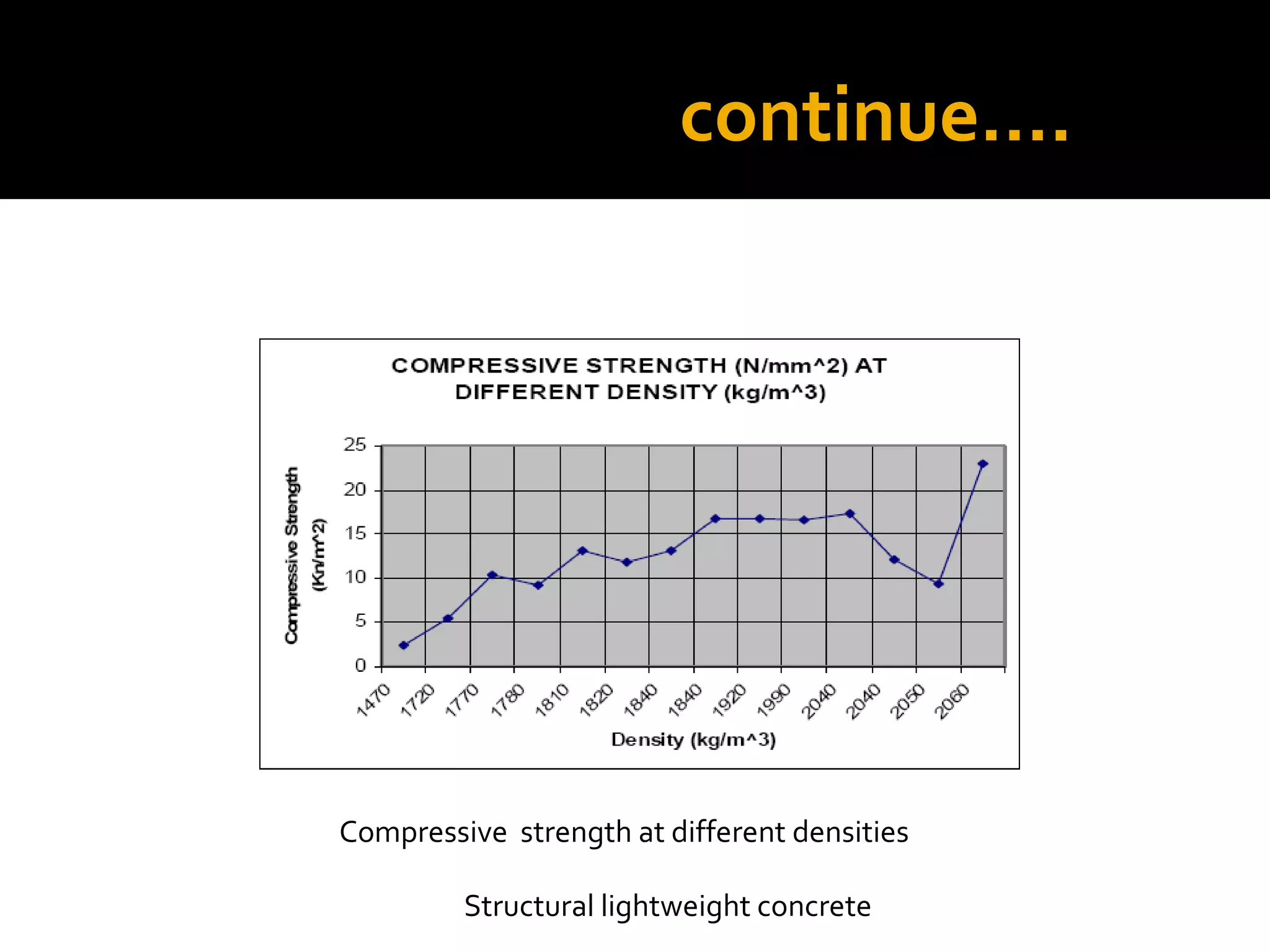
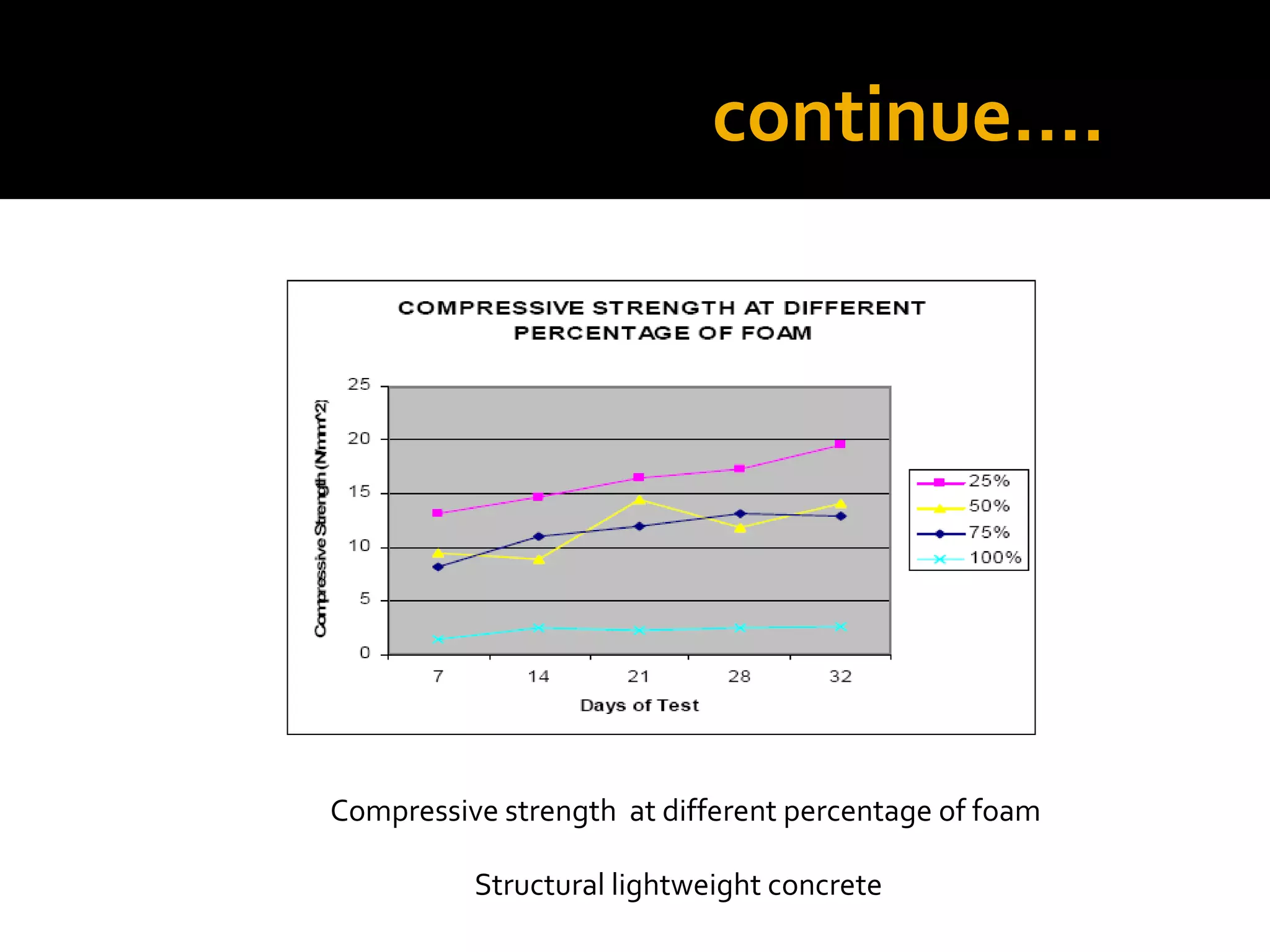
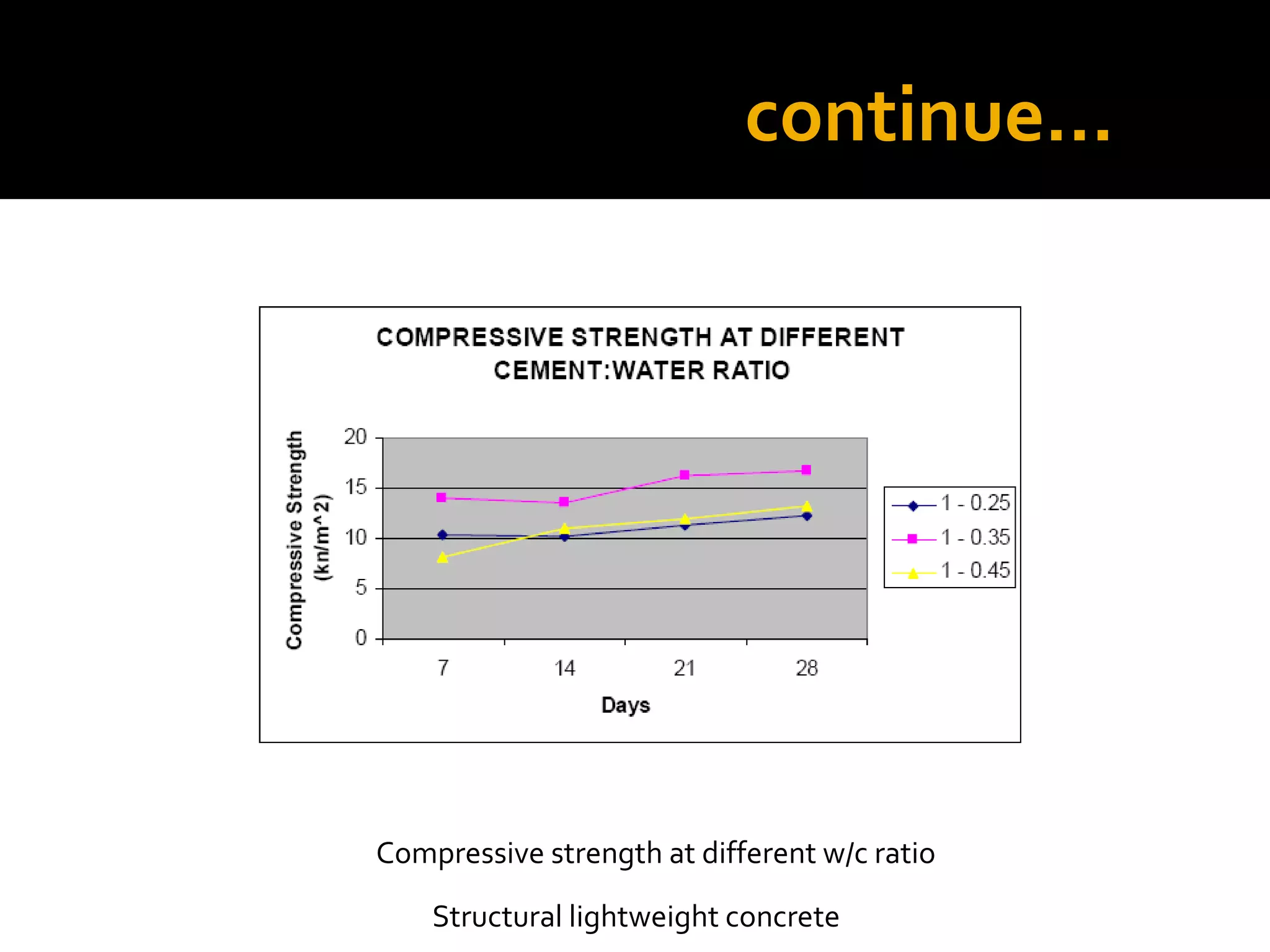
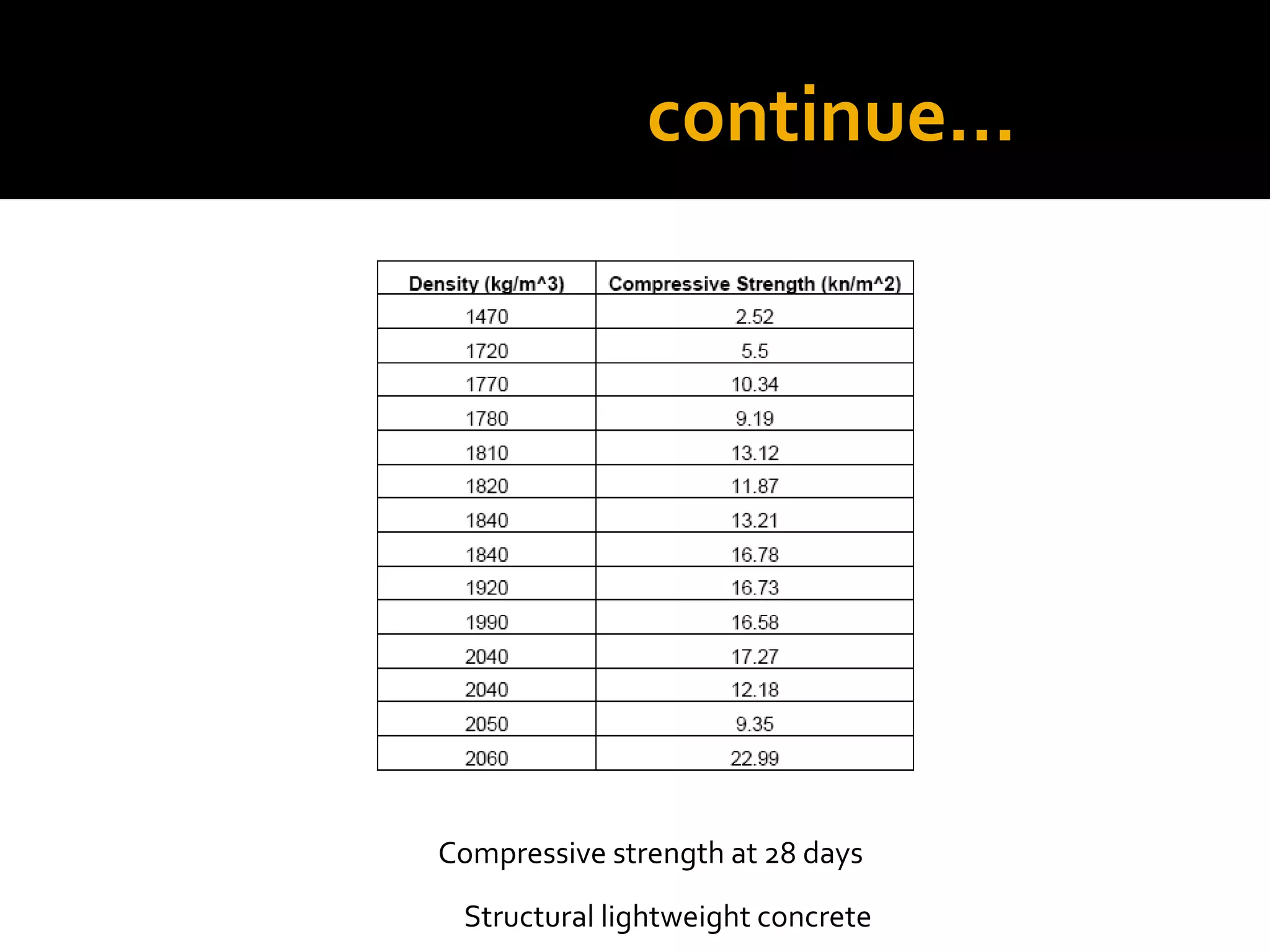
