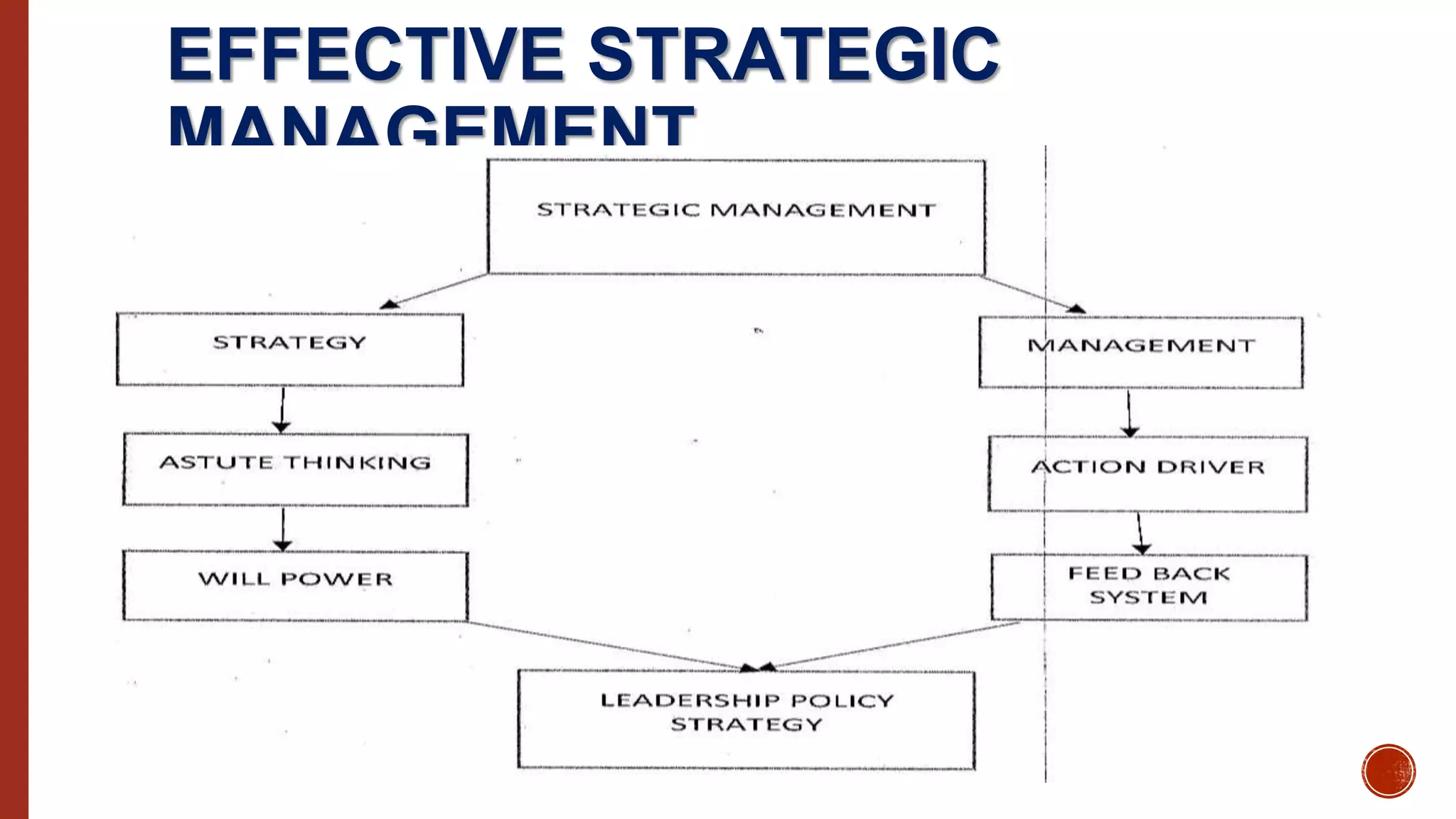
The paper discusses the strategic management process (SMP) as a vital tool for achieving command responsibility in military and organizational contexts, emphasizing the need for effective planning, implementation, and evaluation. It highlights the significance of strong leadership, willpower, and feedback systems in executing SMP to meet goals and objectives. The document also proposes that commanding officers should undergo training to enhance their ability to navigate the complexities of strategic management.