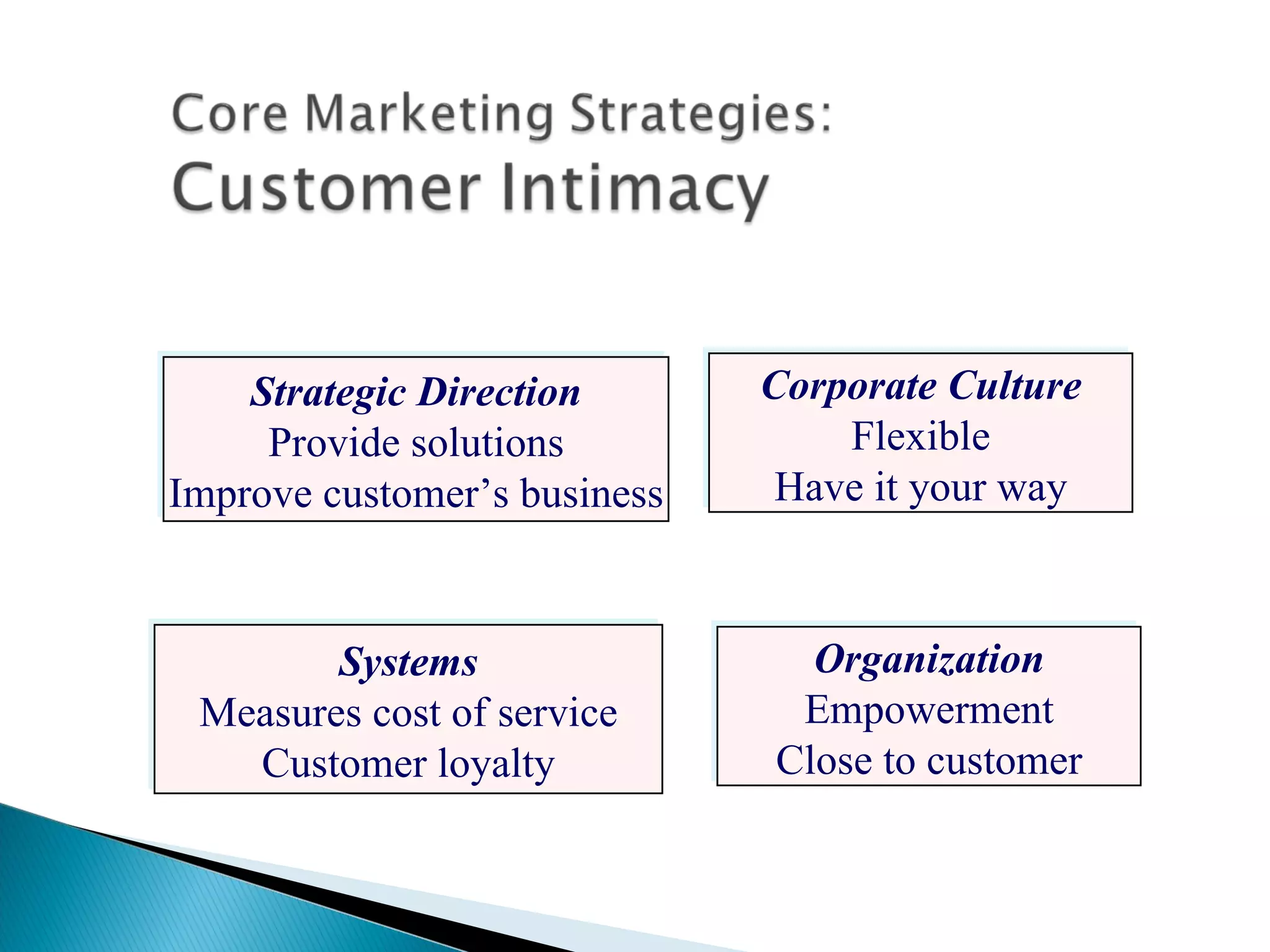
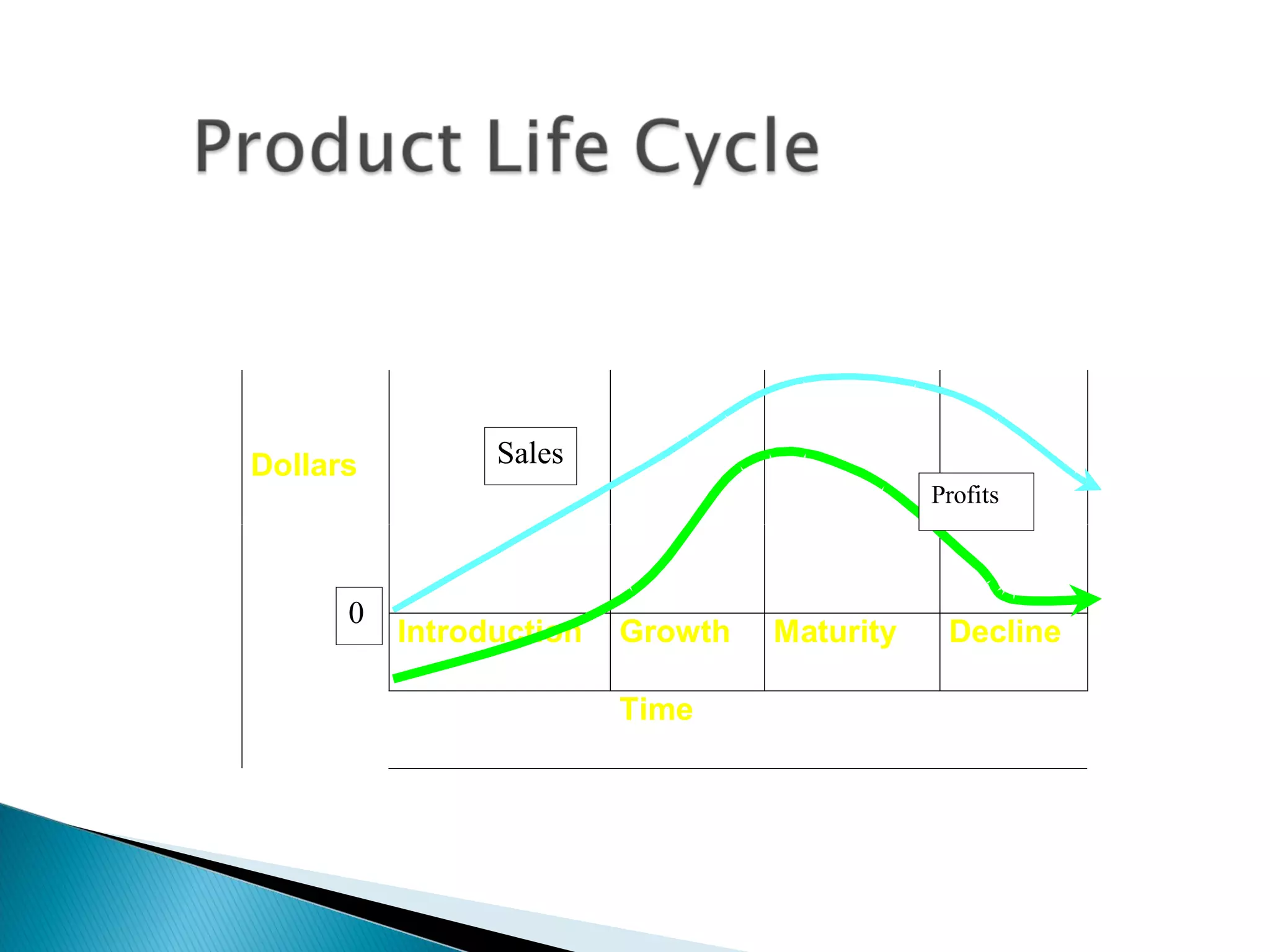
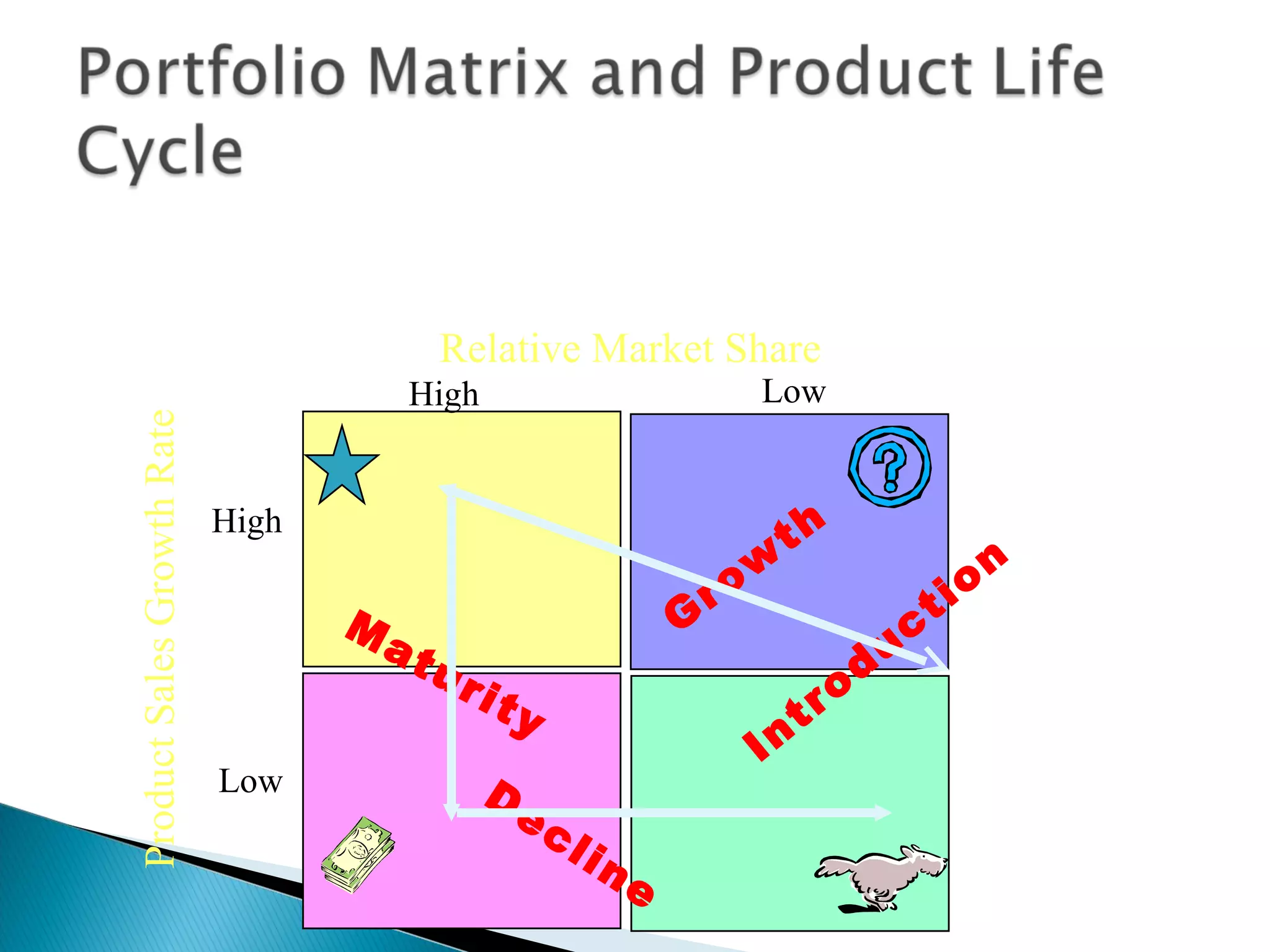