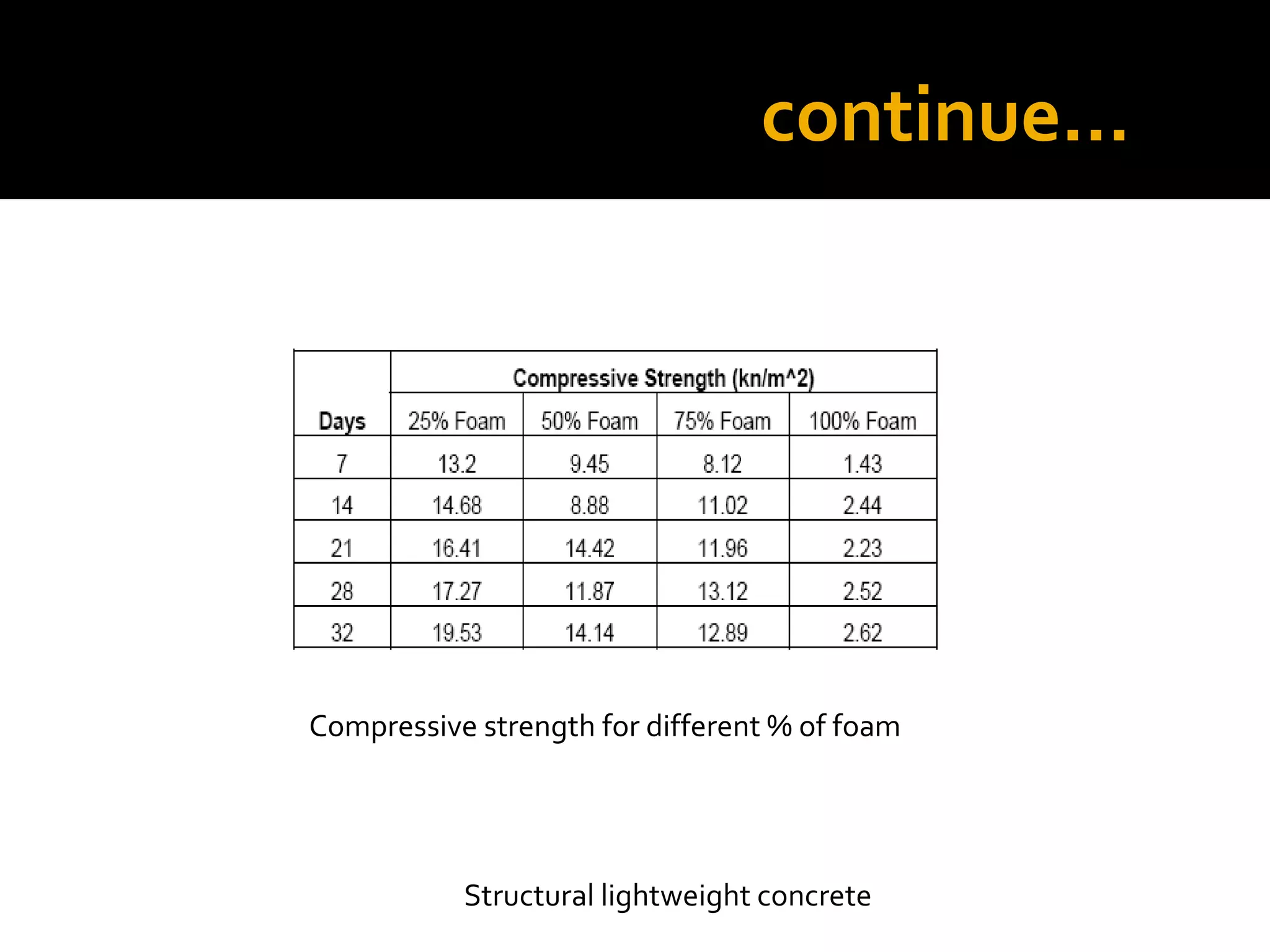
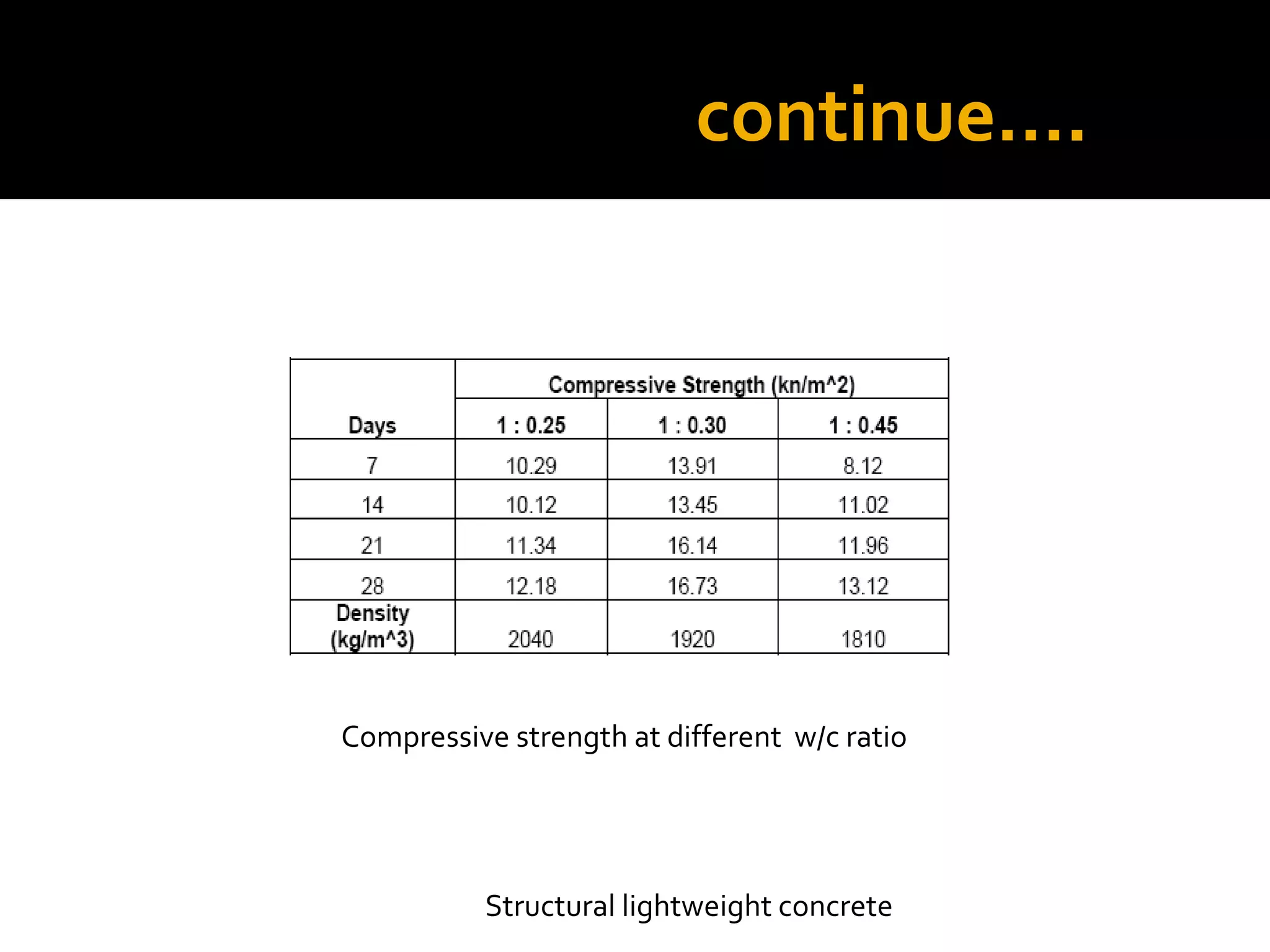
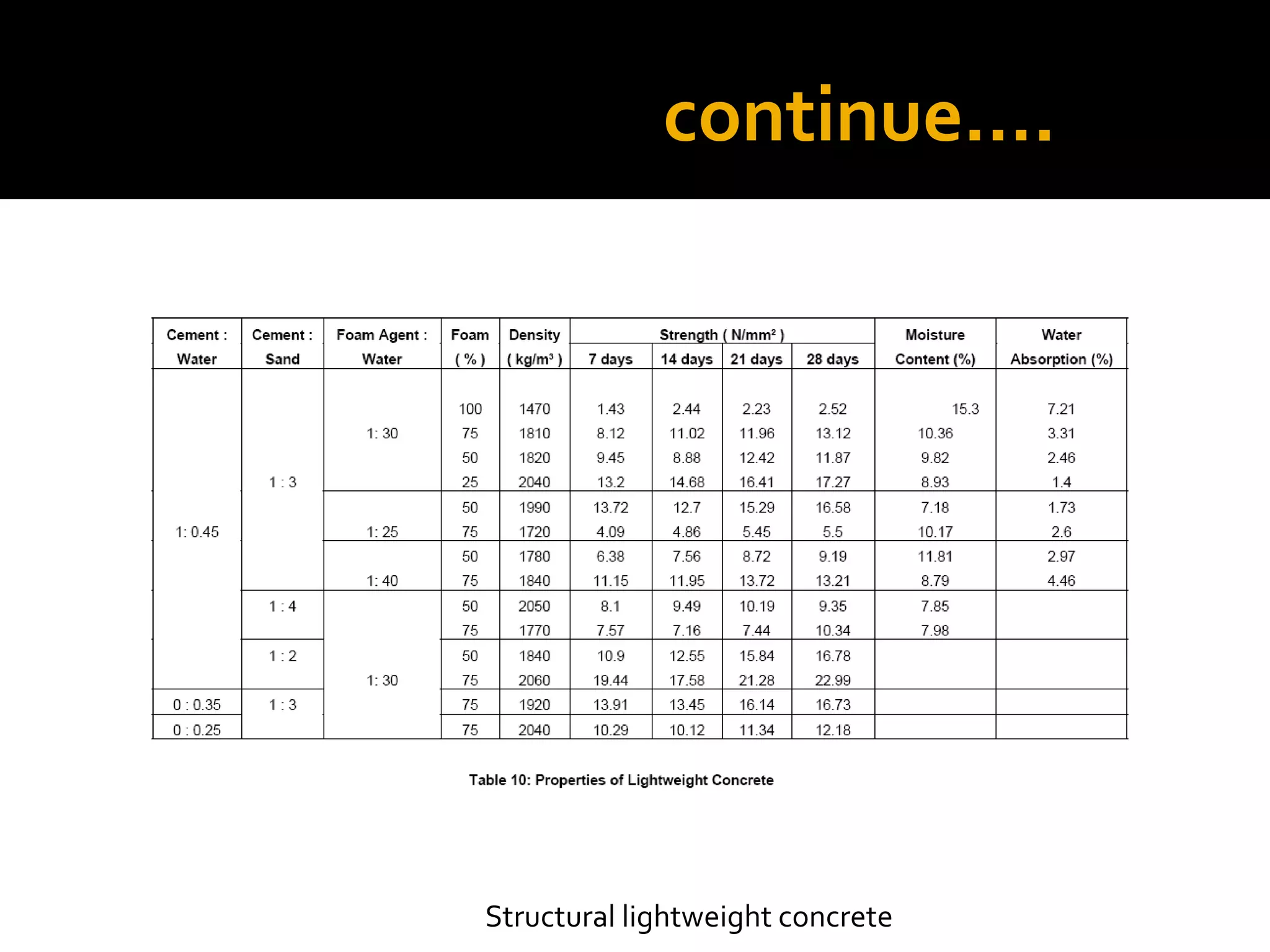
