system..pdf

In today’s fast-changing business environment, it’s extremely important to be able to respond to client needs in the most effective and timely manner. If your customers wish to see your business online and have instant access to your products or services.
Online Grocery Store is an e-commerce website, which retails various grocery products. This project allows viewing various products available enables registered users to purchase desired products instantly using Paytm, UPI payment processor (Instant Pay) and also can place order by using Cash on Delivery (Pay Later) option. This project provides an easy access to Administrators and Managers to view orders placed using Pay Later and Instant Pay options.
In order to develop an e-commerce website, a number of Technologies must be studied and understood. These include multi-tiered architecture, server and client-side scripting techniques, implementation technologies, programming language (such as PHP, HTML, CSS, JavaScript) and MySQL relational databases. This is a project with the objective to develop a basic website where a consumer is provided with a shopping cart website and also to know about the technologies used to develop such a website.
This document will discuss each of the underlying technologies to create and implement an e- commerce website.
在线办理(ANU毕业证书)澳洲国立大学毕业证录取通知书一模一样

学校原件一模一样【微信:741003700 】《(ANU毕业证书)澳洲国立大学毕业证》【微信:741003700 】学位证,留信认证(真实可查,永久存档)原件一模一样纸张工艺/offer、雅思、外壳等材料/诚信可靠,可直接看成品样本,帮您解决无法毕业带来的各种难题!外壳,原版制作,诚信可靠,可直接看成品样本。行业标杆!精益求精,诚心合作,真诚制作!多年品质 ,按需精细制作,24小时接单,全套进口原装设备。十五年致力于帮助留学生解决难题,包您满意。
本公司拥有海外各大学样板无数,能完美还原。
1:1完美还原海外各大学毕业材料上的工艺:水印,阴影底纹,钢印LOGO烫金烫银,LOGO烫金烫银复合重叠。文字图案浮雕、激光镭射、紫外荧光、温感、复印防伪等防伪工艺。材料咨询办理、认证咨询办理请加学历顾问Q/微741003700
【主营项目】
一.毕业证【q微741003700】成绩单、使馆认证、教育部认证、雅思托福成绩单、学生卡等!
二.真实使馆公证(即留学回国人员证明,不成功不收费)
三.真实教育部学历学位认证(教育部存档!教育部留服网站永久可查)
四.办理各国各大学文凭(一对一专业服务,可全程监控跟踪进度)
如果您处于以下几种情况:
◇在校期间,因各种原因未能顺利毕业……拿不到官方毕业证【q/微741003700】
◇面对父母的压力,希望尽快拿到;
◇不清楚认证流程以及材料该如何准备;
◇回国时间很长,忘记办理;
◇回国马上就要找工作,办给用人单位看;
◇企事业单位必须要求办理的
◇需要报考公务员、购买免税车、落转户口
◇申请留学生创业基金
留信网认证的作用:
1:该专业认证可证明留学生真实身份
2:同时对留学生所学专业登记给予评定
3:国家专业人才认证中心颁发入库证书
4:这个认证书并且可以归档倒地方
5:凡事获得留信网入网的信息将会逐步更新到个人身份内,将在公安局网内查询个人身份证信息后,同步读取人才网入库信息
6:个人职称评审加20分
7:个人信誉贷款加10分
8:在国家人才网主办的国家网络招聘大会中纳入资料,供国家高端企业选择人才
Top 10 Oil and Gas Projects in Saudi Arabia 2024.pdf

Saudi Arabia stands as a titan in the global energy landscape, renowned for its abundant oil and gas resources. It's the largest exporter of petroleum and holds some of the world's most significant reserves. Let's delve into the top 10 oil and gas projects shaping Saudi Arabia's energy future in 2024.
RAT: Retrieval Augmented Thoughts Elicit Context-Aware Reasoning in Long-Hori...

