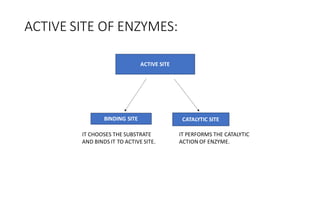
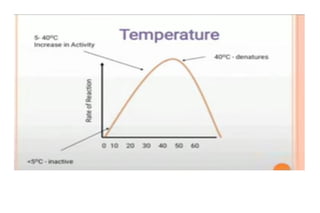
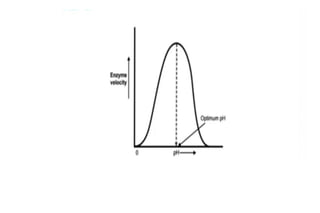
Enzymes are made up of proteins and cofactors. Cofactors include coenzymes, which are loosely bound organic molecules, and cofactors, which can be either tightly or loosely bound inorganic ions that help bind the enzyme and substrate. The active site of an enzyme contains the binding site and catalytic site - the binding site chooses and attaches the substrate, while the catalytic site carries out the chemical reaction. The rate of enzyme-catalyzed reactions is affected by temperature and pH - most enzymes function best within a limited temperature and pH range, and outside that range the enzyme can denature.