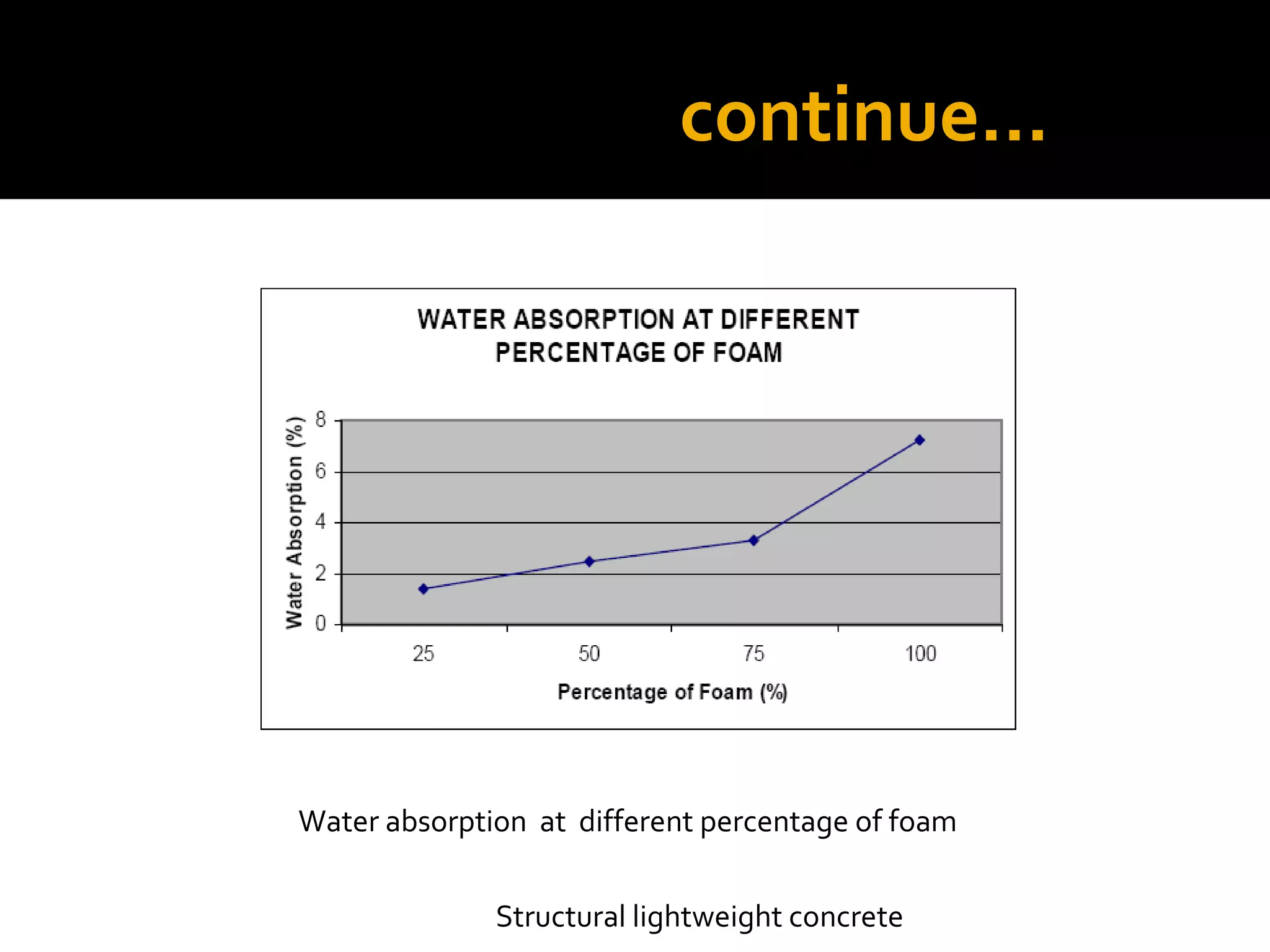
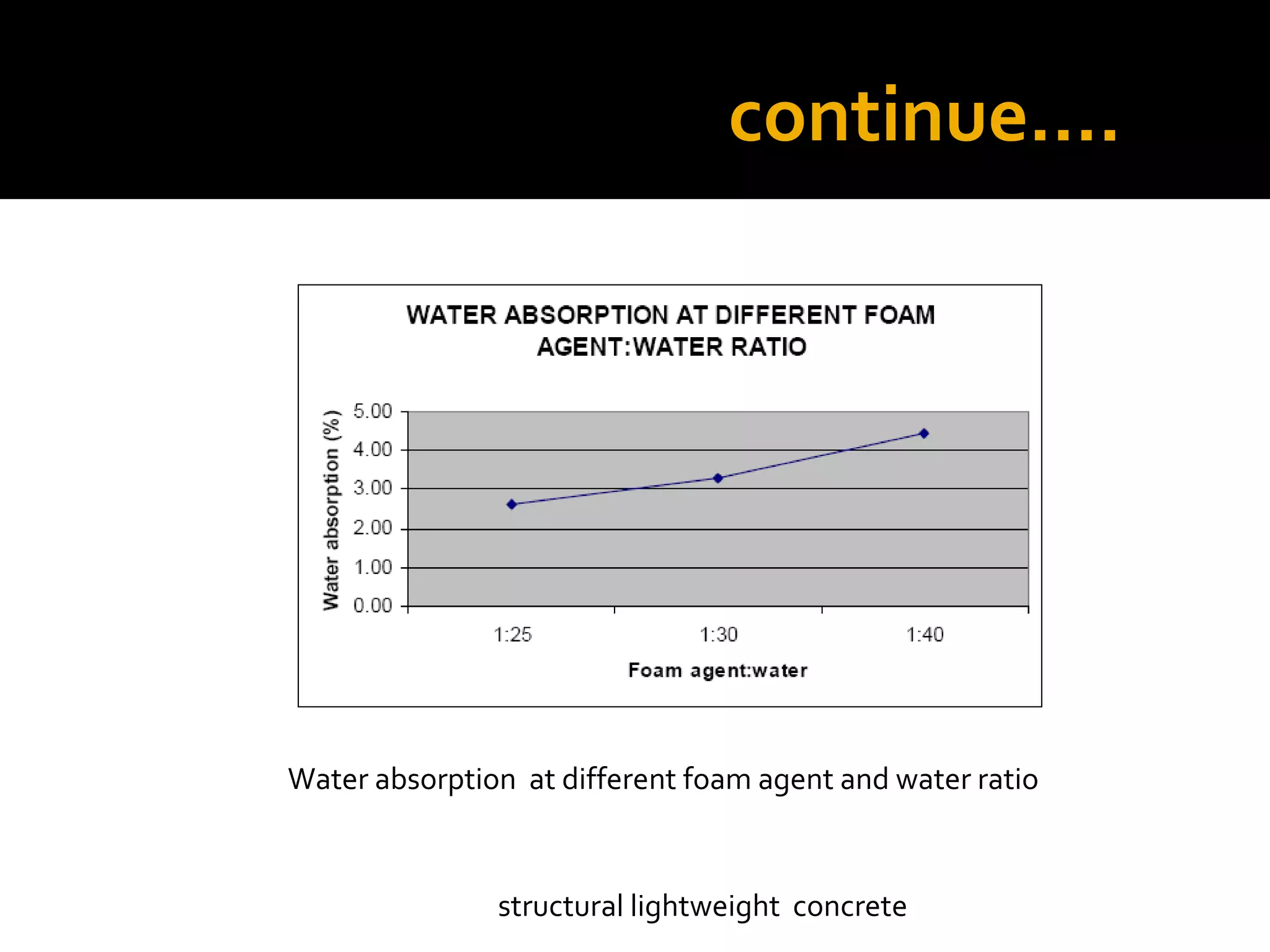
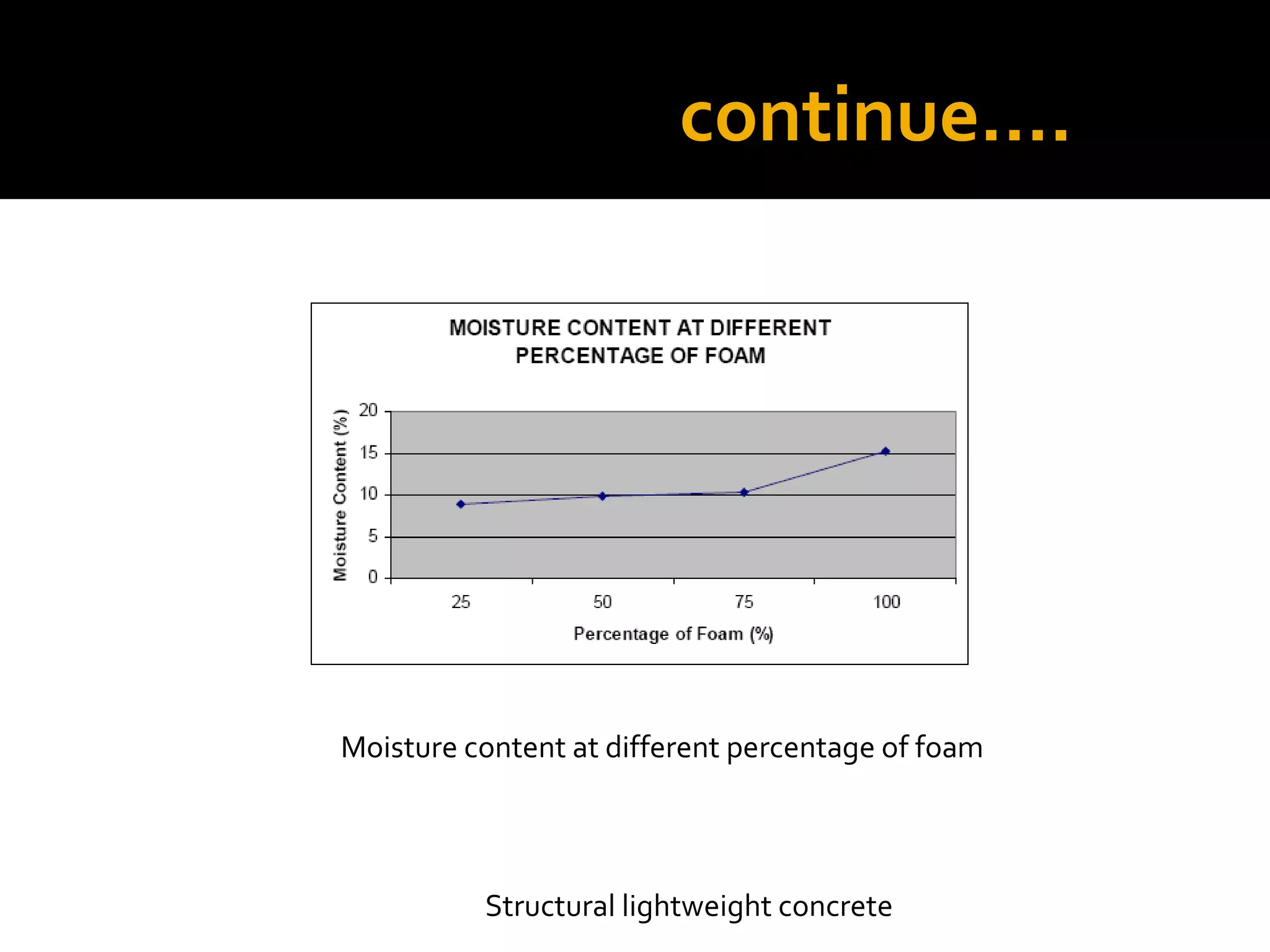
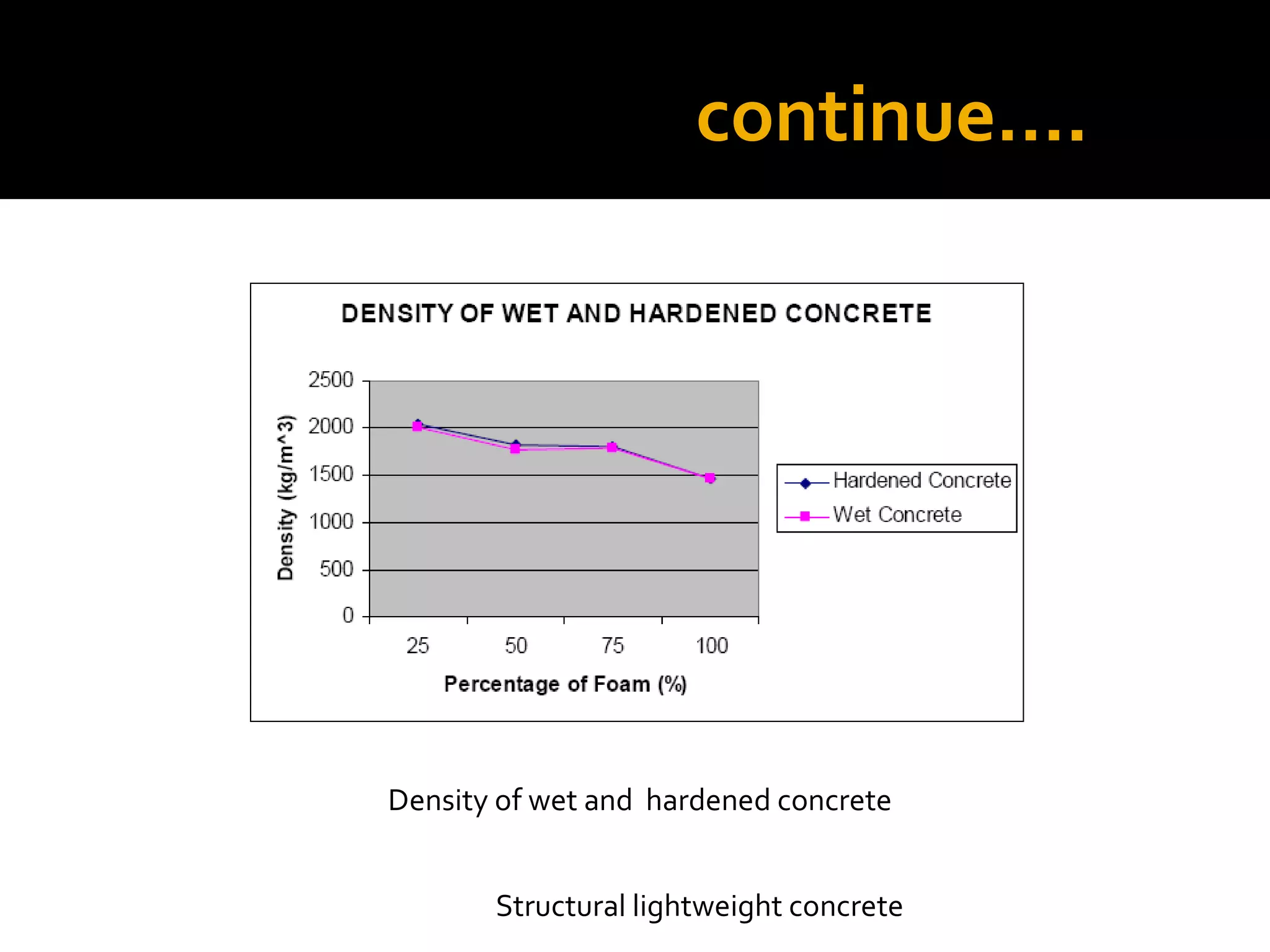
