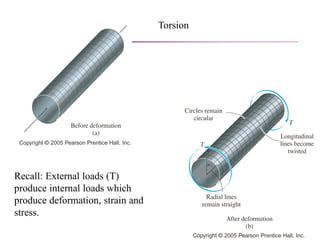
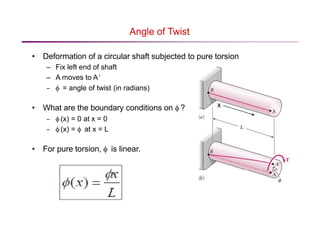
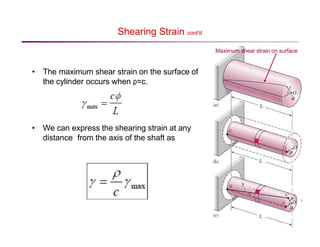
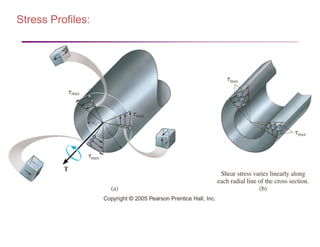
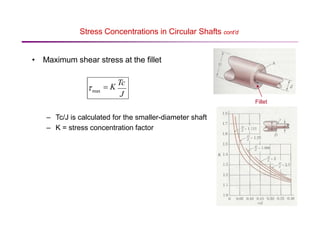
The document discusses torsion and torsional deformation of circular shafts. It defines torsion as a moment that twists a member about its longitudinal axis. For a circular shaft under pure torsion, the angle of twist is linearly proportional to the distance along the shaft. The maximum shear stress occurs at the outer surface of the shaft and is calculated using the torsion formula. Non-uniform torsion is analyzed by dividing the shaft into segments or using differential elements and integrating along the length. The document also provides examples of solving for shear stress and required shaft diameter given applied torques.





































![Sample Problem 1
Apply elastic torsion formulas to
find minimum and maximum
stress on shaft BC.
( ) ( ) ( )
[ ]
4
6
4
4
4
1
4
2
m
10
92
.
13
045
.
0
060
.
0
2
2
−
×
=
−
=
−
=
π
π
c
c
J
( )( )
MPa
2
.
86
m
10
92
.
13
m
060
.
0
m
kN
20
4
6
2
2
max
=
×
⋅
=
=
= −
J
c
TBC
τ
τ
MPa
7
.
64
mm
60
mm
45
MPa
2
.
86
min
min
2
1
max
min
=
=
=
τ
τ
τ
τ
c
c
MPa
7
.
64
MPa
2
.
86
min
max
=
=
τ
τ
Given allowable shearing stress and
applied torque, invert the elastic torsion
formula to find the required diameter.
m
10
9
.
38
m
kN
6
65
3
3
2
4
2
max
−
×
=
⋅
=
=
=
c
c
MPa
c
Tc
J
Tc
π
π
τ
mm
8
.
77
2 =
= c
d
Fig. 3 Shearing stress distribution on cross section. Fig. 4 Free-body diagram of shaft portion AB.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/torsion2-230217163218-95dc13da/85/Torsion_2-pdf-45-320.jpg)