RAT: Retrieval Augmented Thoughts Elicit Context-Aware Reasoning in Long-Horizon Generation
Hybrid optimization of pumped hydro system and solar- Engr. Abdul-Azeez.pdf

Advancements in technology unveil a myriad of electrical and electronic breakthroughs geared towards efficiently harnessing limited resources to meet human energy demands. The optimization of hybrid solar PV panels and pumped hydro energy supply systems plays a pivotal role in utilizing natural resources effectively. This initiative not only benefits humanity but also fosters environmental sustainability. The study investigated the design optimization of these hybrid systems, focusing on understanding solar radiation patterns, identifying geographical influences on solar radiation, formulating a mathematical model for system optimization, and determining the optimal configuration of PV panels and pumped hydro storage. Through a comparative analysis approach and eight weeks of data collection, the study addressed key research questions related to solar radiation patterns and optimal system design. The findings highlighted regions with heightened solar radiation levels, showcasing substantial potential for power generation and emphasizing the system's efficiency. Optimizing system design significantly boosted power generation, promoted renewable energy utilization, and enhanced energy storage capacity. The study underscored the benefits of optimizing hybrid solar PV panels and pumped hydro energy supply systems for sustainable energy usage. Optimizing the design of solar PV panels and pumped hydro energy supply systems as examined across diverse climatic conditions in a developing country, not only enhances power generation but also improves the integration of renewable energy sources and boosts energy storage capacities, particularly beneficial for less economically prosperous regions. Additionally, the study provides valuable insights for advancing energy research in economically viable areas. Recommendations included conducting site-specific assessments, utilizing advanced modeling tools, implementing regular maintenance protocols, and enhancing communication among system components.
Architectural Portfolio Sean Lockwood

This portfolio contains selected projects I completed during my undergraduate studies. 2018 - 2023
Standard Reomte Control Interface - Neometrix

About
Indigenized remote control interface card suitable for MAFI system CCR equipment. Compatible for IDM8000 CCR. Backplane mounted serial and TCP/Ethernet communication module for CCR remote access. IDM 8000 CCR remote control on serial and TCP protocol.
• Remote control: Parallel or serial interface.
• Compatible with MAFI CCR system.
• Compatible with IDM8000 CCR.
• Compatible with Backplane mount serial communication.
• Compatible with commercial and Defence aviation CCR system.
• Remote control system for accessing CCR and allied system over serial or TCP.
• Indigenized local Support/presence in India.
• Easy in configuration using DIP switches.
Technical Specifications
Indigenized remote control interface card suitable for MAFI system CCR equipment. Compatible for IDM8000 CCR. Backplane mounted serial and TCP/Ethernet communication module for CCR remote access. IDM 8000 CCR remote control on serial and TCP protocol.
Key Features
Indigenized remote control interface card suitable for MAFI system CCR equipment. Compatible for IDM8000 CCR. Backplane mounted serial and TCP/Ethernet communication module for CCR remote access. IDM 8000 CCR remote control on serial and TCP protocol.
• Remote control: Parallel or serial interface
• Compatible with MAFI CCR system
• Copatiable with IDM8000 CCR
• Compatible with Backplane mount serial communication.
• Compatible with commercial and Defence aviation CCR system.
• Remote control system for accessing CCR and allied system over serial or TCP.
• Indigenized local Support/presence in India.
Application
• Remote control: Parallel or serial interface.
• Compatible with MAFI CCR system.
• Compatible with IDM8000 CCR.
• Compatible with Backplane mount serial communication.
• Compatible with commercial and Defence aviation CCR system.
• Remote control system for accessing CCR and allied system over serial or TCP.
• Indigenized local Support/presence in India.
• Easy in configuration using DIP switches.
Hierarchical Digital Twin of a Naval Power System

A hierarchical digital twin of a Naval DC power system has been developed and experimentally verified. Similar to other state-of-the-art digital twins, this technology creates a digital replica of the physical system executed in real-time or faster, which can modify hardware controls. However, its advantage stems from distributing computational efforts by utilizing a hierarchical structure composed of lower-level digital twin blocks and a higher-level system digital twin. Each digital twin block is associated with a physical subsystem of the hardware and communicates with a singular system digital twin, which creates a system-level response. By extracting information from each level of the hierarchy, power system controls of the hardware were reconfigured autonomously. This hierarchical digital twin development offers several advantages over other digital twins, particularly in the field of naval power systems. The hierarchical structure allows for greater computational efficiency and scalability while the ability to autonomously reconfigure hardware controls offers increased flexibility and responsiveness. The hierarchical decomposition and models utilized were well aligned with the physical twin, as indicated by the maximum deviations between the developed digital twin hierarchy and the hardware.
HYDROPOWER - Hydroelectric power generation