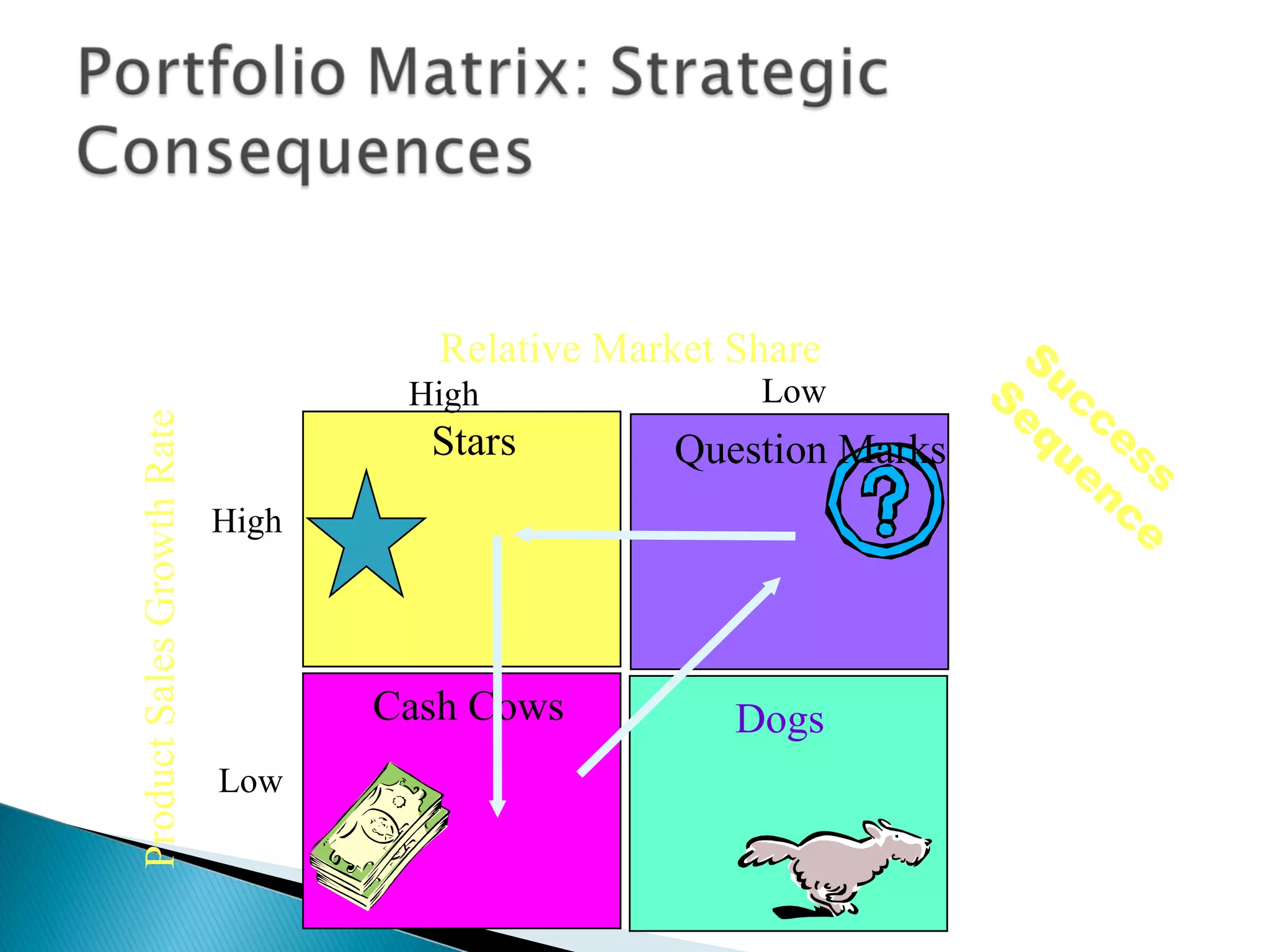
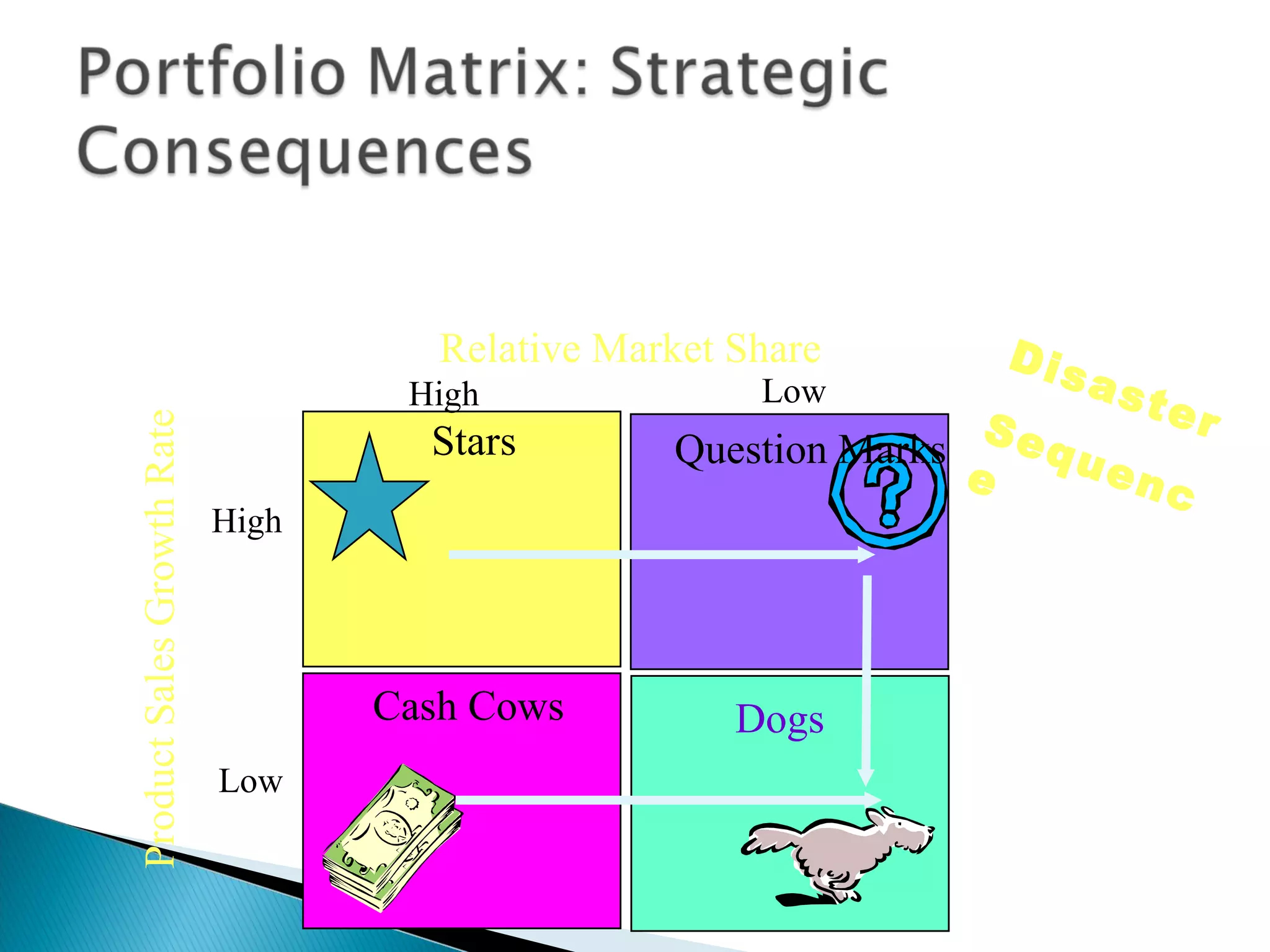
