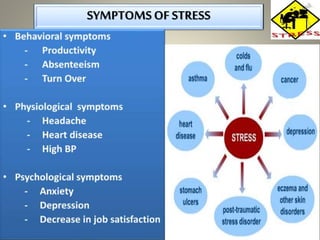
This document discusses stress, its causes, effects, and management. It begins by defining stress as the body's physical and emotional response to change. It then discusses the general adaptation syndrome and types of personalities (Type A vs. Type B) that are more prone to stress. Common stressors like life changes, trauma, conflicts are described. The effects of stress like burnout, behavioral changes, and physical symptoms are explained. Finally, it provides strategies for managing stress through healthy living, defense mechanisms, and addressing its causes.