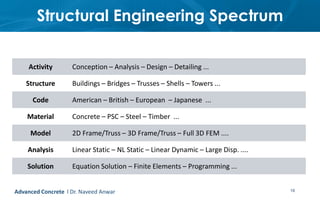
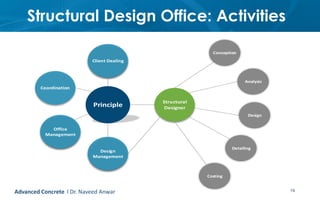
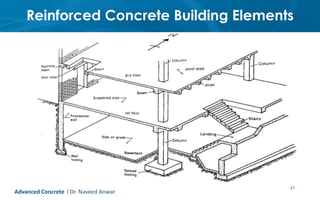
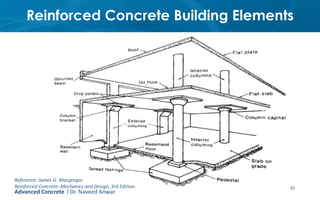
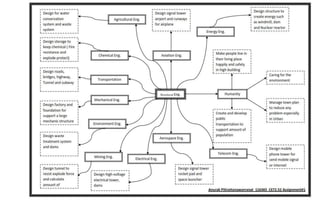
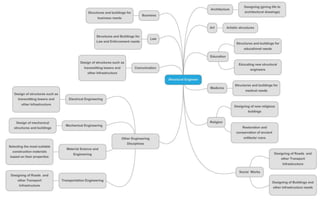
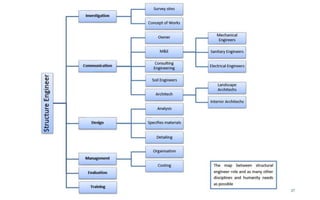
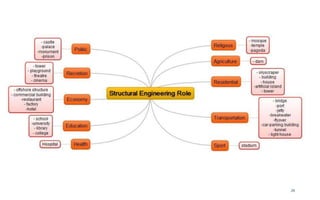
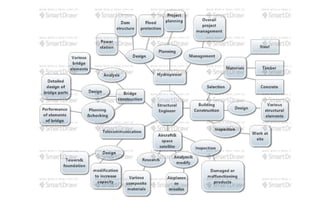
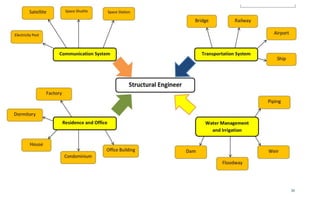
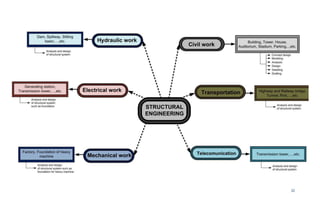
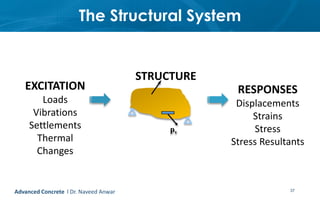
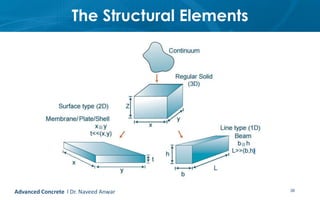
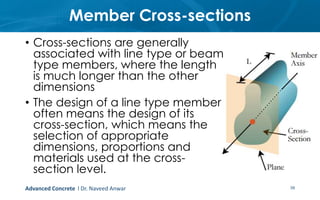
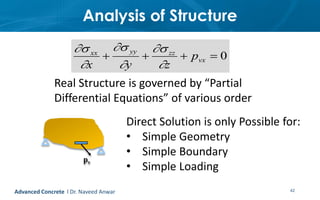
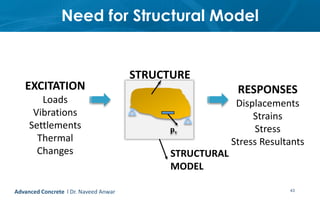
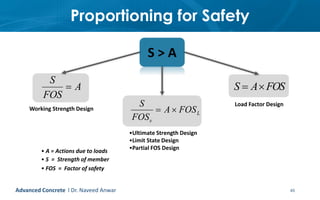
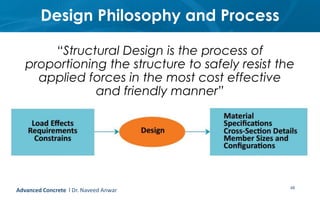
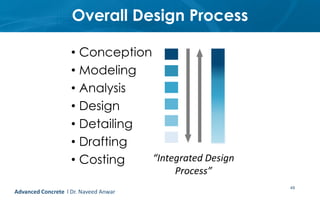
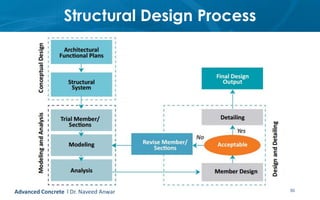
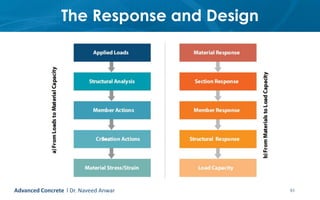
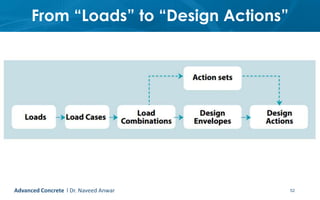
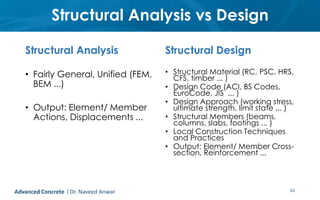
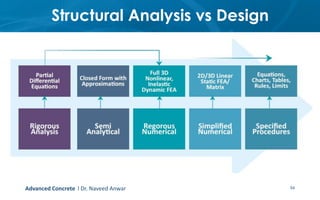
