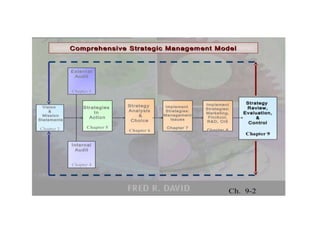
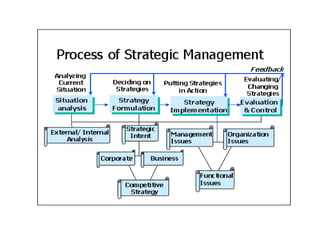
The document discusses the circular nature of the strategic management process, focusing on strategy evaluation, review, and redesign as critical components that enable organizations to adapt and thrive. It emphasizes the need for continuous evaluation and adjustment of strategies in response to environmental changes and complexities. A simulation exercise is included to help participants apply the concepts of strategy evaluation and redesign in a practical context.