Overview of the fundamental roles in Hydropower generation and the components involved in wider Electrical Engineering.
This paper presents the design and construction of hydroelectric dams from the hydrologist’s survey of the valley before construction, all aspects and involved disciplines, fluid dynamics, structural engineering, generation and mains frequency regulation to the very transmission of power through the network in the United Kingdom.
Author: Robbie Edward Sayers
Collaborators and co editors: Charlie Sims and Connor Healey.
(C) 2024 Robbie E. Sayers
NO1 Uk best vashikaran specialist in delhi vashikaran baba near me online vas...

NO1 Uk best vashikaran specialist in delhi vashikaran baba near me online vas...Amil Baba Dawood bangali
Contact with Dawood Bhai Just call on +92322-6382012 and we'll help you. We'll solve all your problems within 12 to 24 hours and with 101% guarantee and with astrology systematic. If you want to take any personal or professional advice then also you can call us on +92322-6382012 , ONLINE LOVE PROBLEM & Other all types of Daily Life Problem's.Then CALL or WHATSAPP us on +92322-6382012 and Get all these problems solutions here by Amil Baba DAWOOD BANGALI
#vashikaranspecialist #astrologer #palmistry #amliyaat #taweez #manpasandshadi #horoscope #spiritual #lovelife #lovespell #marriagespell#aamilbabainpakistan #amilbabainkarachi #powerfullblackmagicspell #kalajadumantarspecialist #realamilbaba #AmilbabainPakistan #astrologerincanada #astrologerindubai #lovespellsmaster #kalajaduspecialist #lovespellsthatwork #aamilbabainlahore#blackmagicformarriage #aamilbaba #kalajadu #kalailam #taweez #wazifaexpert #jadumantar #vashikaranspecialist #astrologer #palmistry #amliyaat #taweez #manpasandshadi #horoscope #spiritual #lovelife #lovespell #marriagespell#aamilbabainpakistan #amilbabainkarachi #powerfullblackmagicspell #kalajadumantarspecialist #realamilbaba #AmilbabainPakistan #astrologerincanada #astrologerindubai #lovespellsmaster #kalajaduspecialist #lovespellsthatwork #aamilbabainlahore #blackmagicforlove #blackmagicformarriage #aamilbaba #kalajadu #kalailam #taweez #wazifaexpert #jadumantar #vashikaranspecialist #astrologer #palmistry #amliyaat #taweez #manpasandshadi #horoscope #spiritual #lovelife #lovespell #marriagespell#aamilbabainpakistan #amilbabainkarachi #powerfullblackmagicspell #kalajadumantarspecialist #realamilbaba #AmilbabainPakistan #astrologerincanada #astrologerindubai #lovespellsmaster #kalajaduspecialist #lovespellsthatwork #aamilbabainlahore #Amilbabainuk #amilbabainspain #amilbabaindubai #Amilbabainnorway #amilbabainkrachi #amilbabainlahore #amilbabaingujranwalan #amilbabainislamabad
AKS UNIVERSITY Satna Final Year Project By OM Hardaha.pdf

AKS UNIVERSITY Satna Final Year Project By OM Hardaha.
Thank me later.
samsarthak31@gmail.com
The Benefits and Techniques of Trenchless Pipe Repair.pdf

Explore the innovative world of trenchless pipe repair with our comprehensive guide, "The Benefits and Techniques of Trenchless Pipe Repair." This document delves into the modern methods of repairing underground pipes without the need for extensive excavation, highlighting the numerous advantages and the latest techniques used in the industry.
Learn about the cost savings, reduced environmental impact, and minimal disruption associated with trenchless technology. Discover detailed explanations of popular techniques such as pipe bursting, cured-in-place pipe (CIPP) lining, and directional drilling. Understand how these methods can be applied to various types of infrastructure, from residential plumbing to large-scale municipal systems.
Ideal for homeowners, contractors, engineers, and anyone interested in modern plumbing solutions, this guide provides valuable insights into why trenchless pipe repair is becoming the preferred choice for pipe rehabilitation. Stay informed about the latest advancements and best practices in the field.
Cosmetic shop management system project report.pdf

