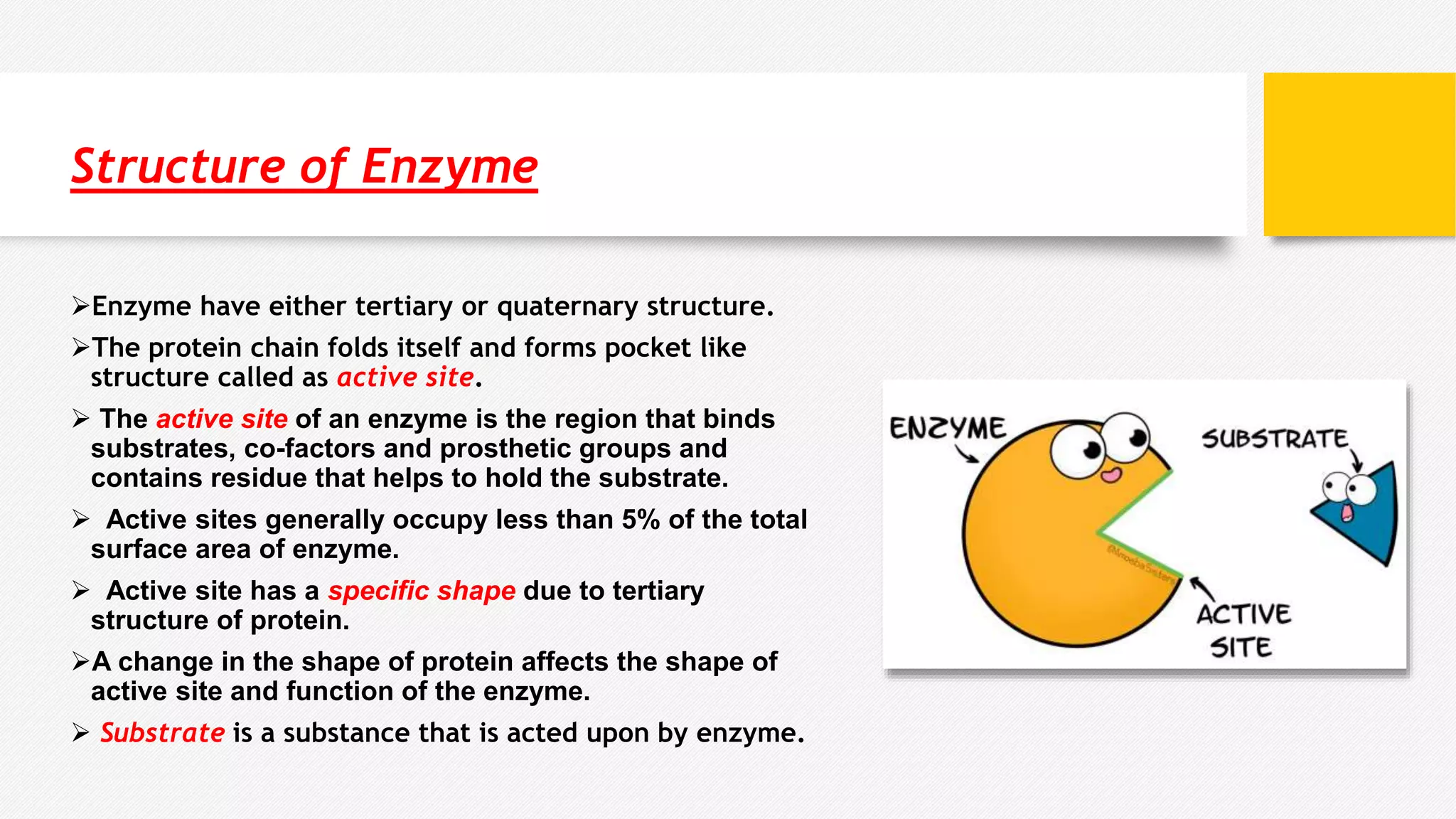
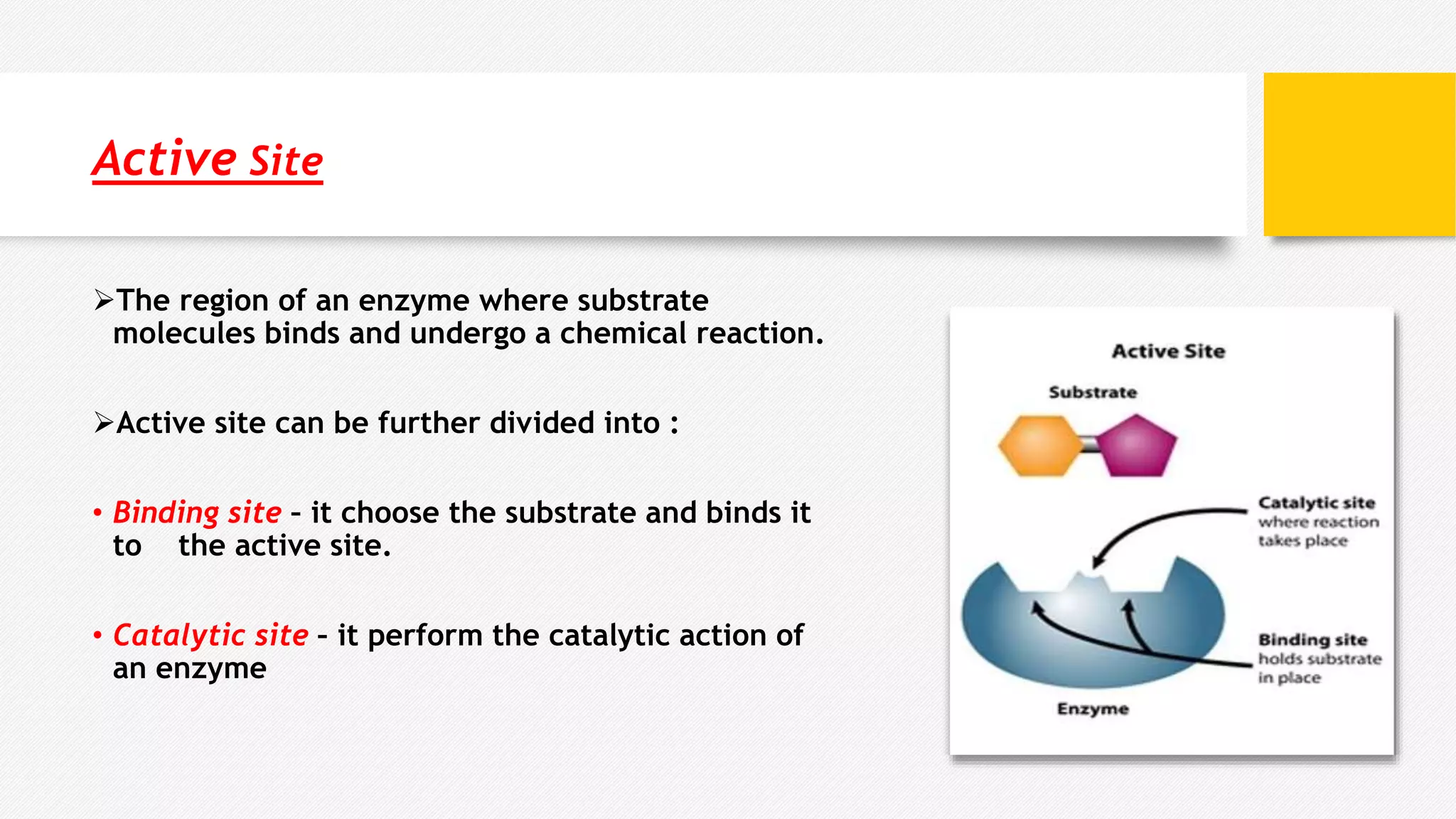
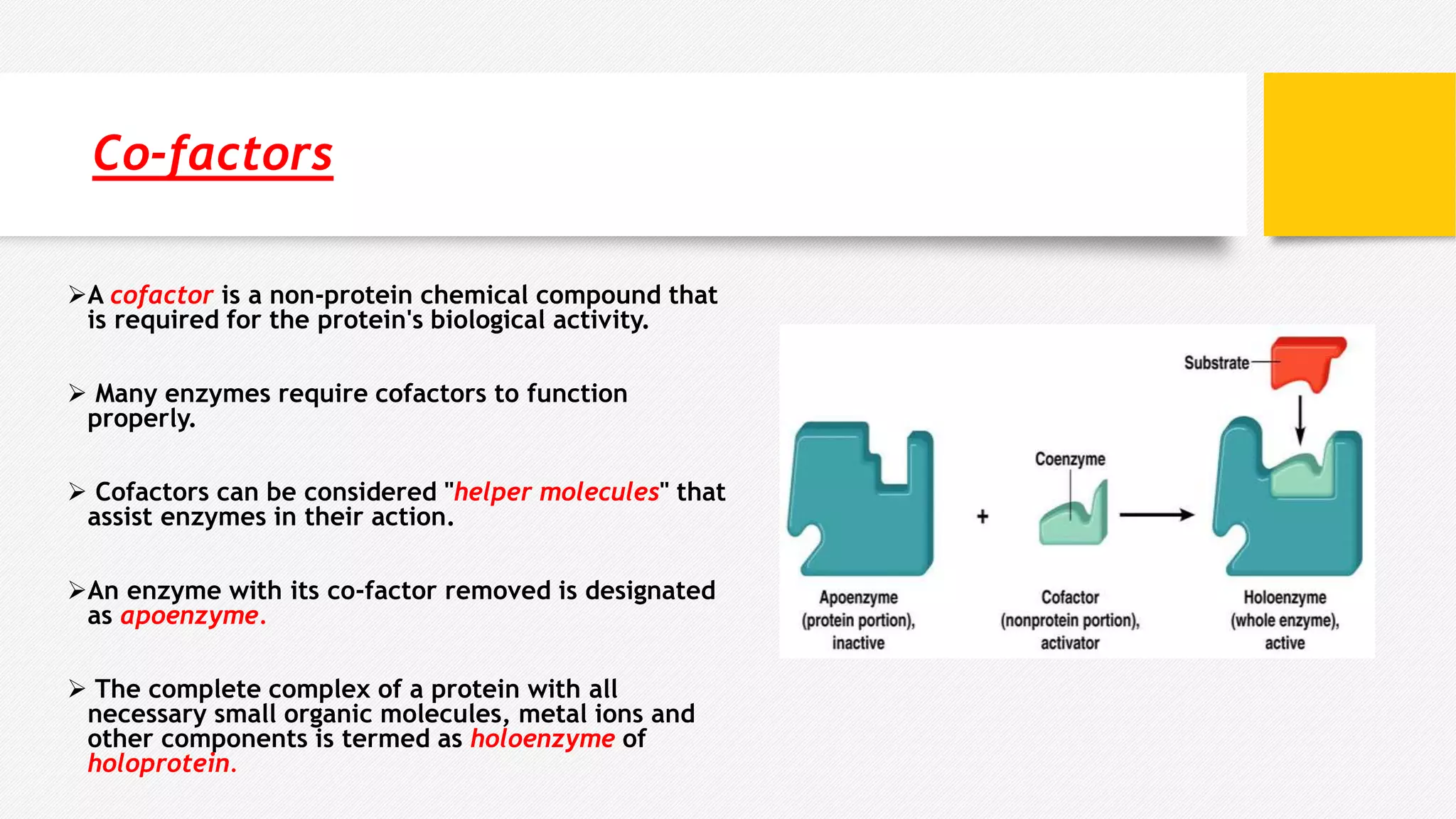
Enzymes are biological catalysts that speed up biochemical reactions. They have tertiary or quaternary protein structures that form an active site pocket, occupying less than 5% of the enzyme's surface area. The active site binds substrates and contains residues that facilitate reactions. Some enzymes also require cofactors to function. Substrates are molecules acted upon by enzymes to produce products. Intracellular enzymes function inside cells, while extracellular enzymes function outside cells like digestive enzymes.