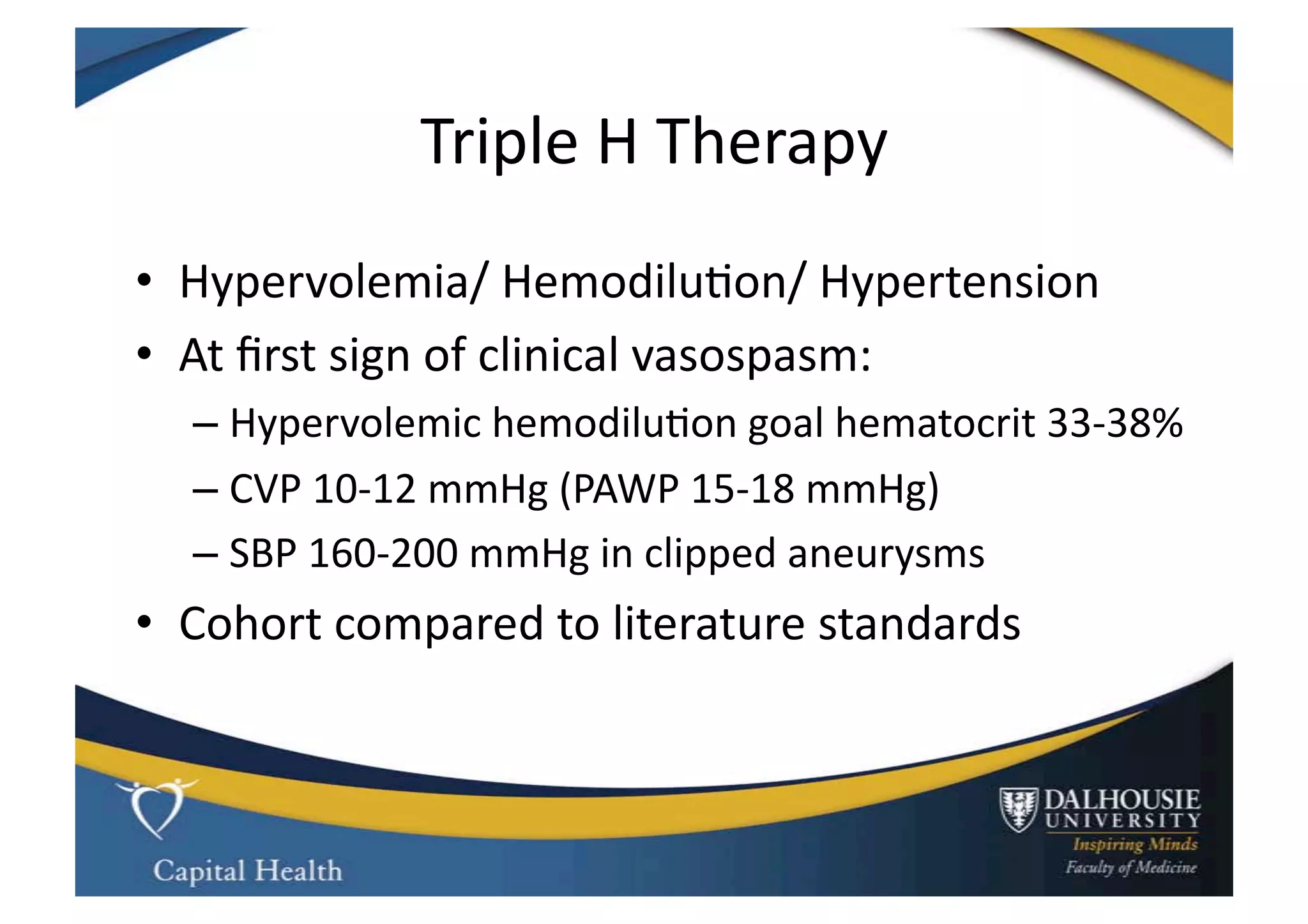
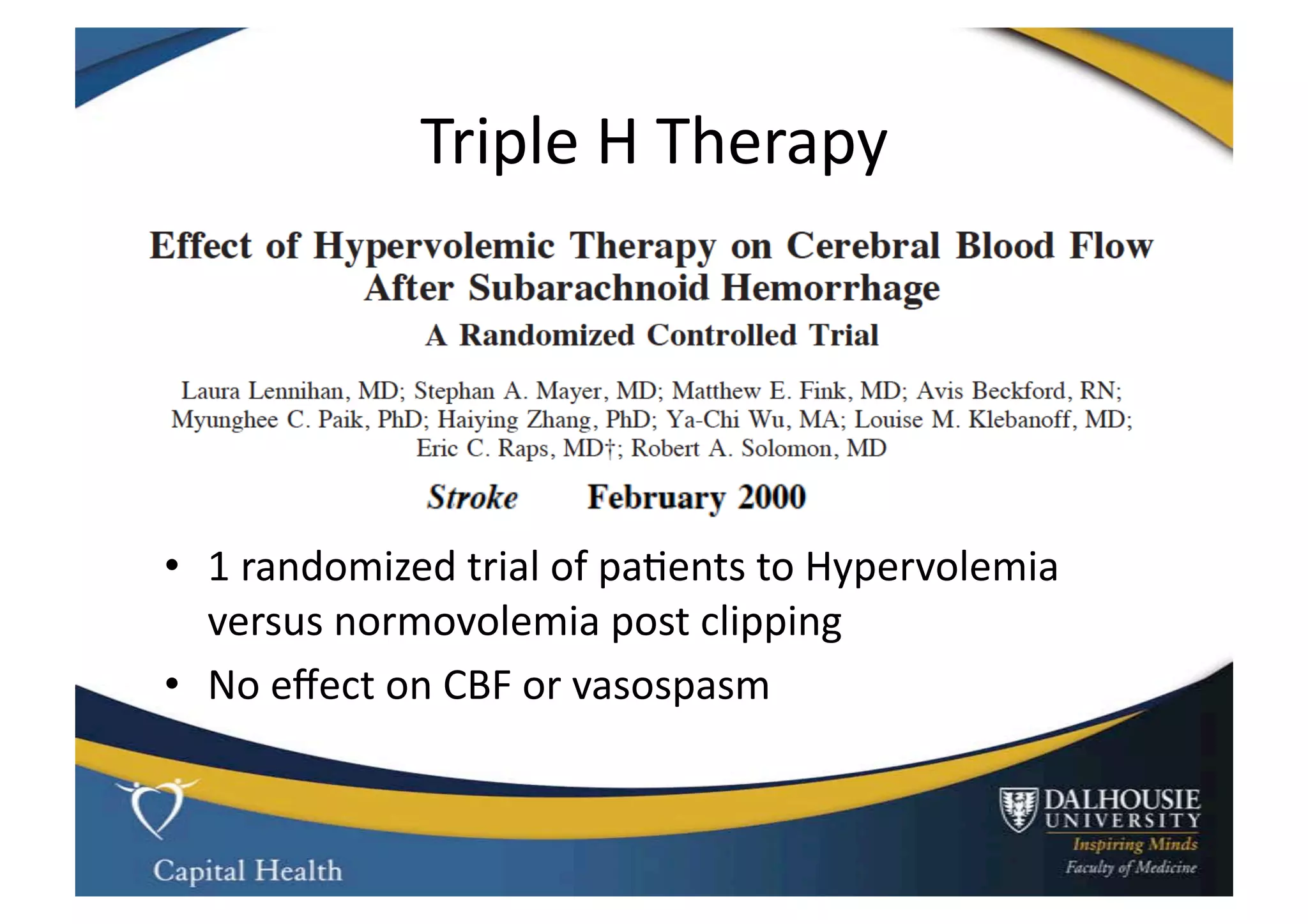
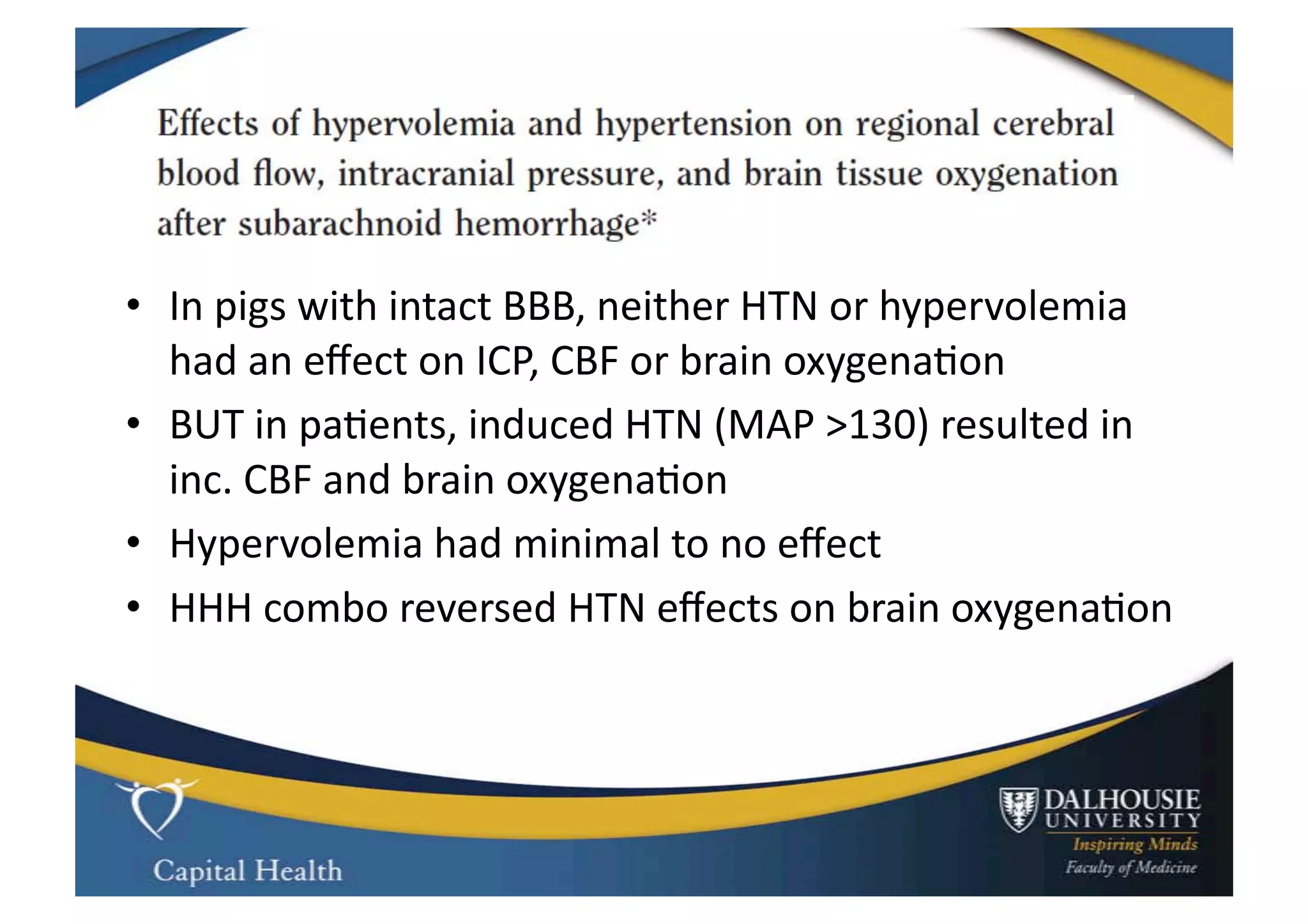
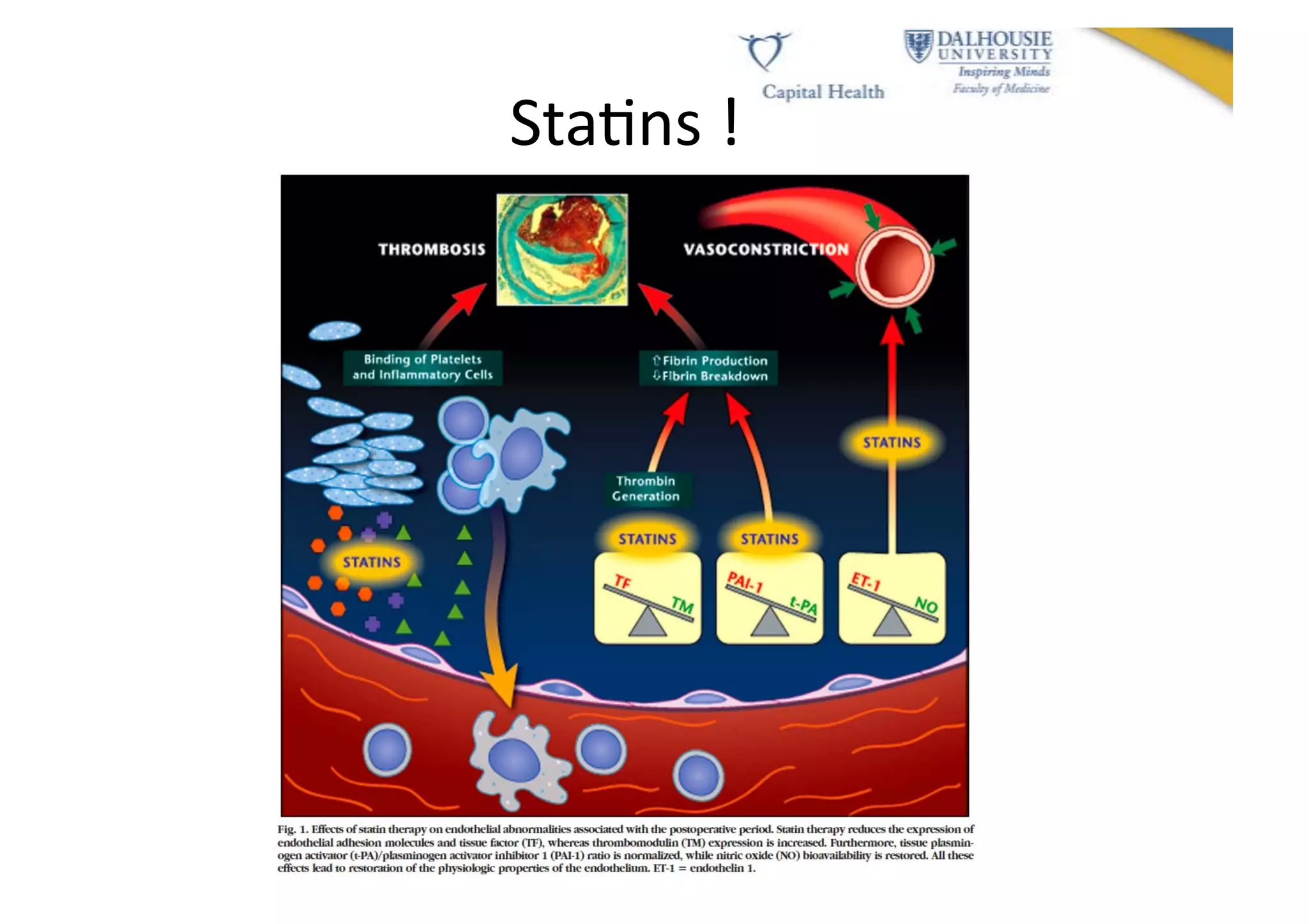
