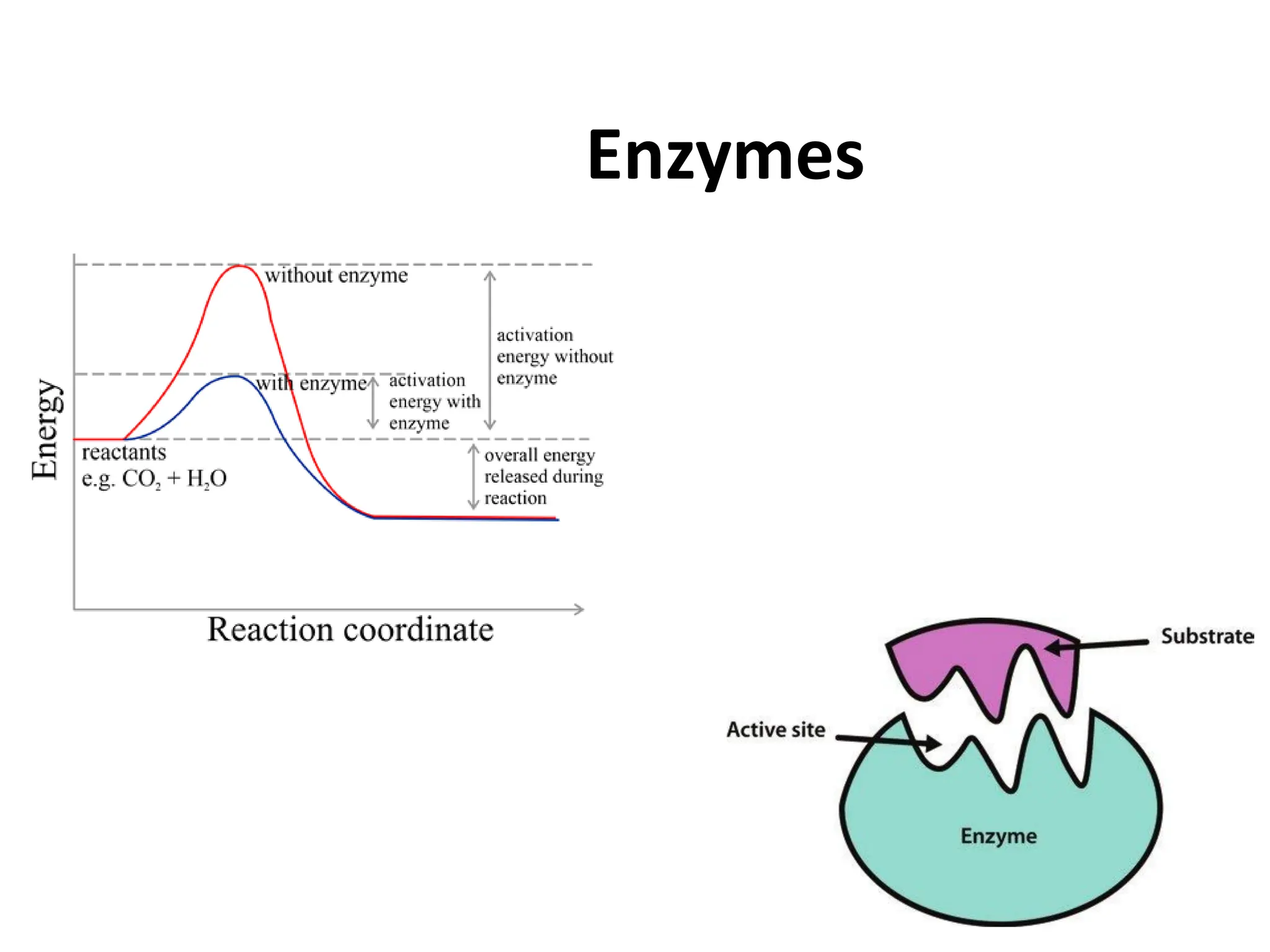
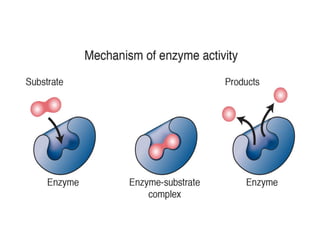
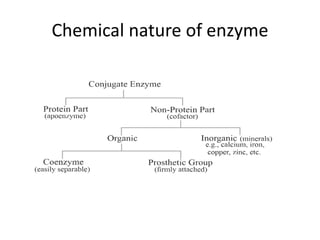
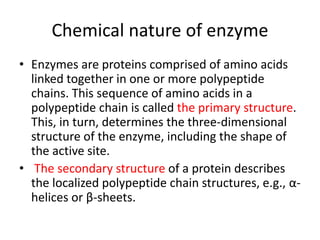
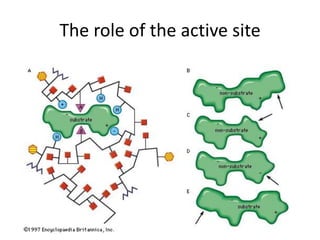
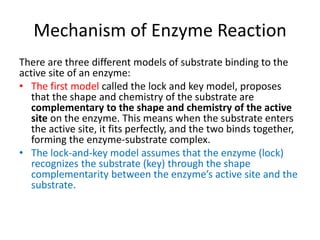
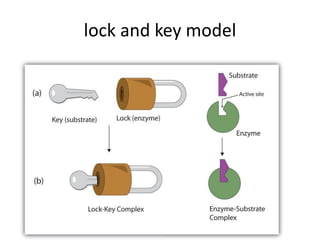
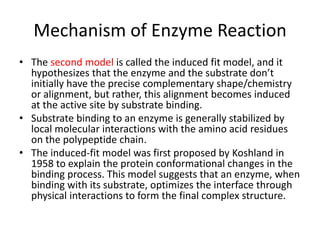
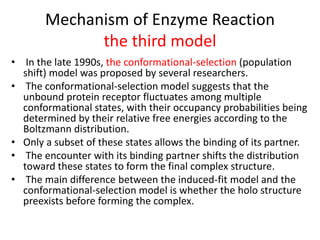
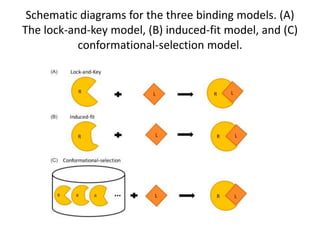
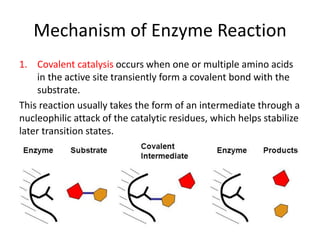
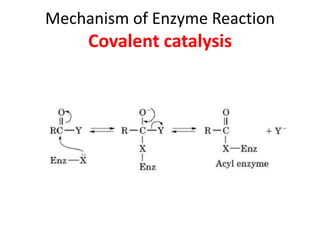
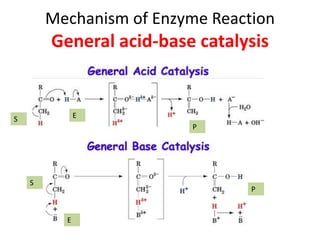
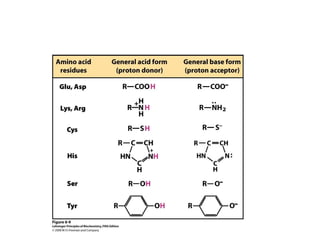
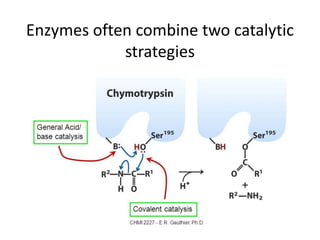
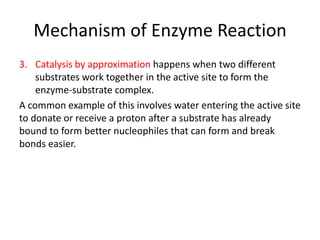
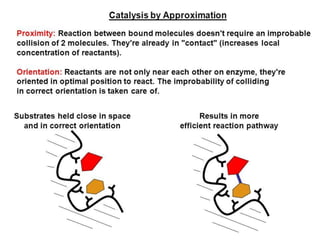
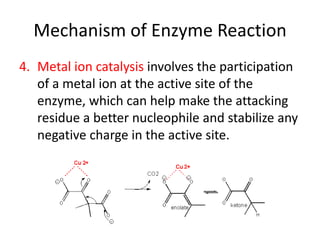