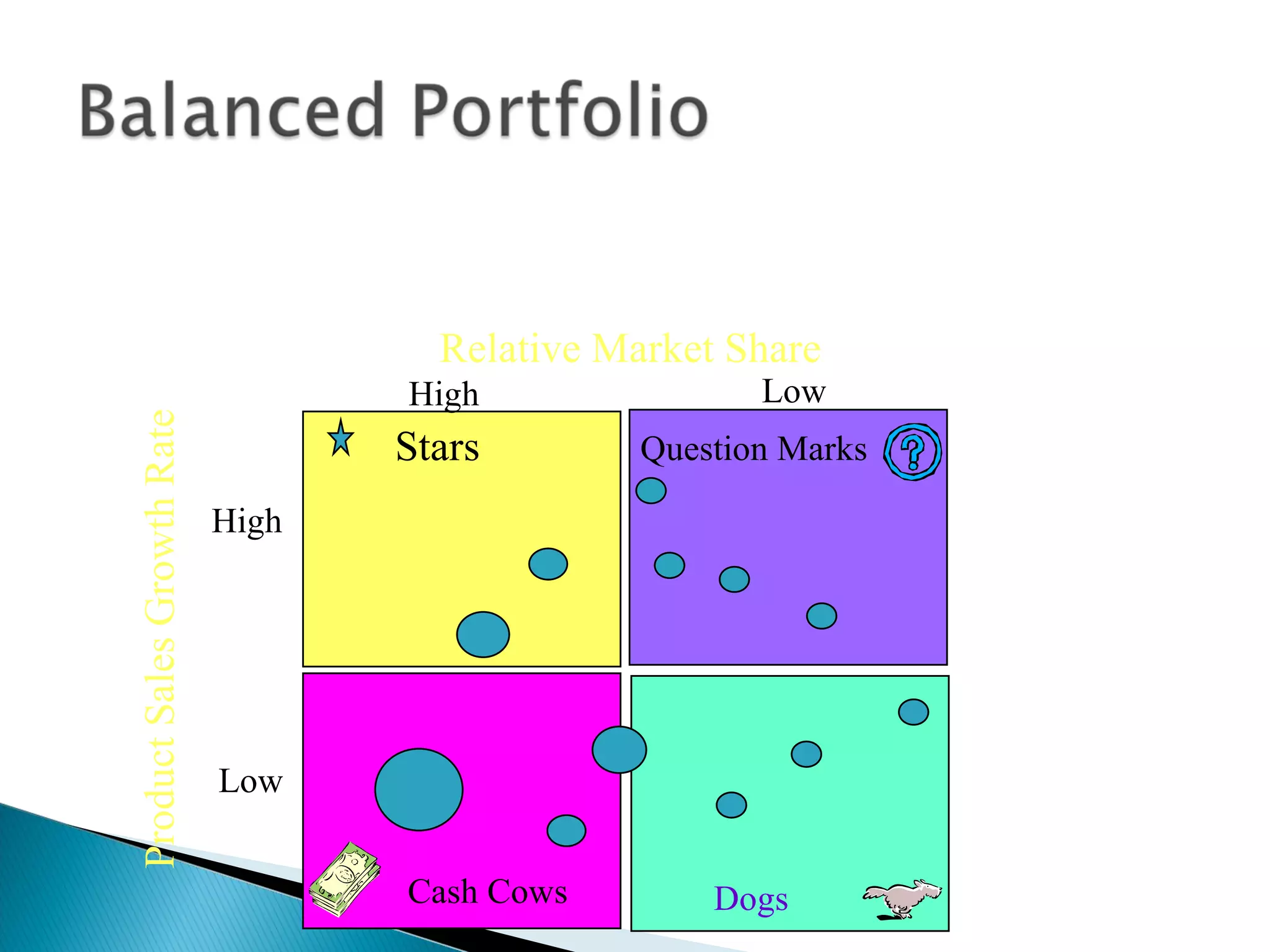
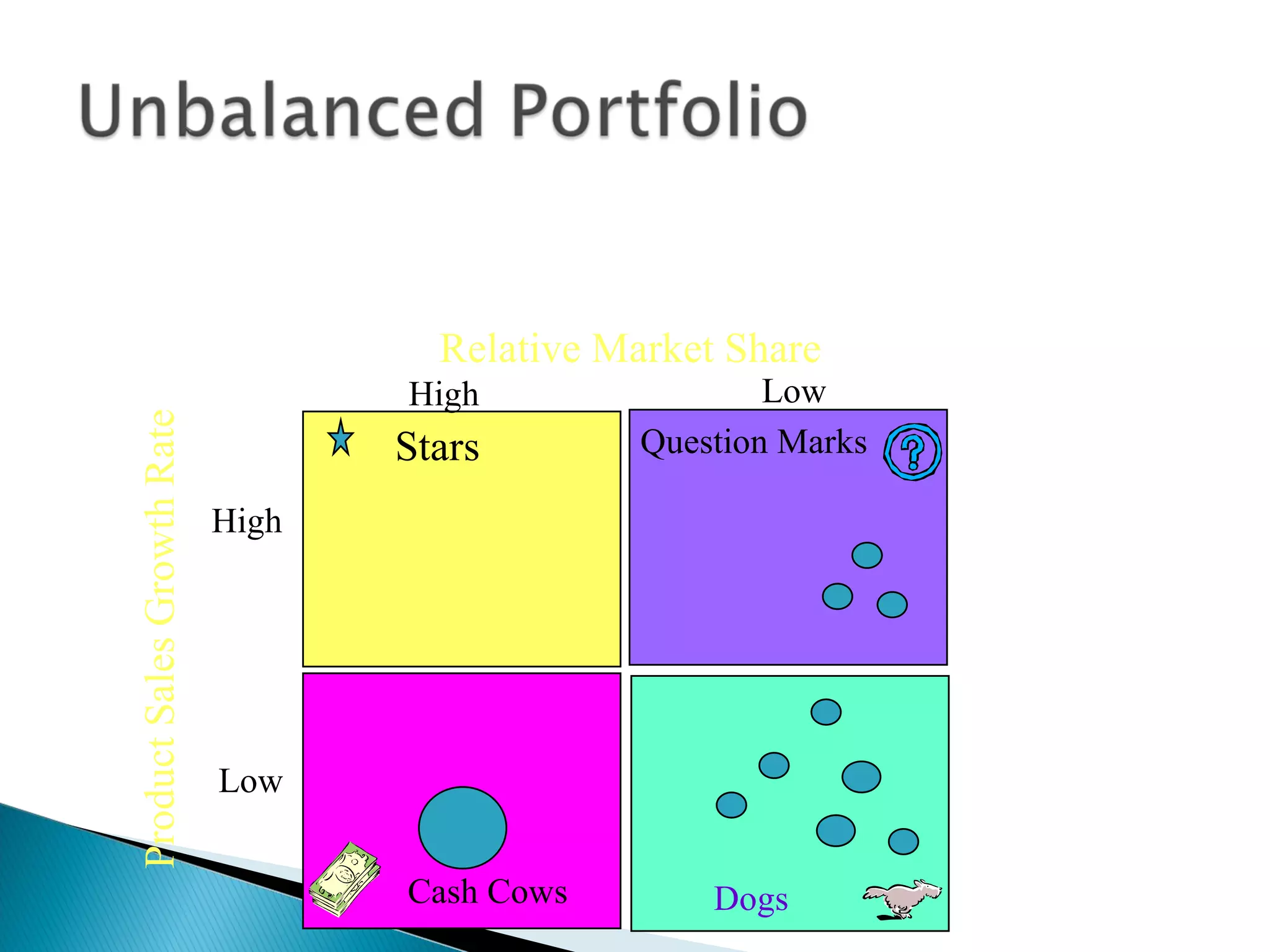
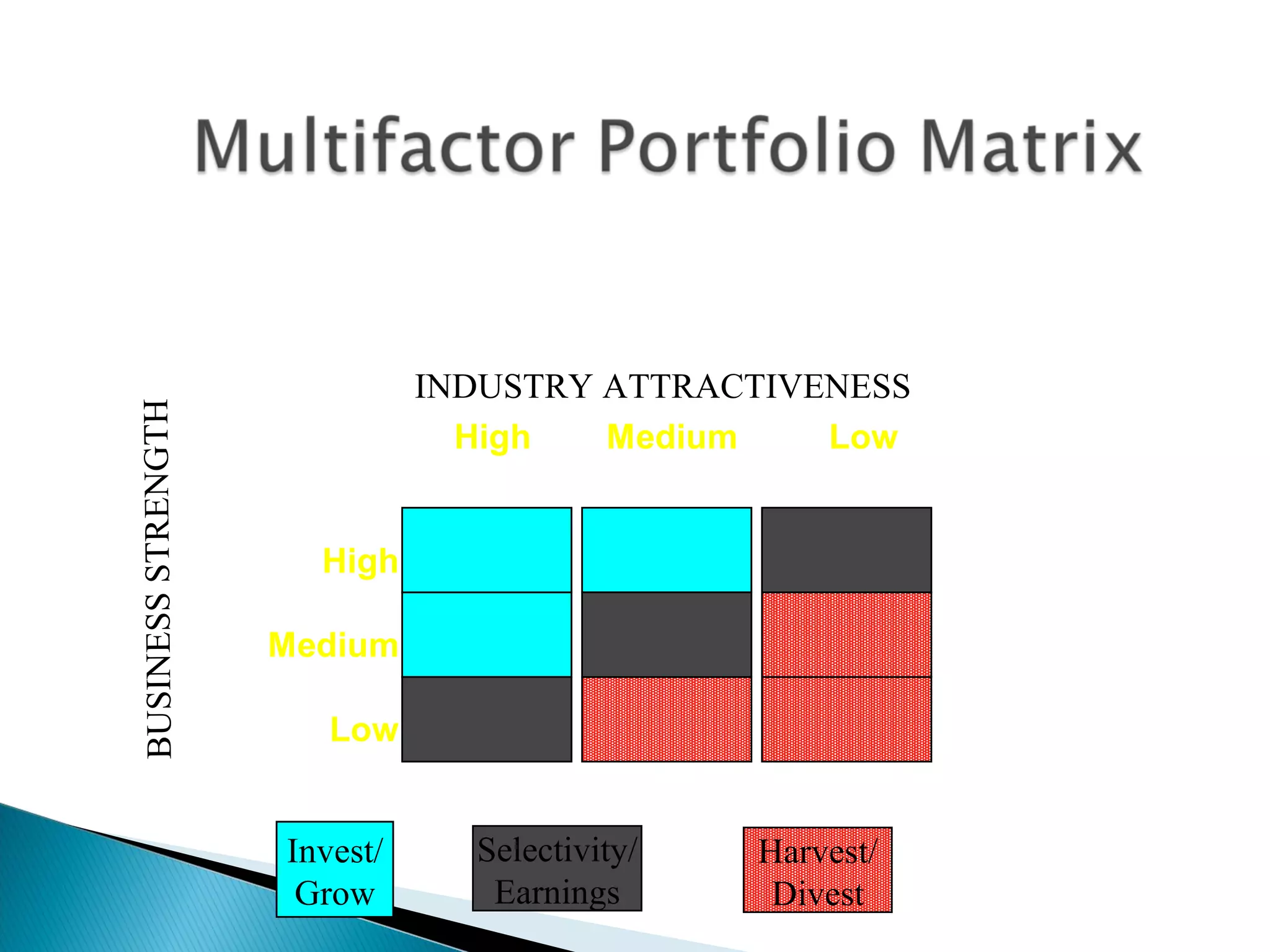
