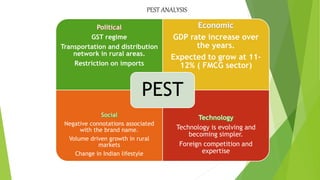
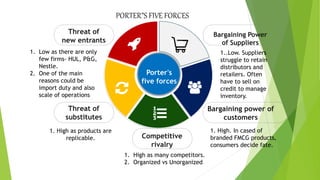
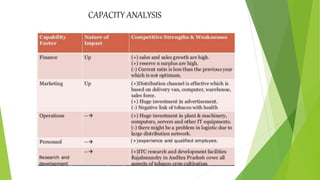
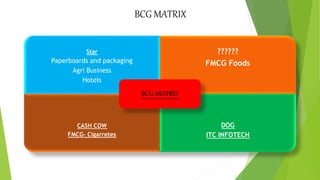
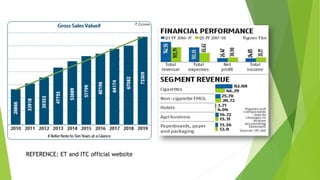
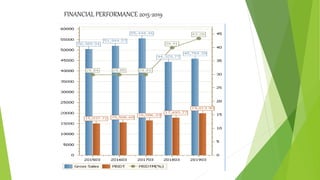
ITC Limited is an Indian conglomerate headquartered in Kolkata, West Bengal with a turnover of US$7.3 billion as of 2019. It employs over 30,000 people across various businesses including cigarettes, FMCG products, hotels, paper, and information technology. The document discusses ITC's history, financial performance from 2015-2019, strategies for expanding its FMCG portfolio through acquisitions and developing health and wellness products. It also analyzes ITC's business using Porter's five forces, BCG matrix, SWOT analysis and recommends investing in IT, using rural distribution, and further disinvesting from tobacco.