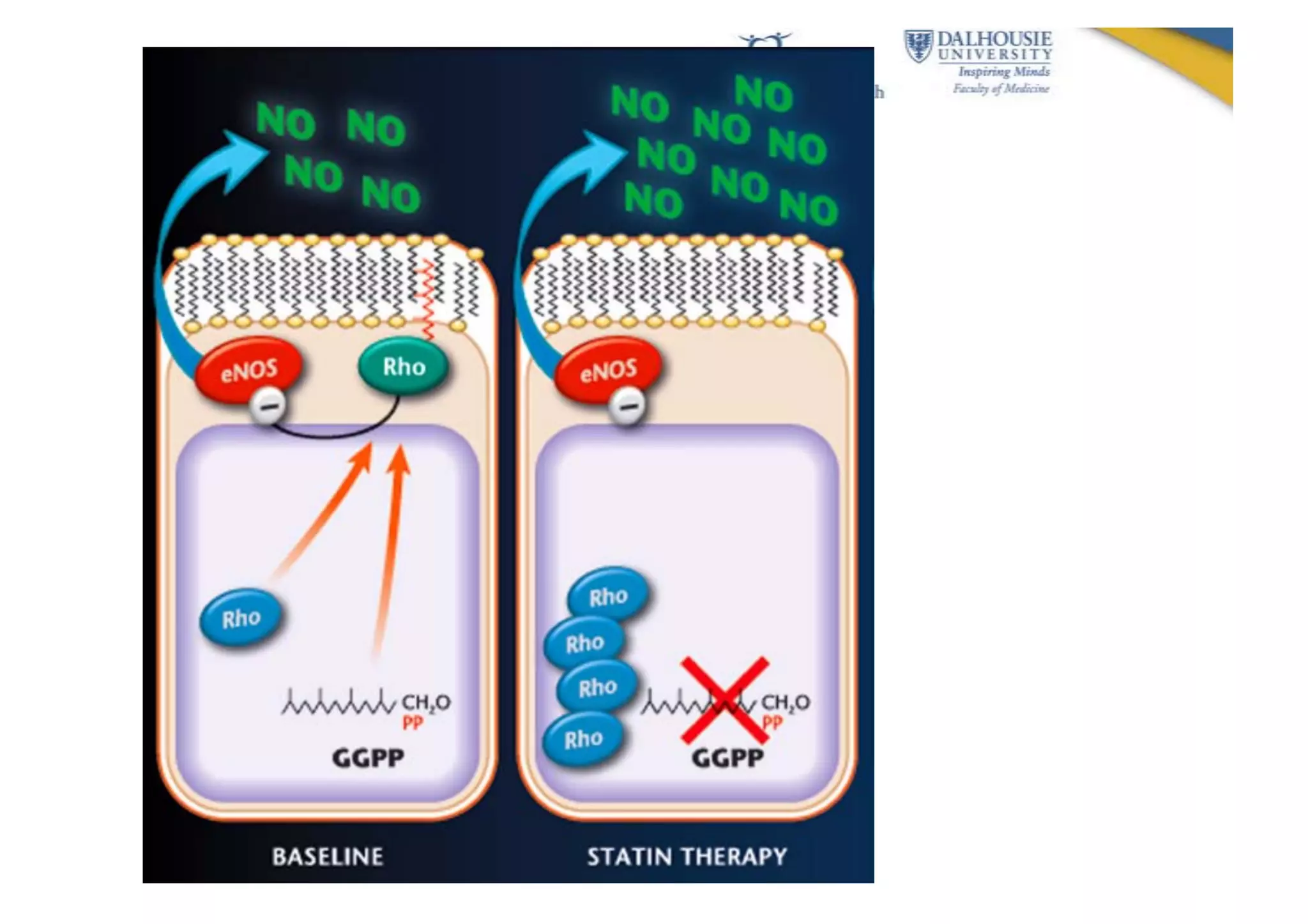
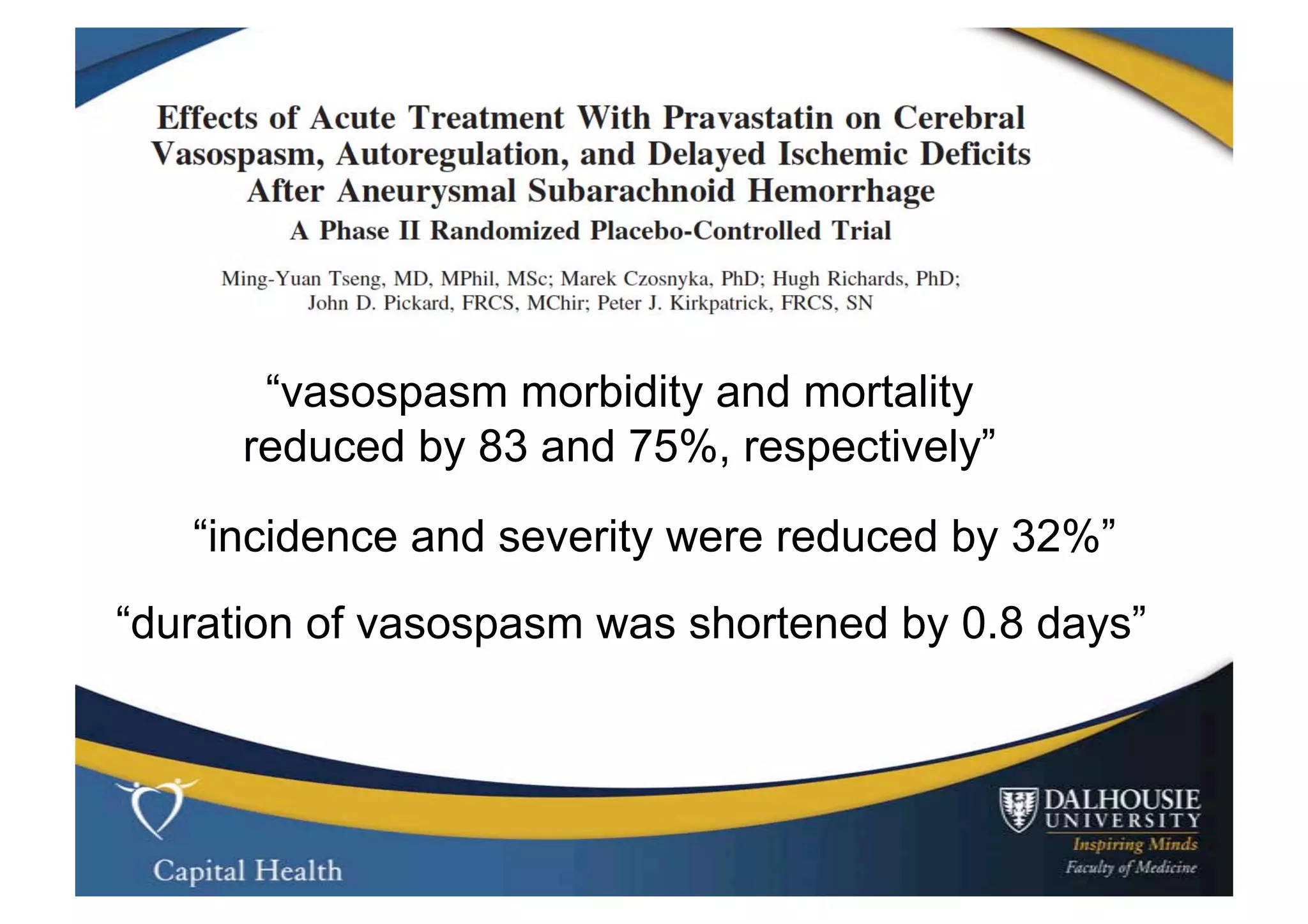
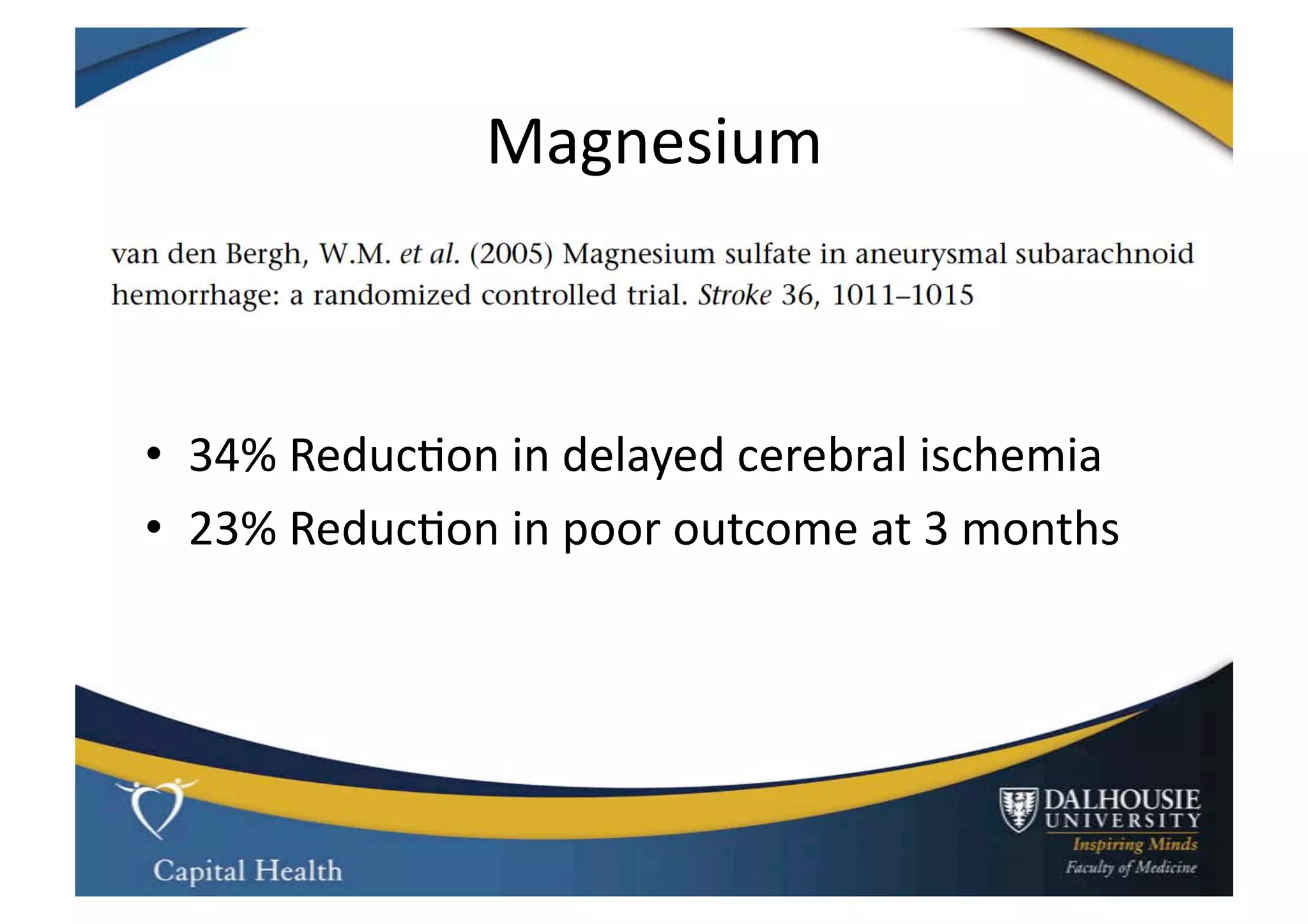
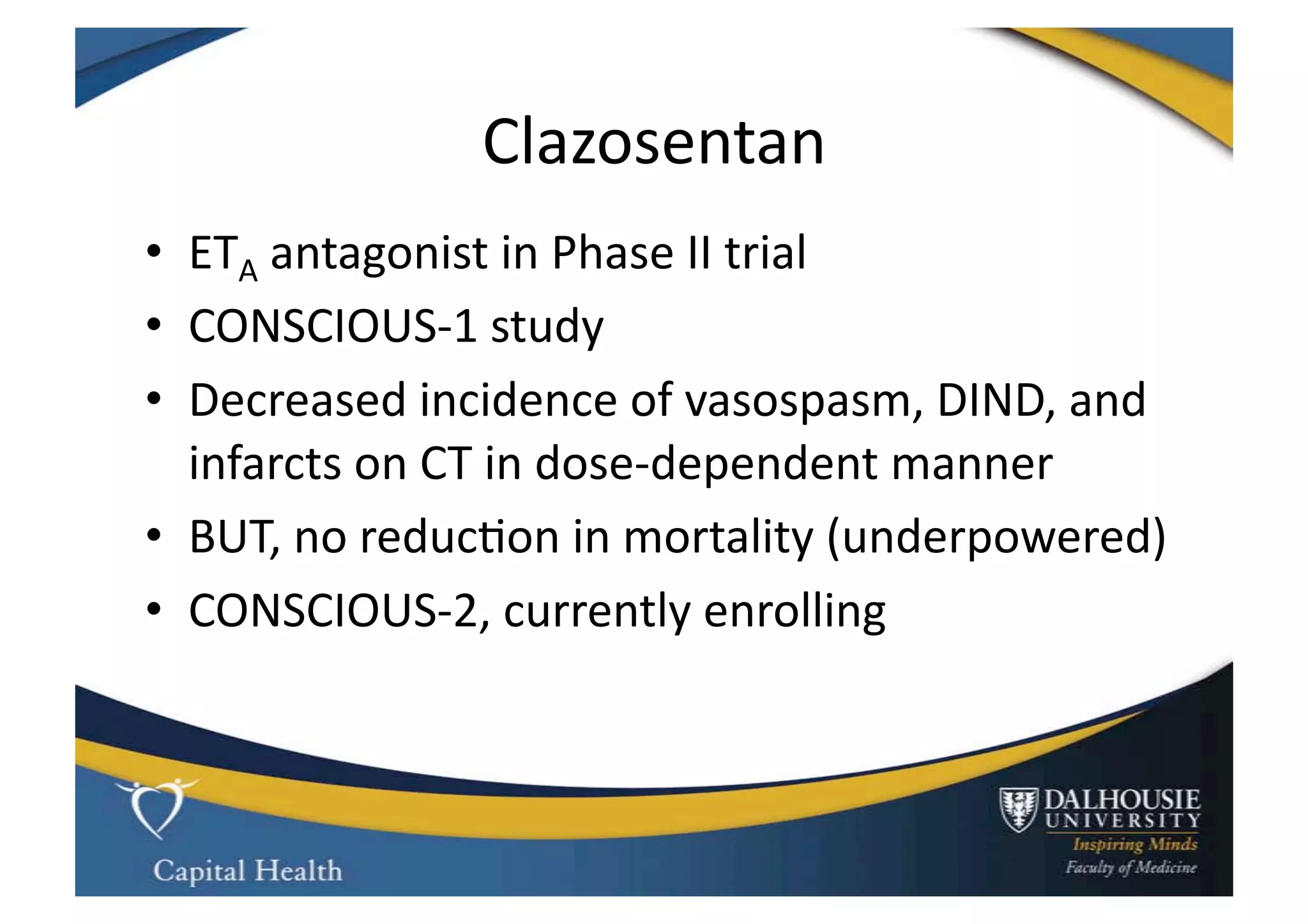
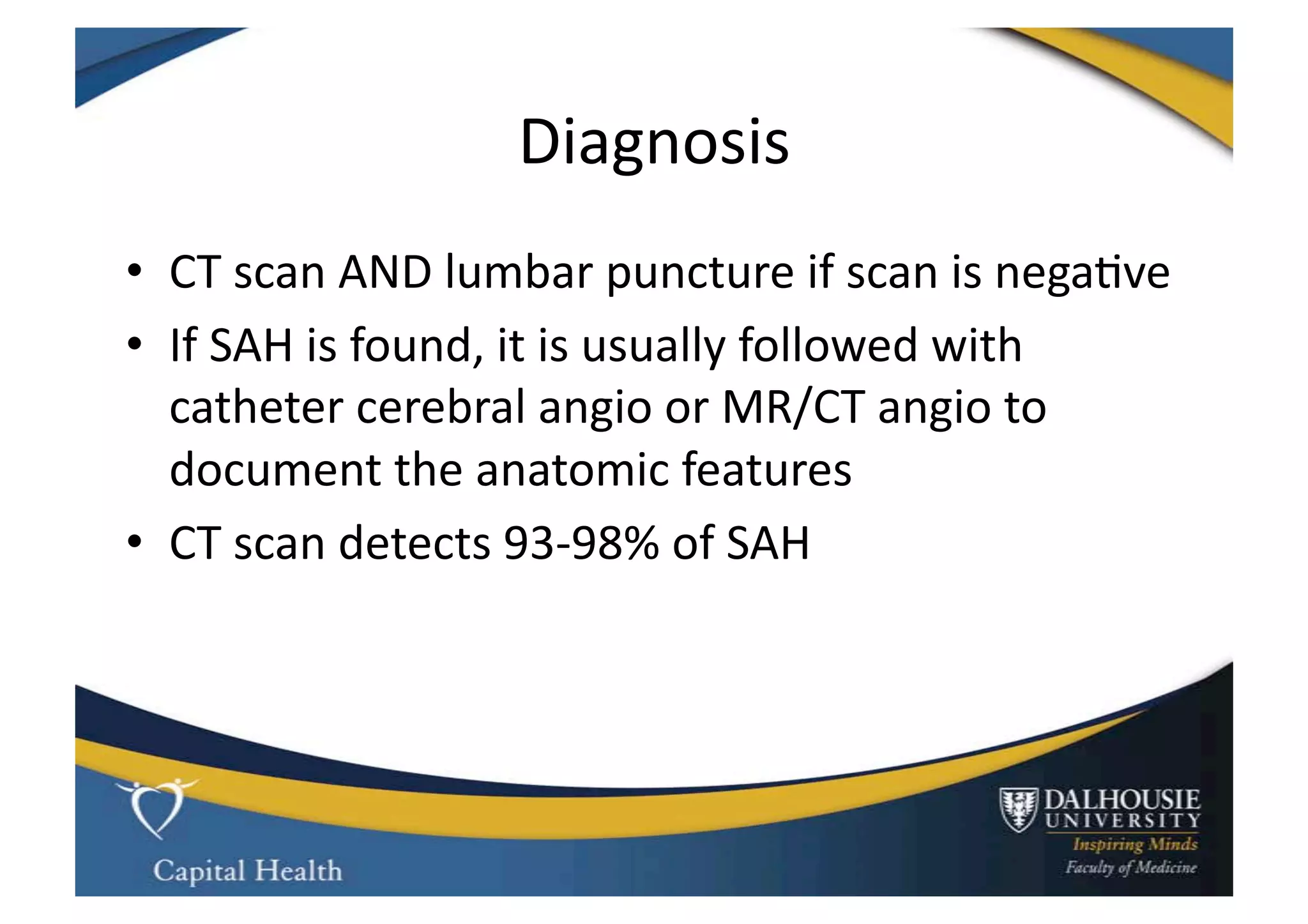