Buying new cosmetic products is difficult. It can even be scary for those who have sensitive skin and are prone to skin trouble. The information needed to alleviate this problem is on the back of each product, but it's thought to interpret those ingredient lists unless you have a background in chemistry.
Instead of buying and hoping for the best, we can use data science to help us predict which products may be good fits for us. It includes various function programs to do the above mentioned tasks.
Data file handling has been effectively used in the program.
The automated cosmetic shop management system should deal with the automation of general workflow and administration process of the shop. The main processes of the system focus on customer's request where the system is able to search the most appropriate products and deliver it to the customers. It should help the employees to quickly identify the list of cosmetic product that have reached the minimum quantity and also keep a track of expired date for each cosmetic product. It should help the employees to find the rack number in which the product is placed.It is also Faster and more efficient way.
Immunizing Image Classifiers Against Localized Adversary Attacks

This paper addresses the vulnerability of deep learning models, particularly convolutional neural networks
(CNN)s, to adversarial attacks and presents a proactive training technique designed to counter them. We
introduce a novel volumization algorithm, which transforms 2D images into 3D volumetric representations.
When combined with 3D convolution and deep curriculum learning optimization (CLO), itsignificantly improves
the immunity of models against localized universal attacks by up to 40%. We evaluate our proposed approach
using contemporary CNN architectures and the modified Canadian Institute for Advanced Research (CIFAR-10
and CIFAR-100) and ImageNet Large Scale Visual Recognition Challenge (ILSVRC12) datasets, showcasing
accuracy improvements over previous techniques. The results indicate that the combination of the volumetric
input and curriculum learning holds significant promise for mitigating adversarial attacks without necessitating
adversary training.
Recently uploaded (20)
Final project report on grocery store management system..pdf

Final project report on grocery store management system..pdf
Top 10 Oil and Gas Projects in Saudi Arabia 2024.pdf

Top 10 Oil and Gas Projects in Saudi Arabia 2024.pdf
RAT: Retrieval Augmented Thoughts Elicit Context-Aware Reasoning in Long-Hori...

RAT: Retrieval Augmented Thoughts Elicit Context-Aware Reasoning in Long-Hori...
block diagram and signal flow graph representation

block diagram and signal flow graph representation
Hybrid optimization of pumped hydro system and solar- Engr. Abdul-Azeez.pdf

Hybrid optimization of pumped hydro system and solar- Engr. Abdul-Azeez.pdf
Fundamentals of Electric Drives and its applications.pptx

Fundamentals of Electric Drives and its applications.pptx
NO1 Uk best vashikaran specialist in delhi vashikaran baba near me online vas...

NO1 Uk best vashikaran specialist in delhi vashikaran baba near me online vas...
AKS UNIVERSITY Satna Final Year Project By OM Hardaha.pdf

AKS UNIVERSITY Satna Final Year Project By OM Hardaha.pdf
The Benefits and Techniques of Trenchless Pipe Repair.pdf

The Benefits and Techniques of Trenchless Pipe Repair.pdf
Cosmetic shop management system project report.pdf

Cosmetic shop management system project report.pdf
Immunizing Image Classifiers Against Localized Adversary Attacks