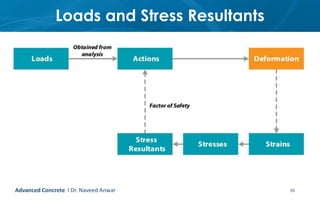
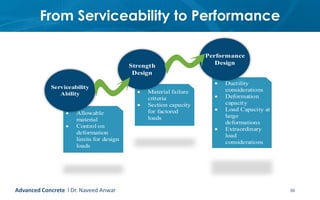
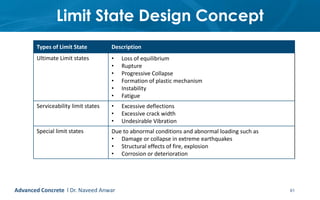
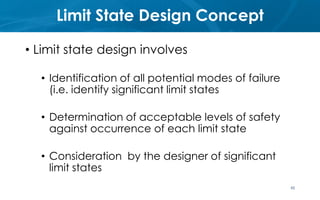
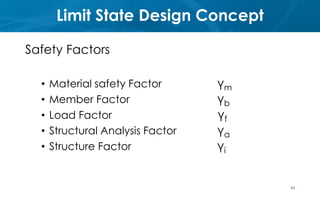
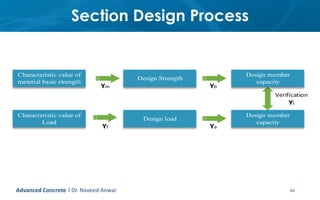
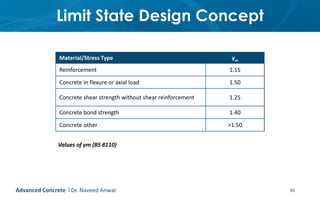
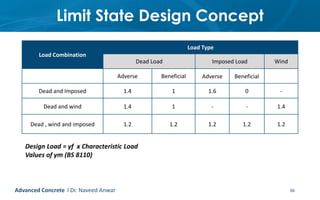
This document provides an introduction to the course CE 72.52 Advanced Concrete. It discusses the key roles of structural engineers in creating safe built environments. It also outlines some of the main topics that will be covered in the course, including material behavior, section design, member design, ductility, seismic detailing, and prestressed concrete. The document includes several images related to reinforced concrete elements, structural analysis and design processes, and limit state design concepts. It provides an overview of the structural design process from modeling and analysis to detailing and drafting.