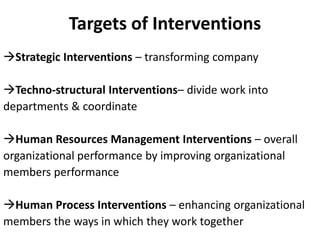
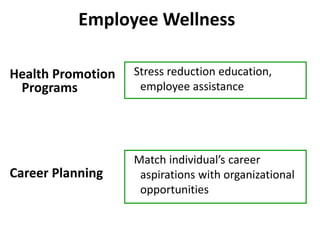
This document discusses various types of organizational interventions including strategic interventions, techno-structural interventions, human resource management interventions, and human process interventions. It provides examples and descriptions of specific interventions such as mergers and acquisitions, culture change, creativity and innovation, sensitivity training, team building, and conflict resolution. The document also discusses structural variables that can affect innovation, advice for structuring interventions, expected results, and the importance of evaluation.