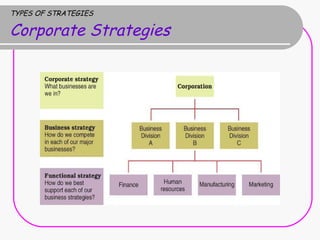
This document discusses strategic management and the types of strategies used by organizations. It covers several key areas:
1) Types of strategies include growth, diversification, restructuring, globalization, and e-business strategies. Growth strategies focus on expansion while restructuring strategies focus on consolidation.
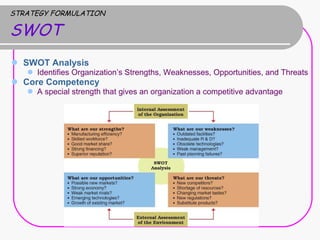
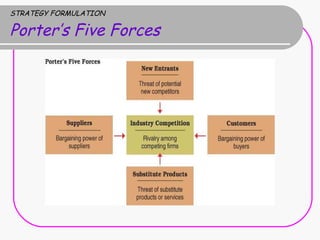
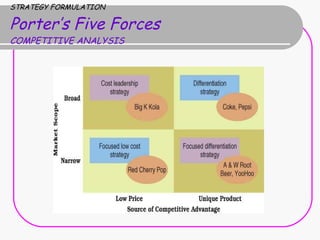
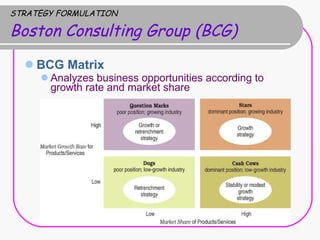
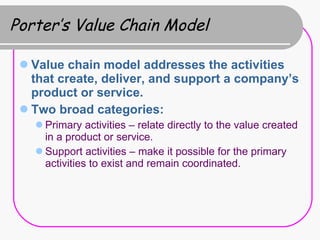
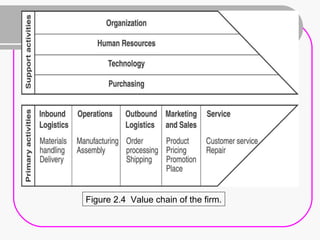
2) Strategy formulation involves analyzing strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats (SWOT analysis), examining industry attractiveness (Porter's five forces model), and evaluating business strategies (Porter's competitive strategies model).
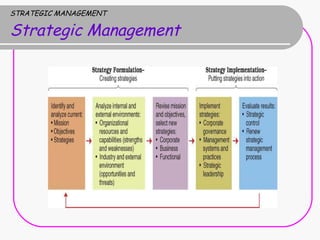
3) Strategy implementation is the process of executing strategies and requires strategic leadership to activate the organization for change and continuous performance enhancement.