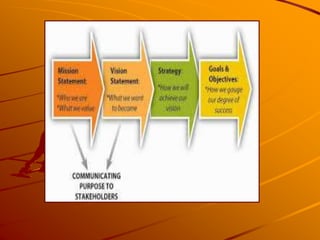
Mintzberg identifies 5 perspectives on strategy:
1. Strategy as plan - a consciously intended course of action.
2. Strategy as ploy - a specific scheme to outwit competitors.
3. Strategy as pattern - consistency in behavior whether intended or not.
4. Strategy as position - how an organization locates itself in its environment.
5. Strategy as perspective - a shared way of perceiving the world among organizational members.
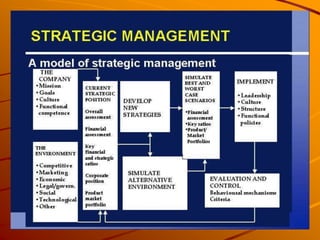
Strategic management involves defining an organization's vision and mission, assessing external opportunities and threats, identifying strategic options, implementing strategies, and reviewing performance. The level of formality in strategic decisions depends on factors like organizational size, complexity, and