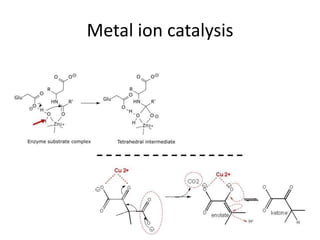
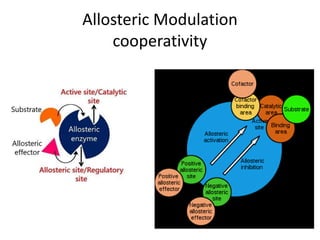
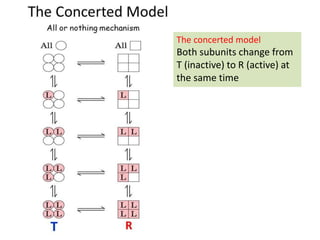
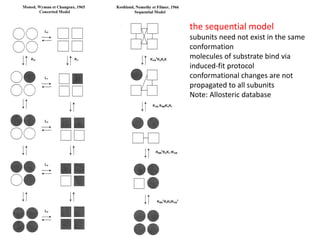
Enzymes are biological catalysts, primarily proteins that facilitate and accelerate chemical reactions by decreasing activation energy through specific binding at their active sites. They are classified into six functional categories based on the types of reactions they catalyze, such as hydrolases and transferases. The mechanisms of enzyme activity include different models of substrate binding and various catalytic strategies, including covalent and metal ion catalysis, along with concepts of allosteric modulation and cooperativity among subunits.