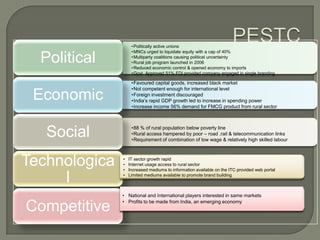
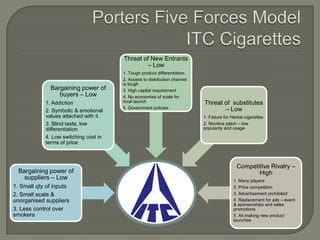
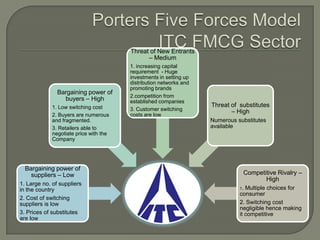
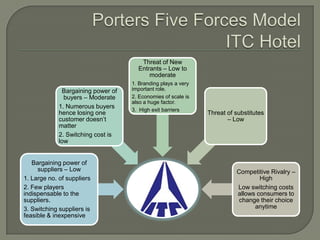
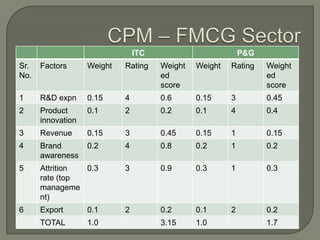
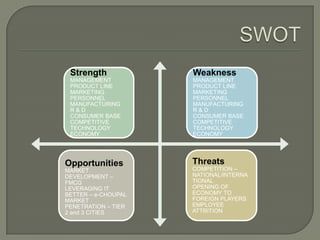
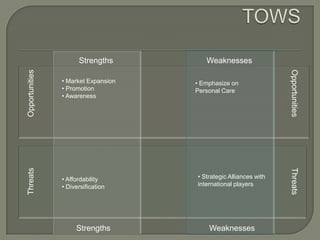
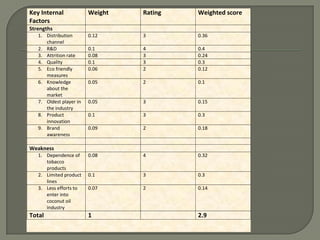
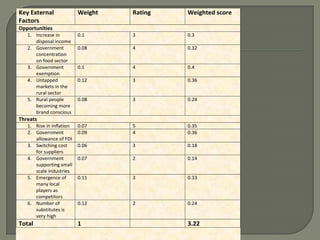
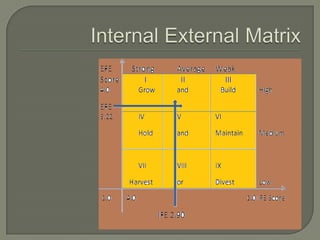
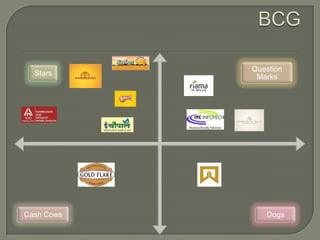
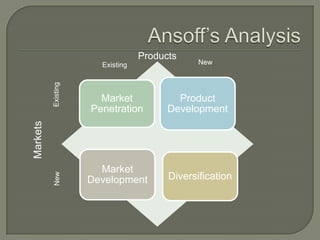
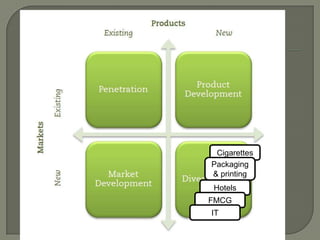
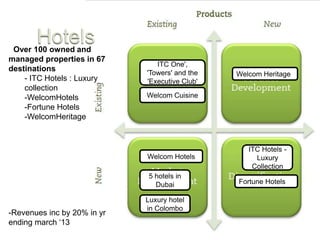
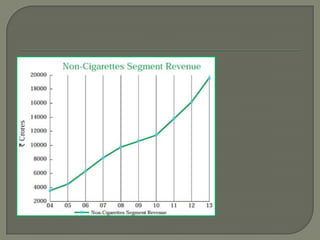
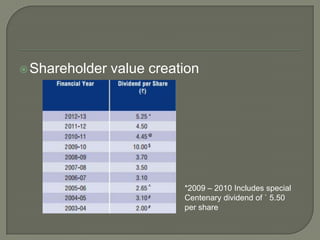
ITC has diversified from its origins in tobacco into various business segments including FMCG, hotels, paper, and IT. It has the largest distribution network in India. While still reliant on cigarettes, ITC is focusing on growing its non-cigarette businesses like FMCG which saw 15.7% revenue growth. ITC aims to leverage its distribution to become a major FMCG player. Further investments in areas like agriculture, R&D, and expanding markets can help ITC reduce reliance on cigarettes over time.