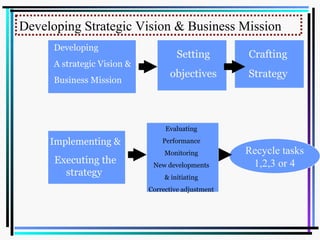
The document outlines the strategic management process, which consists of 5 key tasks: [1] Developing a strategic vision and mission, [2] Setting objectives, [3] Crafting a strategy, [4] Implementing and executing the strategy, and [5] Evaluating performance and initiating corrective adjustments. It emphasizes that strategy involves managerial choices to achieve organizational goals and compete successfully. Effective strategic management requires continuously monitoring performance, the external environment, and making adjustments to the strategy as needed.