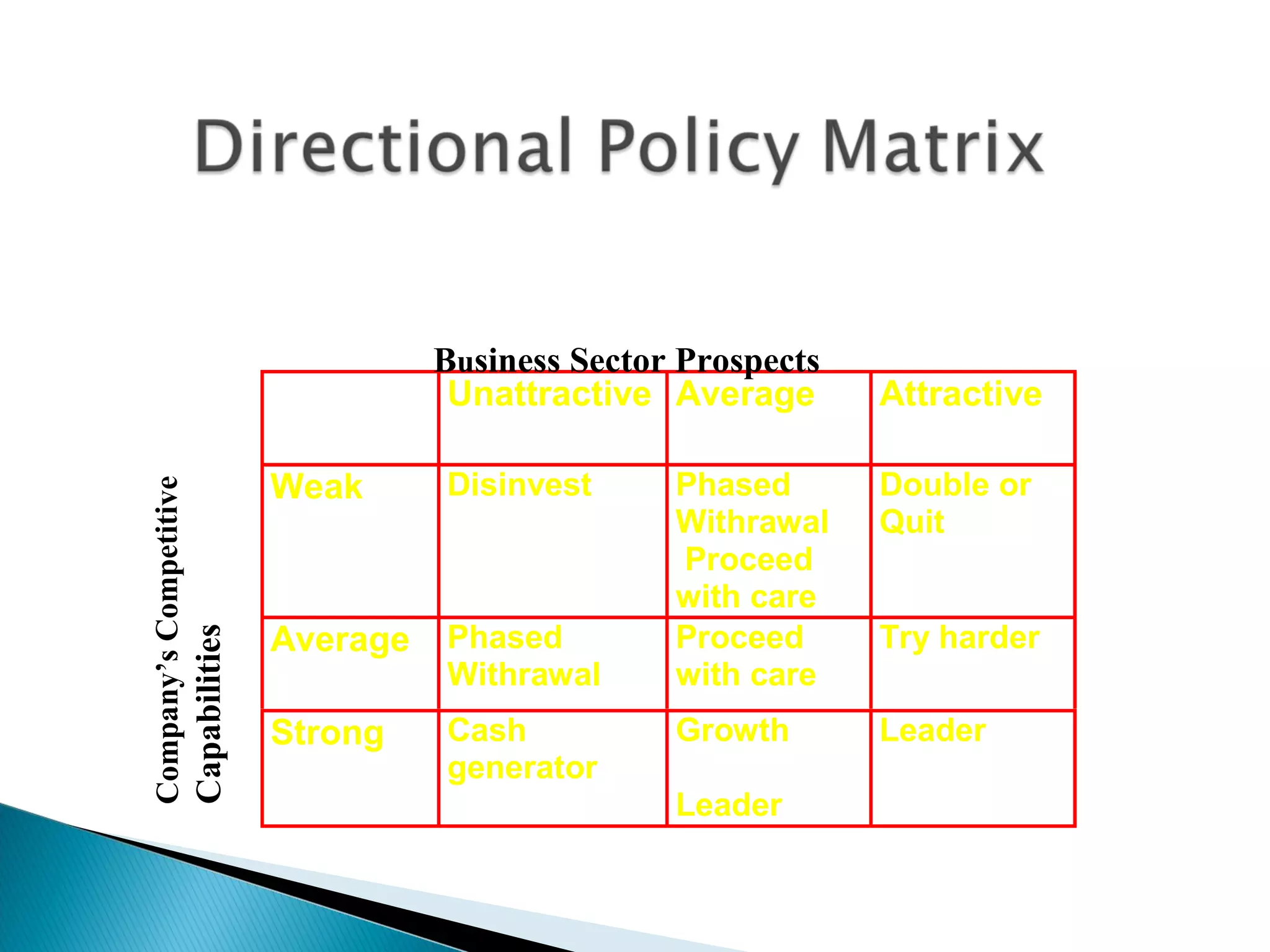
The document outlines a comprehensive approach to product/market strategy, emphasizing the evaluation of current business momentum and environmental forecasts to formulate effective marketing strategies. It discusses the importance of identifying strengths and weaknesses, competitive positioning, and adapting strategies based on market conditions and consumer behavior. Additionally, it provides a framework for assessing strategic alternatives and the critical factors for success within different stages of industry maturity.