Immunizing Image Classifiers Against Localized Adversary Attacks
Strut and Tie Model for Pile Cap
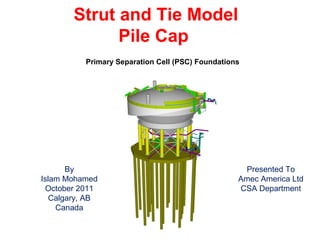
- 1. Strut and Tie Model Pile Cap Primary Separation Cell (PSC) Foundations By Islam Mohamed October 2011 Calgary, AB Canada Presented To Amec America Ltd CSA Department
- 2. •A Conceptual framework represent the load flow in structural elements as a truss analogy consists of compression Struts and tension Ties interconnected at Nodes. •A design tool for disturbed regions “D-Region” where non uniform stress distribution occur. •A unified approach that considers all load effects(M, N, V) simultaneously. •A flexible method that recognize several possible solutions for the same structural configuration. •Useful tool to improves the reinforcement lay out . Basic Description of Strut and Tie Models (STM)
- 3. Examples of Strut-and-Tie Models
- 4. Strut and Tie Model Components 1- Strut: • Diagonal struts are generally oriented parallel to the expected axis of cracking. • They serve as the compression chord of the truss mechanism which resists moment. • They serve as the diagonal struts which transfer shear to the supports.
- 5. -There are three types of struts: •The simplest type is the “prism” which has a constant width. •The second form is the “bottle” in which the strut expands or contracts along its length. •The final type is the “fan” where an array of struts with varying inclination meet at or radiate from a single node.
- 6. 2- Ties: • Tensions ties include stirrups, longitudinal(tension chord) reinforcement, and any special detail reinforcement. • A critical consideration in the detailing of the STM is the provision of adequate anchorage for the reinforcement. 3- Nodes: • Nodes are analogous to joints in a truss where forces are transferred between struts and ties. • Nodes are subject to a multidirectional state of stress. • Nodes are classified by the types of forces being connected. Basic Type of Nodes: (a) CCC (b) CCT (c) CTT (d) TTT (Schlaich et al. 1987)
- 8. • Based on St. Venant's principle, a D-Region assumed to extent about one section depth from the load or discontinuity. • Hence, for a deep beam the D-region has a depth of h and length up to 2h one way or two way from the disturbance, this establishes the smallest angle between a strut and tie attached to one node as arctan (h/2h) = 26.5o . •Two dimensional strut and tie models are used to represent planar structures such as deep beams and corbels. Three dimensional strut and tie models are used for structures such as pile caps for two or more rows of piles.
- 9. Prerequisites in STM • Equilibrium must be maintained. • Ties yield before struts crush (for ductility). • Tension in concrete is neglected. • Forces in struts and ties are uni-axial. • External forces apply at nodes. • Prestressing is treated as a load. • Detailing for adequate anchorage. • Developing STM is an iterative graphical procedure.
- 10. STM Formulation procedure • Specify the Geometrical configuration. • Indicate load paths from loading Points to supporting points. • Draw a truss member along load paths. • Calculate reactions and member forces. • Repeat the previous 2 procedures until approaching the least tie force. • Check stresses in truss members.
- 11. PSC Foundations
- 12. PSC Pile Cap Layout PSC 10 Columns 20 Piles
- 13. •Finite Element Analysis model for PSC Pile Cap to help in figuring out the load path. •Deflection shape for the pile cap FEA model showing positive bending under PSC columns within loading span and negative bending outside loading span.
- 14. Strut Tie •This truss leads to very high tie tension force (T1) relative to results from FEA model because it ignores the pile cap continuity. T1 STM First Approach Column Load Pile Reaction Pile Reaction Pile Cap Effective Depth
- 15. Strut Tie • Tie tension forces (T1) in this truss is about 90% of previous one, the difference in tension is attracted by member T2 . T1 T1 T2 STM Second Approach Pile Reaction Pile Reaction Pile ReactionPile Reaction Column LoadColumn Load Pile Cap Effective Depth
- 16. STM Final Truss Model Struts Ties • By repeating the truss in the second approach at all column-pile locations, we get the above 3D Strut and Tie Model .
- 17. 3D-Staad Model for final truss approach
- 18. Upper Cord and Diagonal Members.
- 19. Lower Cord •Additional ties added between piles to represent the pile cap continuity. •Tension force in (T1) is about 50% of the first truss approach.
- 20. •3m-wide lower reinforcement developed based on tension force in (T1). •Regular mesh spread along the 7.5m width loading strip based on tension force in the other ties. •Nominal reinforcement is provided outside loading strip for serviceability consideration. Reinforcement Layout Considering the STM Results
- 21. Conclusion • For deep structures such as pile caps STM more closely addresses reality. • STM allows flexibility in arriving at solutions. • Typically STM results in higher flexure reinforcement, but you don’t have to check shear. • Understanding the STM helps distribute reinforcement appropriately. • The most representative STM results in the least reinforcement.