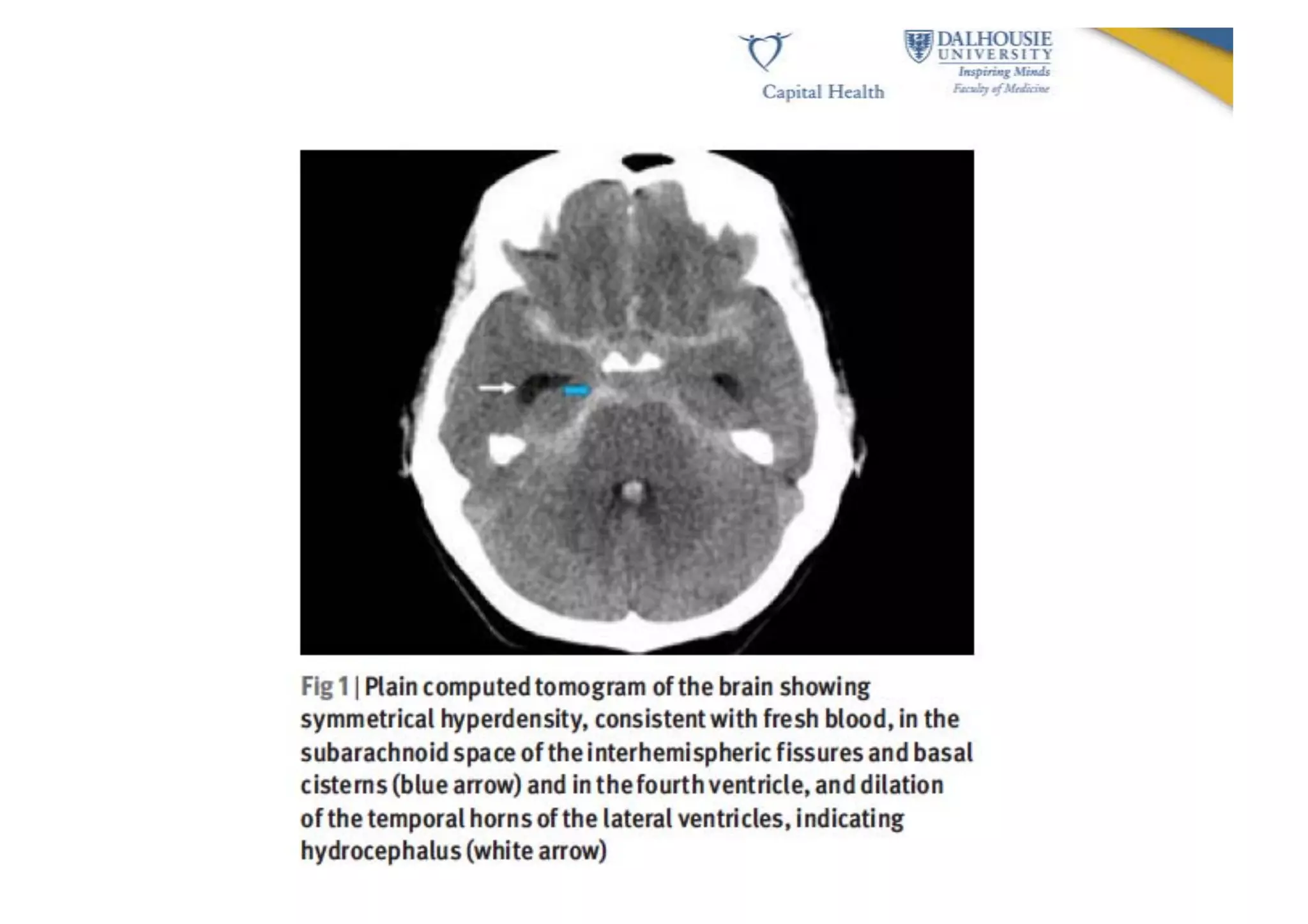
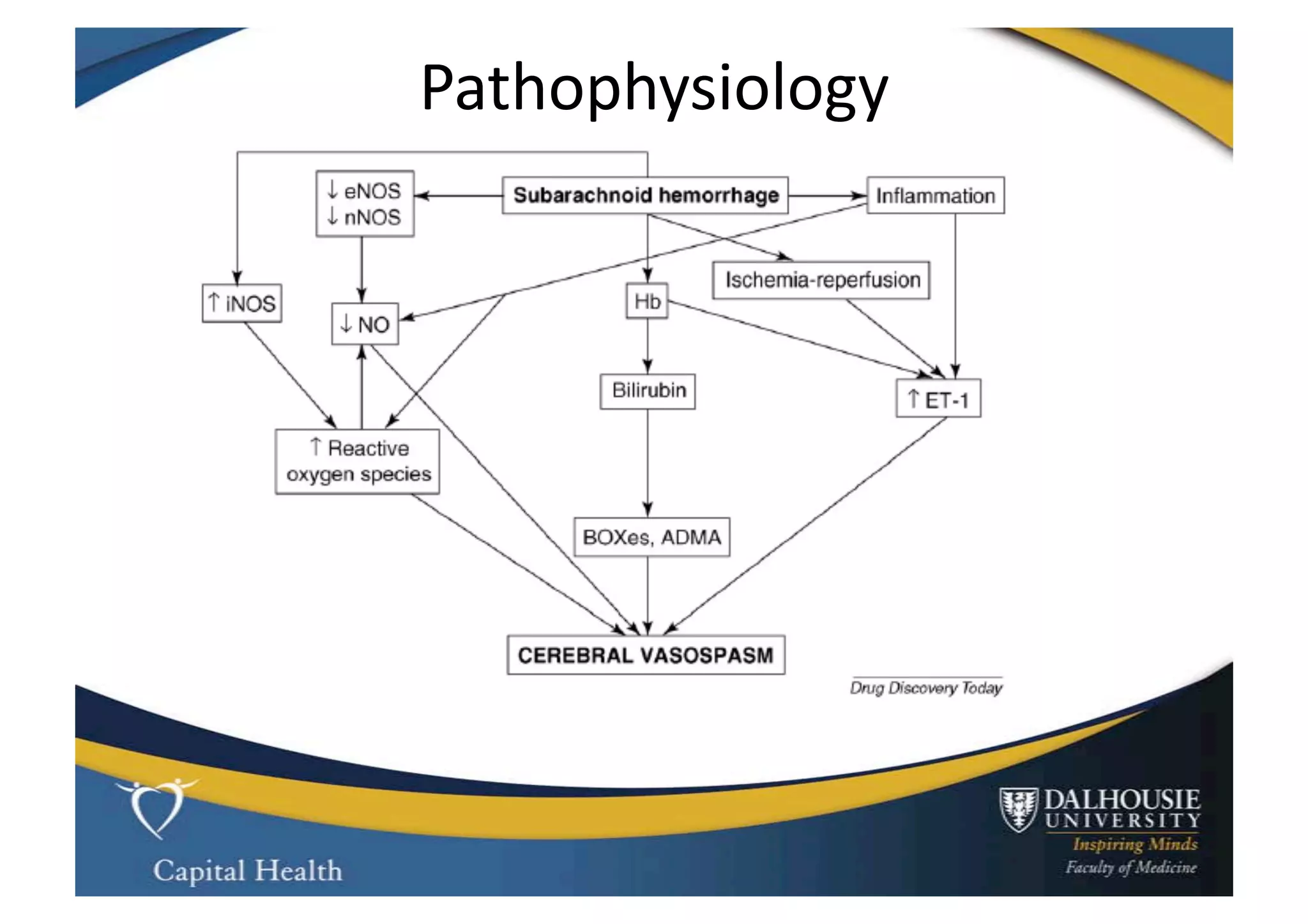
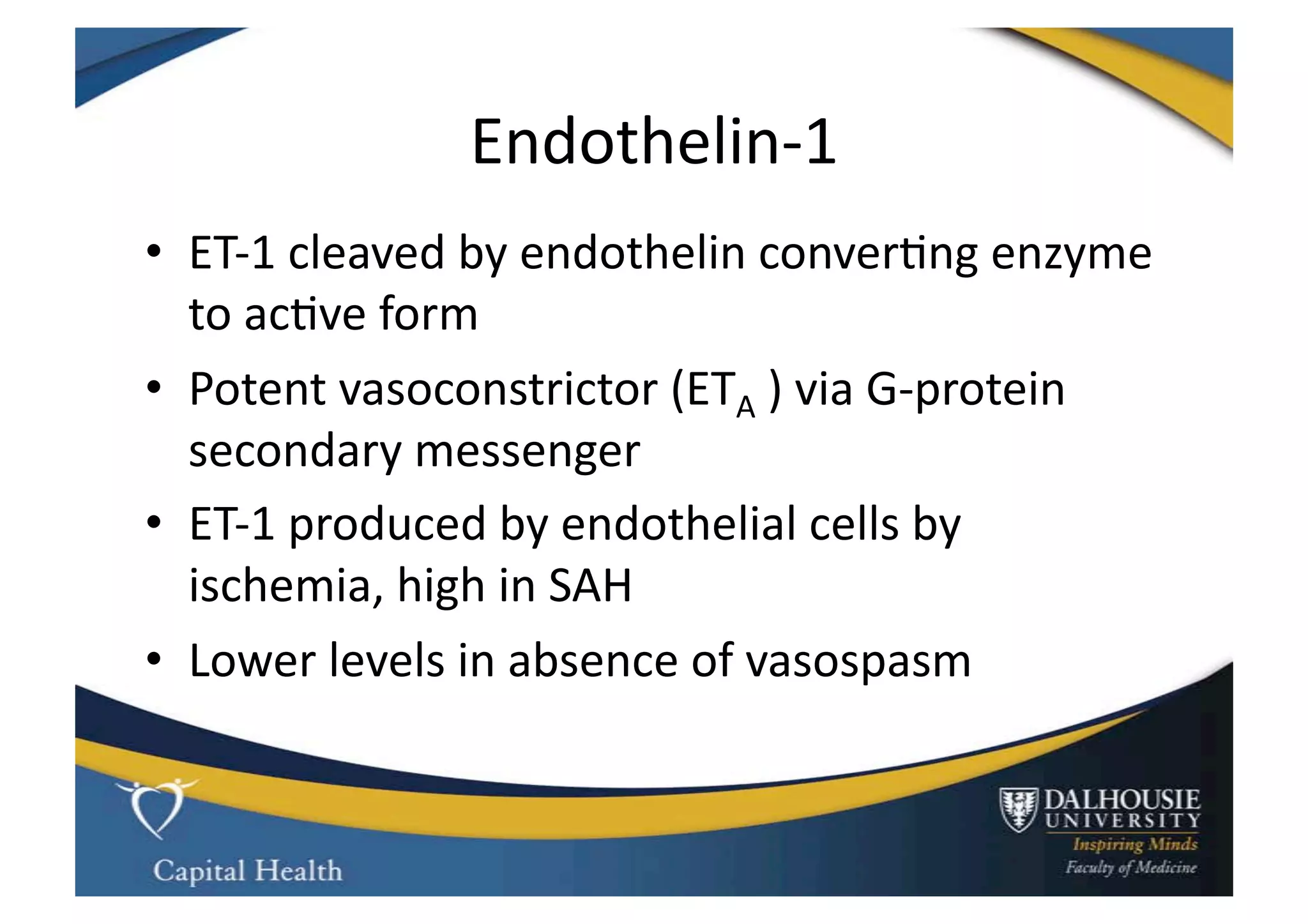
This document discusses subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH) and vasospasm, which is a common complication of SAH. It provides an overview of the pathophysiology of SAH and vasospasm, involving factors such as nitric oxide, endothelin-1, and oxidative stress. Current standard therapies aim to prevent rebleeding and improve cerebral blood flow, but have limitations. Emerging therapies are being investigated to more effectively treat and prevent vasospasm.















![Standard
Therapy
• Preven9on
of
rebleed:
– by
securing
intracranial
aneurysm
within
24-‐48h
• Can
allow
SBP
to
rise
to
200
mmHg
• Avoid:
– hypovolemia,
hypotension,
anemia,
fever
and
increased
ICP
• Nimodipine
60
mg
Q4h
PO
for
21
days
– IV
form
in
Europe
but
no
difference
in
clinical
effect
[Kronvall
2009]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sahandvasospasm-100119150702-phpapp02/75/Subarachnoid-hemorrhage-and-Vasospasm-24-2048.jpg)