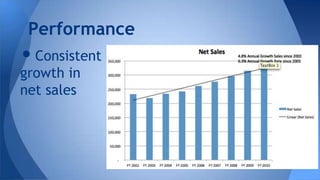
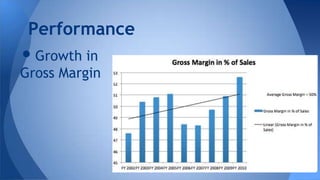
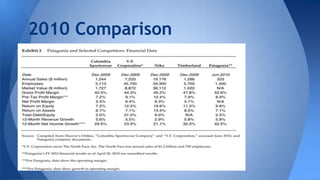
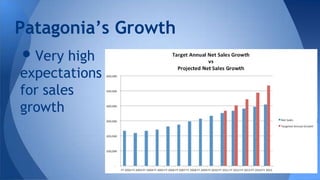
The document analyzes Patagonia's business evolution from its inception in 1957 to present, highlighting its growth strategies, environmental commitment, and competitive advantages in the outdoor apparel industry. It discusses the company's unique value proposition focusing on quality, sustainability, and innovation, which allows it to command premium prices in a highly competitive market. Additionally, it presents a SWOT analysis, addressing strengths such as environmental reputation and weaknesses like limited customer accessibility.