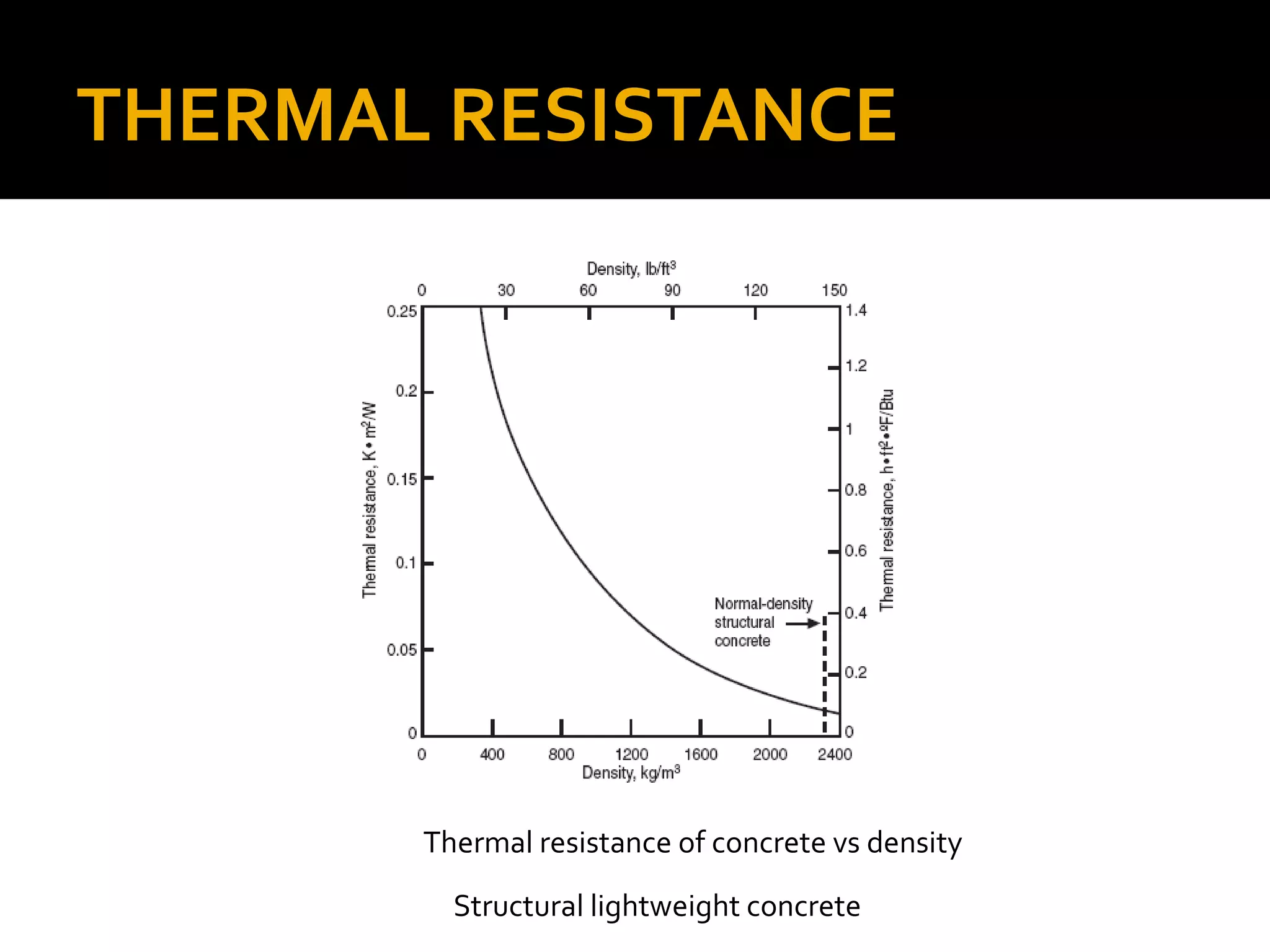
This document discusses structural lightweight concrete. It begins by defining lightweight concrete and noting its lighter weight compared to conventional concrete. It then discusses properties like compressive strength and water absorption tested at different densities, foam percentages, and water-cement ratios. Applications include construction, vessels, and roof decks. Advantages include reduced weight and transportation costs, while disadvantages include sensitivity to water and difficulty in placement. A case study examines the Wellington Stadium project in New Zealand, where lightweight concrete allowed rapid construction in a seismic area with poor foundation conditions.